Seeds of future trends are sown in the evolution of blockchain, piloting on blockchain and results thereof. By now, almost every possible use case or potential of blockchain has been discussed in research reports, articles, TV shows and social media. Most large organizations are looking at this technology seriously, whether this wave of blockchain poses danger of tsunami to their businesses or it is perfect wave, which they can surf and extract pleasure of profits. Every technological reform has always been realized on the hindsight e.g. world before and after internet, world before and after Google, etc. Most technological advancement coming from large IT companies, come with force e.g. new versions/updates in MS products, Apple phones, Intel CPUs, where people are literally forced to adopt changes. However, technological advancement coming from open source community is not forceful. To that extent technological advancement from private corporations is push type, where as it is pull type, in case of open source development. Applying the same logic to Blockchain being an open source initiative, it will move with its own pace, much like Linux.

It will have its place, but not necessarily that of leader, because much depends on the large corporations, who currently are custodians or intermediaries of the existing setups and their businesses may get impacted by blockchain. Another factor to our mind, implementation of blockchain is one way street. We don’t see that people can have option of rolling back blockchain implementation, which can be easily done in current computing environment. Hence, piloting will have to be rigorous one.

There is rampant corruption across countries at every level of governance, be it release of subsidies, tax compliance, public benefits, etc. Because of this menace people are deprived of the benefits, they are entitled to. This can change with implementation of blockchain in governance. It will enforce transparency and trust in the governance. However, precisely this could be the challenge for acceptance of such a system by powerful people in governments. However, if implemented properly, it will change the governance mechanism for good. It can optimize delivery of public services and create value for its citizens. In will add efficiencies in governance. Public blockchain, can record all activities & transactions on the decentralized database permanently and more so, securely. By allowing people to track the movement of government funds, government spending, subsidies, etc. blockchain can establish accountability for state and create a cohesive environment across layers of governance and public life and restrict misappropriations of public tax money. Blockchain not only can deter corruption through accountability, but it can also do so by bypassing the middleman entirely. It can be deployed to manage international missions of humanitarian aid, refugee management, medical aid, etc.
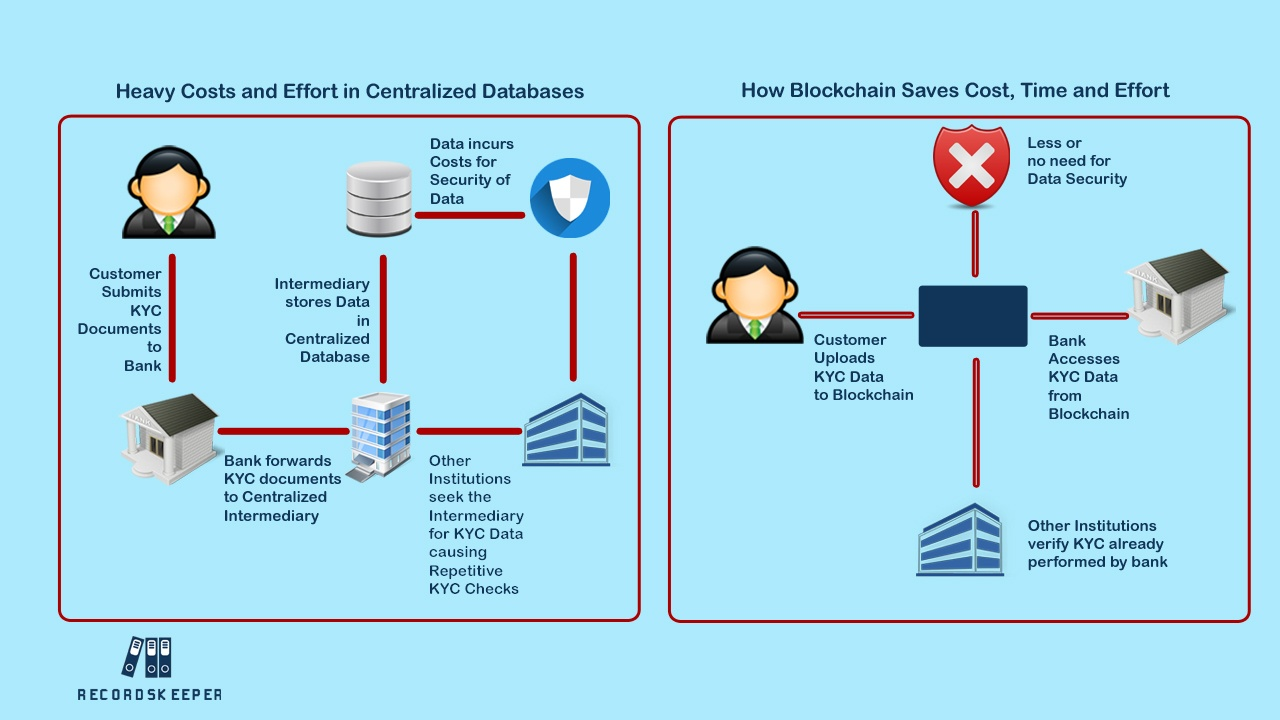
Every nation has a national ID system for its citizens to first prove he/she is a legitimate citizen of the country, then to rationalize services and processes in areas such as social services, taxes, local voting and administration but also to promote private services by stimulating the digital economy, all while reducing costs and adding transparency. However, there have been frauds recorded, often abusing this system. Blockchain can be deployed in National ID systems such as India’s Aadhaar. It can be deployed with ‘Privacy by Design‘. approach. It is all the more important that digital identities be handled with the utmost care, keeping human values front and center. It can lead to be truly a digital economy, wherein tax compliance and public services such as subsidy transfers, utilities, etc can be seamlessly managed. Given the immutable nature of the technology, there can’t be any fraud committed on this system and if committed, it will be caught in real time.
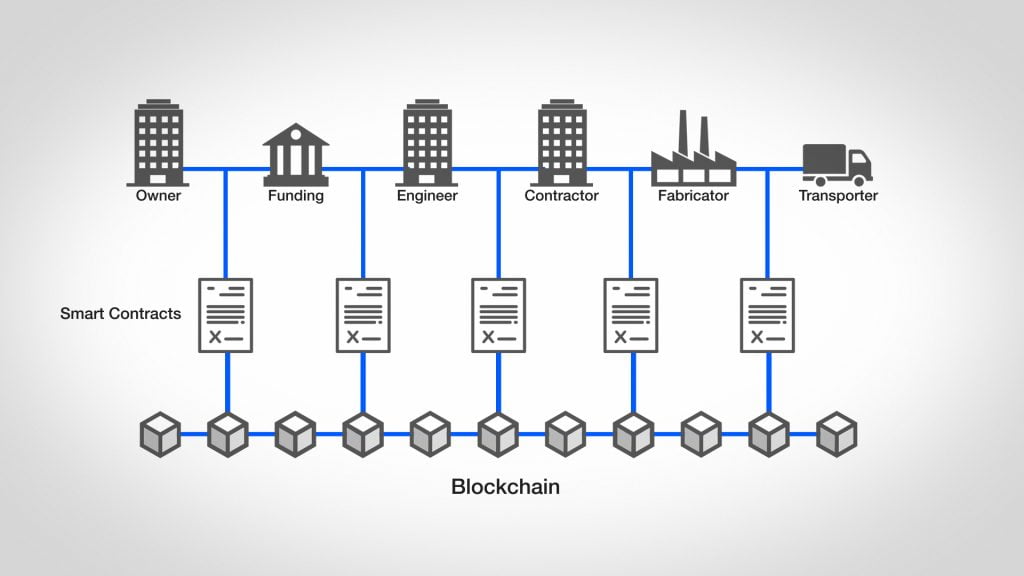
Every project has few stakeholders – e.g promoter of project (private or government), contractors, beneficiaries. Every project is governed by project specifications and framework within which every stakeholder play their roles. Currently project management has lot of pitfalls due to many challenges e.g. lack of clarity about work specifications, payment delays, lack of failure trail, etc. If blockchain is deployed in project management right from agreement to delivery under binding principles of smart contracts, the execution will be smooth. At every stage, process and activities get registered on blockchain, leaving audit trail for failures, if any. By automating payments through escrow account, upon completion of stages, it will create an environment of dependability, which arises out of trust embedded in the system. It will dilute the risk perspective towards project of the stakeholders themselves.

In customer relationship management entire value chain is people dependant. Hence, there is a risk due to negligence or acts of omission, commission, etc. Such vulnerabilities are impacting businesses adversely. Customer Relationship Management will have a utility of Permissioned/private blockchain, which can be implemented across value chains of the customers and suppliers. It will create an atmosphere of transparency and clarity across various organizations, which are blockchained. Every immutable transaction recorded on the system, be it purchase order, invoice, shipment documents, etc. will facilitate audit trail. Smart contracts can be deployed as closed loop control system for all processes, e.g. invoicing, payments, etc.
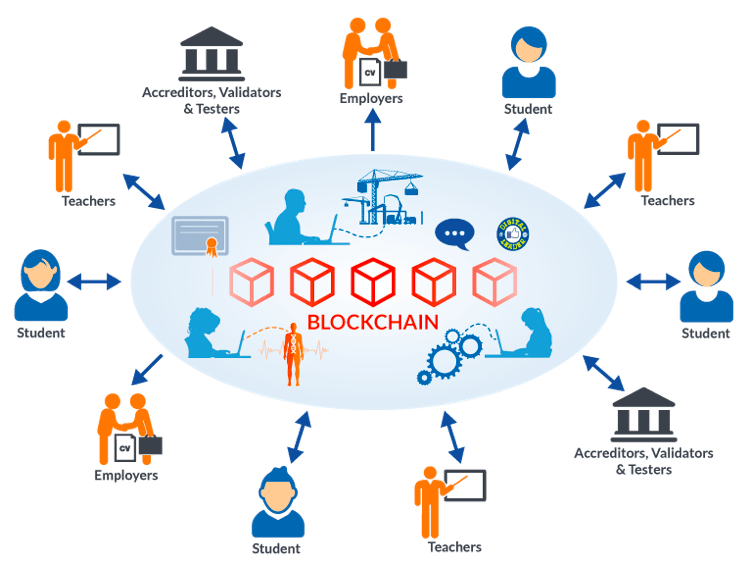
There is an alarming state of education, in developing countries. There is low accountability for the institutions, teachers and even students. There are vulnerabilities around entire training process, examinations/ assessment and certification. Also existing paper-based certification systems may be subject to loss or fraud. If blockchain is embraced by or forced up on educational institutions, most activities can be streamlined right from admissions to certifications. Frauds, if tried can be traced quickly. While, actual certificates and other relevant documents could be in “data lakes”, but references can be part of blockchain. There will be transparent system of records, easy for institution to mine from and students & alumna access. Same applies to learning processes in corporate training, in terms of keeping track of continuing professional development and learning. Blockchain could potentially take data from conference attendances, courses & other forms of learning and store them securely in reputable systems. Imagine a blockchain of a student or a professional, which showcases entire learning curve, across the education institutions, detailing what happened and how it happened.
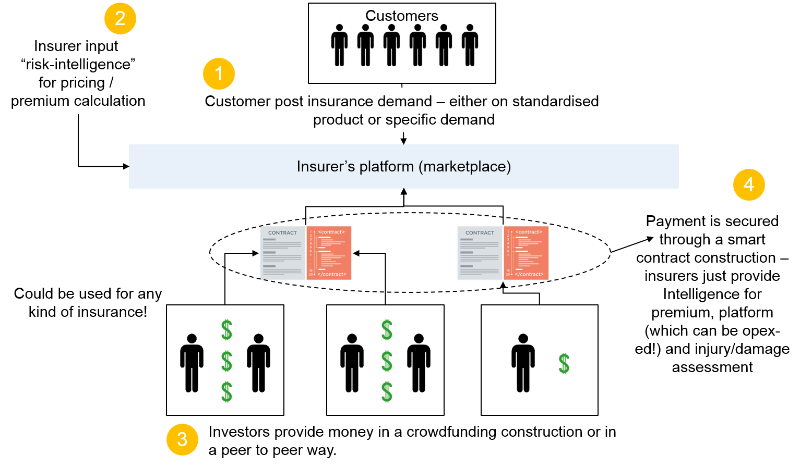
There are large no of NGOs working in social sector with different focus areas such as health, sanitation, agriculture, women empowerment, malnutrition, etc. However, biggest challenge for the social sector is fund raising, due to issues related to non-transparency, lack of clarity of past work, financial compliance, etc. There few miscreants in social sector, as in every field, because of them people look at every NGO with suspicion. Good NGOs can adopt blockchain for all their activities, financial recording, fund-raising, subsequent deployment of funds and all such activities. It will reflect transparency in their operations and offer audit trail for every activity. Thereby donors can get details of utilization of their funds. Same applies to Crowd-funding in social sector, a transparent link between donors, NGOs or fund raisers and beneficiaries will ensure growth of the eco-system.
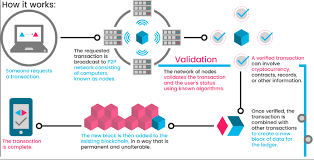
Given vulnerabilities of voting machines and allegations of malpractices, election procedures, world over are under cloud of doubt. This can be eliminated with deployment of public blockchain in election process. Credibility can be achieved with immutable transactions and verification of digital identity of voter through private keys, while maintaining anonymity of voter. Every casted vote can be audited, while maintaining secrecy of voter identity. Some countries are already piloting this technology in electoral procedures.
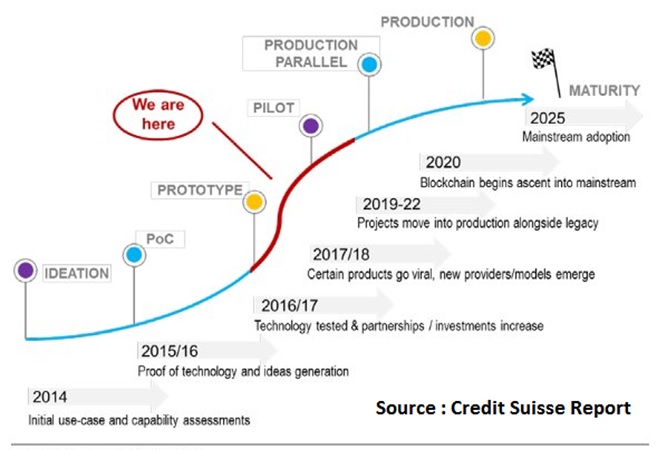
According to Credit Suisse report, a survey conducted by the World Economic Forum found 58% of executives anticipate 10% of global GDP to “be stored on the blockchain before 2025.” That’s the year Credit Suisse expects the technology to reach full maturity. At the moment, the technology is in the middle of the prototype and pilot stage. In 2018, the bank said it will be a critical year. “Blockchain solutions will come into production as the “low-hanging fruit” of the industry is addressed – i.e. where blockchain’s use is immediately obvious, such as payments and trade finance,” the bank said.



![Relationship Goals Review: Is It Your Next Favorite Rom-Com? [2026]](https://outfluent.blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Relationship-Goals-Review-1-180x135.jpg)
![Cradle of Kindness: A Mumbai Cop’s Heartwarming Gift| Viral Stories [2026] Cradle of kindness](https://outfluent.blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Mumbai-cop-kindness-180x135.webp)




































Fine-art photography often focuses on highlighting the beauty of the human form.
It is about composition rather than exposure.
Experienced photographers use subtle contrasts to convey atmosphere.
Such images celebrate artistry and character.
https://xnudes.ai/
Each photo aims to tell a story through form.
The purpose is to portray human beauty in an respectful way.
Viewers often value such work for its emotional power.
This style of photography blends emotion and vision into something truly expressive.
Modern websites for adult audiences feature a variety of interesting opportunities.
These platforms are designed for communication and sharing personal interests.
Members can find others who have similar goals.
A lot of of these sites encourage respectful interaction and welcoming communication.
https://midnightracing.us/lifestyle/pregnant-porn-understanding-the-niche-in-adult-entertainment/
The design is usually intuitive, making it easy to navigate.
Such platforms allow people to express themselves in a free online environment.
Privacy remains an key part of the user experience, with many sites offering control tools.
Overall, these platforms are designed to support adult communication in a respectful digital space.
Онлайн сервисы для общения дают возможность взрослым людям находить друзей в удобном формате.
Такое знакомство поднимает настроение.
Множество людей отмечают, что онлайн-знакомства дают шанс расслабиться после работы.
Это понятный формат для новых контактов.
https://gaudiya-math.ru/onlajn-razvlecheniya/bdsm-sczeny-s-russkimi-modelyami-populyarnost-i-kultura/
Главное — сохранять открытость и уважение в разговоре.
Позитивное общение улучшает эмоциональное состояние.
Такие площадки созданы для тех, кто ценит новых людей.
Общение через интернет становятся способом провести время с пользой.
Английский сегодня считается необходимым умением для современного человека.
Он помогает находить общий язык с людьми со всего мира.
Без владения языком трудно развиваться профессионально.
Многие компании требуют сотрудников, владеющих английским.
английский язык для детей 3 лет
Регулярная практика английского расширяет кругозор.
Благодаря английскому, можно читать оригинальные источники без перевода.
Кроме того, изучение языка повышает концентрацию.
Таким образом, знание английского языка играет важную роль в саморазвитии каждого человека.
Английский язык сегодня считается обязательным умением для жителя современного мира.
Английский язык помогает находить общий язык с иностранцами.
Не зная английский трудно строить карьеру.
Организации предпочитают сотрудников, владеющих английским.
semeistvo.by
Регулярная практика английского делает человека увереннее.
Зная английский, можно учиться за границей без перевода.
Также, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, знание английского языка играет важную роль в успехе каждого человека.
Приобретение ПМЖ за границей становится всё более популярным среди граждан РФ.
Такой шаг даёт новые возможности для жизни.
Гражданство другой страны помогает беспрепятственно путешествовать и упрощать поездки.
Кроме того такой документ может улучшить уверенность в будущем.
Гражданство Антигуа и Барбуда
Многие россияне рассматривают возможность переезда как способ расширения возможностей.
Получив ВНЖ или второй паспорт, человек может инвестировать за рубежом.
Разные направления предлагают индивидуальные возможности получения статуса резидента.
Именно поэтому идея второго паспорта становится приоритетной для тех, кто ищет стабильность.
Casino Roulette: Spin for the Ultimate Thrill
Experience the timeless excitement of Casino Roulette, where every spin brings a chance to win big and feel the rush of luck. Try your hand at the wheel today at https://k8o.jp/ !
321chat rooms omegle alternative 321chat
бонуси казино казіно з бонусами
ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
Открих https://mdgt.top какъв грунд да използвам върху ОСБ плоскости
Поради https://remontuem.if.ua щодо електромонтажні роботи прочитав тут.
Друзі https://seetheworld.top порадили для поїздки в доновали.
Независимый сюрвей в Москве: проверка грузов и объектов, детальные отчёты, фотофиксация и экспертные заключения. Прозрачная стоимость сюрвейерских услуг, официальные гарантии и быстрая выездная работа по столице и области.
Идеальные торты на заказ — для детей и взрослых. Поможем выбрать начинку, оформление и размер. Десерт будет вкусным, свежим и полностью соответствующим вашей идее.
ЦВЗ в Краснодаре https://cvzcentr.ru место, где пациентов внимательно выслушивают, проводят глубокую диагностику и составляют эффективный план улучшения состояния при вегетативных расстройствах.
Explore a true elephant sanctuary where welfare comes first. No chains or performances — only open landscapes, gentle care, rehabilitation programs and meaningful visitor experiences.
La infraestructura https://novo-sancti-petri.es y la tecnologia vial europeas equilibran la innovacion y la sostenibilidad. Semaforos inteligentes, carreteras verdes, centros de transporte seguros y proyectos que marcan la pauta para la industria global.
La Rome Espresso https://laromeespresso.es es un lugar donde la cultura del cafe se convierte en arte. Descubre el camino del grano a la taza: el sabor profundo, las tecnicas precisas y los rituales que crean la bebida perfecta.
Do you love excitement? roulettino casino delights players with high-quality slots, live tables, tournaments, and ongoing promotions. The gameplay is smooth and dynamic.
Rodaballo al Horno https://rodaballoalhorno.es es un viaje a las raices musicales del mundo, donde los sabores de las culturas se entrelazan con sus melodias. Exploramos los ritmos de las naciones, los sonidos de las tradiciones y como diferentes historias se fusionan en un solo sonido armonioso.
Un portal sobre videojuegos https://tejadospontevedra.es, noticias y tendencias para quienes viven y respiran videojuegos: resenas, guias, parches, anuncios, analisis de tecnologia y torneos de esports. Todo para gamers y quienes quieran mantenerse informados.
Нужна легализация? закон о легализации в Черногории проводим аудит объекта, готовим документы, улаживаем вопросы с кадастром и муниципалитетом. Защищаем интересы клиента на каждом этапе.
Скрайд MMORPG https://t.me/scryde культовая игра, где магия переплетается с технологией, а игрокам доступны уникальные классы, исторические миссии и масштабные PvP-сражения. Легенда, которую продолжают писать тысячи игроков.
Постоянно мучает насморк – по ссылке
Бренд MAXI-TEX https://maxi-tex.ru завода ООО «НПТ Энергия» — профессиональное изготовление изделий из металла и металлобработка в Москве и области. Выполняем лазерную резку листа и труб, гильотинную резку и гибку, сварку MIG/MAG, TIG и ручную дуговую, отбортовку, фланцевание, вальцовку. Производим сборочные единицы и оборудование по вашим чертежам.
Эвакуатор в Москве https://eva77.ru вызов в любое время дня и ночи. Быстрая подача, профессиональная погрузка и доставка авто в сервис, гараж или на парковку. Надёжно, безопасно и по фиксированной цене.
1win официальный 1win 2025
Хочешь развлечься? купить мефедрон федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить гашиш, купить мефедрон, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази, купить альфа пвп, купить гаш в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
бонуси казино бонусы казино
Файне Хмельницкий https://faine-misto.km.ua події та новини Хмельницького, огляди, статті.
У Куми https://u-kumy.com жіночий сайт з порадами на всі випадки життя. Мода, краса, діти, стосунки, сонник та смачні рецепти.
Компания Таврнеруд https://tareksa.ru производство и продажа нерудных материалов, сервис логистических услуг, а также проектирование в области технологии обогащения нерудных материалов, проведение лабораторных испытаний нерудных материалов.
Do you love puzzles? This free puzzle games game features challenging levels, well-thought-out mechanics, and relaxing gameplay. Solve riddles, unlock new levels, and test your problem-solving skills anytime, anywhere.
Нужен сайт? https://laboratory-site.ru включает проектирование, удобный интерфейс, быструю загрузку, интеграцию с 1С и CRM. Подбираем решения под задачи бизнеса и обеспечиваем техническое сопровождение.
Нужен сервер? vps для юристов лучшие по мощности и стабильности. Подходят для AI-моделей, рендеринга, CFD-симуляций и аналитики. Гибкая конфигурация, надежное охлаждение и поддержка нескольких видеокарт.
ігри слоти онлайн слоти
ігри казино казіно ігри
oficjalne pobieranie mostbet rejestracja w mostbet
Познавательный блог Нотатки https://notatky.net.ua объясняет сложные вещи простым языком. Интересные факты, история, биографии, наука и много интересного.
mostbet android mostbet android
новости беларуси 2025 новости беларуси
новости беларуси последние свежие смотреть новости беларусь
Visit an elephant sanctuary to see elephants living in natural landscapes, receiving care, rehabilitation and freedom from exploitation. Ethical tours focus on education, conservation and respectful observation.
Experience an elephant sanctuary where welfare comes first. Walk alongside elephants, watch them bathe, feed them responsibly and discover how conservation efforts help protect these majestic animals.
An ethical https://mark-travel.ru provides rescued elephants with medical care, natural habitats and social groups. Visitors contribute to conservation by learning, observing and supporting sustainable wildlife programs.
Бренд MAXI-TEX https://maxi-tex.ru завода ООО «НПТ Энергия» — это металлообработка полного цикла с гарантией качества и соблюдением сроков. Выполняем лазерную резку листа и труб, гильотинную резку и гибку, сварку MIG/MAG, TIG и ручную дуговую, отбортовку, фланцевание, вальцовку, а также изготовление сборочных единиц и оборудования по вашим чертежам.
Нужен сервер? тут лучшие по мощности и стабильности. Подходят для AI-моделей, рендеринга, CFD-симуляций и аналитики. Гибкая конфигурация, надежное охлаждение и поддержка нескольких видеокарт.
Регулярно мучает насморк – Серебряный Углерон купить
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Изготавливаем каркас лестницы из металла на современном немецком оборудовании — по цене стандартных решений. Качество, точность реза и долговечность без переплаты.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Latest why buy crypto: price rises and falls, network updates, listings, regulations, trend analysis, and industry insights. Follow market movements in real time.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
The latest crypto news: Bitcoin, altcoins, NFTs, DeFi, blockchain developments, exchange reports, and new technologies. Fast, clear, and without unnecessary noise—everything that impacts the market.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Купить шпон https://opus2003.ru в Москве прямо от производителя: широкий выбор пород, стабильная толщина, идеальная геометрия и высокое качество обработки. Мы производим шпон для мебели, отделки, дизайна интерьеров и промышленного применения.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
доктор вывода из запоя вывод из запоя стационарно
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
вывод из запоя вывод из запоя с выездом врача
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
вывод из запоя анонимно вывод из запоя и кодирование в москве
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Доставка грузов https://china-star.ru из Китая под ключ: авиа, авто, море и ЖД. Консолидация, проверка товара, растаможка, страхование и полный контроль транспортировки. Быстро, надёжно и по прозрачной стоимости.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Доставка грузов https://lchina.ru из Китая в Россию под ключ: море, авто, ЖД. Быстрый расчёт стоимости, страхование, помощь с таможней и документами. Работаем с любыми объёмами и направлениями, соблюдаем сроки и бережём груз.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Гастродача «Вселуг» https://gastrodachavselug1.ru фермерские продукты с доставкой до двери в Москве и Подмосковье. Натуральное мясо, молоко, сыры, сезонные овощи и домашние заготовки прямо с фермы. Закажите онлайн и получите вкус деревни без лишних хлопот.
For informed buying decisions visit https://topbuyingidea.com
Логистика из Китая https://asiafast.ru без головной боли: доставка грузов морем, авто и ЖД, консолидация на складе, переупаковка, маркировка, таможенное оформление. Предлагаем выгодные тарифы и гарантируем сохранность вашего товара.
Независимый сюрвейер https://gpcdoerfer1.com в Москве: экспертиза грузов, инспекция контейнеров, фото- и видеопротокол, контроль упаковки и погрузки. Работаем оперативно, предоставляем подробный отчёт и подтверждаем качество на каждом этапе.
Файне місто Дніпро https://faine-misto.dp.ua новини та події Дніпра та області. Огляди, транспорт, події та цікаве.
У Кума https://u-kuma.com блог для чоловіків про армію, авто, ремонт та життя. Корисні поради на всі випадки життя.
Онлайн-ферма https://gvrest.ru Гастродача «Вселуг»: закажите свежие фермерские продукты с доставкой по Москве и Подмосковью. Мясо, молоко, сыры, овощи и домашние деликатесы без лишних добавок. Удобный заказ, быстрая доставка и вкус настоящей деревни.
Доставка грузов https://china-star.ru из Китая для бизнеса любого масштаба: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Разработаем оптимальный маршрут, оформим документы, застрахуем и довезём груз до двери. Честные сроки и понятные тарифы.
Зефірка https://zefirka.net.ua легкий сайт з приметами, значення снів, імена та свята. Корисні життєві поради.
Extended Review: https://chanceskraw.blogunteer.com/37378460/nppr-team-shop-the-definitive-hub-for-social-media-marketing-mastery
Latest Updates: https://www.doubleh.smitly.pl/akkaunty-dlja-zapuska-reklamnyh-kampanij-na-5/
Платформа для работы https://skillstaff.ru с внешними специалистами, ИП и самозанятыми: аутстаффинг, гибкая и проектная занятость под задачи вашей компании. Найдем и подключим экспертов нужного профиля без длительного найма и расширения штата.
Клиника проктологии https://proctofor.ru в Москве с современным оборудованием и опытными врачами. Проводим деликатную диагностику и лечение геморроя, трещин, полипов, воспалительных заболеваний прямой кишки. Приём по записи, без очередей, в комфортных условиях. Бережный подход, щадящие методы, анонимность и тактичное отношение.
Колодцы под ключ https://kopkol.ru в Московской области — бурение, монтаж и обустройство водоснабжения с гарантией. Изготавливаем шахтные и бетонные колодцы любой глубины, под ключ — от проекта до сдачи воды. Работаем с кольцами ЖБИ, устанавливаем крышки, оголовки и насосное оборудование. Чистая вода на вашем участке без переплат и задержек.
Инженерные изыскания https://sever-geo.ru в Москве и Московской области для строительства жилых домов, коттеджей, коммерческих и промышленных объектов. Геология, геодезия, экология, обследование грунтов и оснований. Работаем по СП и ГОСТ, есть СРО и вся необходимая документация. Подготовим технический отчёт для проектирования и согласований. Выезд на объект в короткие сроки, прозрачная смета, сопровождение до сдачи проекта.
Доставка дизельного топлива https://ng-logistic.ru для строительных компаний, сельхозпредприятий, автопарков и промышленных объектов. Подберём удобный график поставок, рассчитаем объём и поможем оптимизировать затраты на топливо. Только проверенные поставщики, стабильное качество и точность дозировки. Заявка, согласование цены, подача машины — всё максимально просто и прозрачно.
Доставка торфа https://bio-grunt.ru и грунта по Москве и Московской области для дач, участков и ландшафтных работ. Плодородный грунт, торф для улучшения структуры почвы, готовые земляные смеси для газона и клумб. Быстрая подача машин, аккуратная выгрузка, помощь в расчёте объёма. Работаем с частными лицами и организациями, предоставляем документы. Сделайте почву на участке плодородной и готовой к посадкам.
Строительство домов https://никстрой.рф под ключ — от фундамента до чистовой отделки. Проектирование, согласования, подбор материалов, возведение коробки, кровля, инженерные коммуникации и внутренний ремонт. Работаем по договору, фиксируем смету, соблюдаем сроки и технологии. Поможем реализовать дом вашей мечты без стресса и переделок, с гарантией качества на все основные виды работ.
Геосинтетические материалы https://stsgeo.ru для строительства купить можно у нас с профессиональным подбором и поддержкой. Продукция для укрепления оснований, армирования дорожных одежд, защиты гидроизоляции и дренажа. Предлагаем геотекстиль разных плотностей, георешётки, геомембраны, композитные материалы.
Официальный Tor браузер обеспечивает кракен tor доступ через предустановленные настройки безопасности с отключенным JavaScript и строгой изоляцией каждой вкладки от других процессов.
зеркало новости беларусь новости беларуси свежие
Доставка грузов https://avalon-transit.ru из Китая «под ключ» для бизнеса и интернет-магазинов. Авто-, ж/д-, морские и авиа-перевозки, консолидация на складах, проверка товара, страхование, растаможка и доставка до двери. Работаем с любыми партиями — от небольших отправок до контейнеров. Прозрачная стоимость, фотоотчёты, помощь в документах и сопровождение на всех этапах логистики из Китая.
Читать дальше: как оформить персональный кредит
Проверенный кракен официальный сайт работает круглосуточно с технической поддержкой пользователей и быстрой модерацией всех возникающих споров между участниками.
Strona internetowa mostbet – zaklady sportowe, zaklady e-sportowe i sloty na jednym koncie. Wygodna aplikacja mobilna, promocje i cashback dla aktywnych graczy oraz roznorodne metody wplat i wyplat.
Odkryj mostbet casino: setki slotow, stoly na zywo, serie turniejow i bonusy dla aktywnych graczy. Przyjazny interfejs, wersja mobilna i calodobowa obsluga klienta. Ciesz sie hazardem, ale pamietaj, ze masz ukonczone 18 lat.
Got a breakdown? https://locksmithsinwatford.com service available to your home or office.
Хочешь айфон? iphone магазин выгодное предложение на новый iPhone в Санкт-Петербурге. Интернет-магазин i4you готов предложить вам решение, которое удовлетворит самые взыскательные требования. В нашем каталоге представлена обширная коллекция оригинальных устройств Apple. Каждый смартфон сопровождается официальной гарантией производителя сроком от года и более, что подтверждает его подлинность и надёжность.
Дополнительная информация: https://medim-pro.ru/kupit-spravku-ot-dermatologa/
порно шлюхи вк шлюхи ебутся
Оформление медицинских анализов https://medim-pro.ru и справок без очередей и лишней бюрократии. Запись в лицензированные клиники, сопровождение на всех этапах, помощь с документами. Экономим ваше время и сохраняем конфиденциальность.
The best undress ai for digital art. It harnesses the power of neural networks to create, edit, and stylize images, offering new dimensions in visual creativity.
Free video chat this website find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
Free video chat beta emerald chat find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
Учёба английского языка считается необходимым инструментом в глобальном обществе.
Он позволяет поддерживать контакты за границей.
Большинство людей понимают, что английский помогает в карьере.
Знание языка позволяет свободно путешествовать и обогащает культурный опыт.
https://theplenty.net/forums/thread-23919.html
Он также развивает когнитивные способности и даёт чувство уверенности в различных ситуациях.
Учёба английского даёт доступ к информации в науке, технике и бизнесе.
Регулярное изучение помогает совершенствовать навыки и достигает высоких результатов.
Таким образом, знание английского языка необходимо для развития и карьерного роста в современном обществе.
Free video chat emerald chat mobile find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
Recent Changes: https://www.metal-archives.com/users/yuna42085
Responsible play is crucial for maintaining a safe approach to entertainment.
It helps players stay in control and prevents harmful consequences.
By setting limits, individuals can enjoy gaming comfortably without overextending themselves.
Awareness one’s habits encourages smarter behavior during gameplay.
Reliable platforms often promote helpful options that assist users in staying protected.
Maintaining self-control ensures that gaming remains a rewarding activity.
For many players, responsible play helps reduce stress while keeping the experience comfortable.
In the end, a thoughtful approach supports long-term well-being and keeps gaming sustainable.
chip’n win review
Learn More: https://podcasts.apple.com/se/podcast/puzzlefree/id1697682168?i=1000737823170
Beginners with no formal theory training can compose complex symphonies simply by typing prompts into an ai music generator.
Интернет-магазин https://stsgeo-krd.ru геосинтетических материалов в Краснодар: геотекстиль, георешётки, геоматериалы для дорог, фундаментов и благоустройства. Профессиональная консультация и оперативная доставка.
Геосинтетические материалы https://stsgeo-spb.ru для строительства и благоустройства в Санкт-Петербурге и ЛО. Интернет-магазин геотекстиля, георешёток, геосеток и мембран. Работаем с частными и оптовыми заказами, быстро доставляем по региону.
Строительные геоматериалы https://stsgeo-ekb.ru в Екатеринбурге с доставкой: геотекстиль, объемные георешётки, геосетки, геомембраны. Интернет-магазин для дорожного строительства, ландшафта и дренажа. Консультации специалистов и оперативный расчет.
Нужна работа в США? стоимость курса трак диспетчера в сша с нуля : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
Анонимная торговая площадка кракен маркетплейс использует escrow систему для защиты сделок, PGP шифрование для конфиденциальных сообщений и многофакторную аутентификацию.
Нужна работа в США? онлайн обучение диспетчера грузоперевозок в сша с практикой : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
Blockchain Trends | Outfluent
asffbwekcc
[url=http://www.g5h2s6hn3p01032tz7eue7nh8tm288l0s.org/]usffbwekcc[/url]
sffbwekcc http://www.g5h2s6hn3p01032tz7eue7nh8tm288l0s.org/
Срочный вызов электрика https://vash-elektrik24.ru на дом в Москве. Приедем в течение часа, быстро найдём и устраним неисправность, заменим розетки, автоматы, щиток. Круглосуточный выезд, гарантия на работы, прозрачные цены без скрытых доплат.
Uwielbiasz hazard? https://online-nv-casino.com: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
Gates of Olympus https://gatesofolympus.win is a legendary slot from Pragmatic Play. Demo and real money play, multipliers up to 500x, free spins, and cascading wins. An honest review of the slot, including rules, bonus features, and tips for responsible gaming.
Онлайн курс диспетчер траков в сша обучение: обучение с нуля до уверенного специалиста. Стандарты сервиса, документооборот, согласование рейсов и оплата. Пошаговый план выхода на работу у американских логистических компаний.
Хочешь ТОП? сео продвижение сайтов как инструмент усиления SEO: эмуляция реальных пользователей, рост поведенческих факторов, закрепление сайта в ТОПе. Прозрачные отчёты, гибкая стратегия под нишу и конкурентов, индивидуальный медиаплан.
Хочешь сайт в ТОП? накрутка пф яндекса для быстрого роста позиций сайта. Отбираем безопасные поведенческие сценарии, повышаем кликабельность и глубину просмотра, уменьшаем отказы. Тестовый запуск без оплаты, подробный отчёт по изменениям видимости.
See details: https://www.scdmtj.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=6103951&do=profile
Комплексное seo продвижение в сша: анализ конкурентов, стратегия SEO, локальное продвижение в городах и штатах, улучшение конверсии. Прозрачная отчетность, рост позиций и трафика из Google и Bing.
Современный ремонт офиса москва под ключ. Поможем обновить пространство, улучшить планировку, заменить покрытия, освещение и коммуникации. Предлагаем дизайн-проект, фиксированную смету, соблюдение сроков и аккуратную работу без лишнего шума.
Нужно остекление? застеклить балкон в самаре: тёплое и холодное, ПВХ и алюминий, вынос и объединение с комнатой. Бесплатный замер, помощь с проектом и документами, аккуратный монтаж и гарантия на конструкции и работу.
Online platform ht xyz exchange for active digital asset trading: spot trading, flexible order settings, and portfolio monitoring. Market analysis tools and convenient access to major cryptocurrencies are all in one place.
Нужен керосин? 1 тонна авиационного керосина сертифицированное топливо по ГОСТ, поставки для аэропортов, авиапредприятий и вертолётных площадок. Помощь в подборе марки, оформление документов и быстрая доставка.
Comprehensive whitecirclegroup.com: feasibility studies, market analysis, strategy, optimization of costs and processes. We help you strengthen your position in Dubai, Abu Dhabi and other Emirates.
Нужен манипулятор? аренда манипулятора в москве и области организуем подачу спецтехники на стройку, склад или частный участок. Погрузка, разгрузка, перевозка тяжёлых и негабаритных грузов. Оперативный расчёт стоимости и выезд в день обращения.
Профессиональная транспортировка лежачих больных подъем на этаж, помощь при пересадке, фиксирующие носилки, заботливое отношение. Организуем транспортировку в больницы, реабилитационные центры и домой.
Профессиональное агентства маркетинга полного цикла: аудит, позиционирование, digital-стратегия, запуск рекламных кампаний и аналитика. Поможем вывести бренд в онлайн, увеличить трафик и заявки из целевых каналов.
Нужна ботулинотерапия? уколы диспорта помогаем смягчить мимику, освежить взгляд и предупредить появление новых морщин. Осмотр врача, противопоказания, грамотное введение и контроль результата на приёме.
Нужен бетон? москва купить бетон о выгодной цене с доставкой на объект. Свежий раствор, точное соблюдение пропорций, широкий выбор марок для фундамента, стяжек и монолитных работ. Быстрый расчет, оперативная подача миксера.
Trading platform hyperevm dex combines a user-friendly terminal, analytics, and portfolio management. Monitor quotes, open and close trades, and analyze market dynamics in a single service, available 24/7.
Use hypertrade swap to manage cryptocurrencies: a user-friendly dashboard, detailed statistics, and trade and balance tracking. Tools for careful risk management in a volatile market.
The best deepnude ai services for the USA. We’ll explore the pros and cons of each service, including speed, available effects, automation, and data privacy. Undress people in just a few clicks.
Simple phrasing allows tiktok likes buy quick discovery. Clear service descriptions facilitate efficient matching between providers and creators seeking specific engagement types.
Новинний портал Ужгорода https://88000.com.ua головні події міста, політика, економіка, культура, спорт та життя городян. Оперативні новини, репортажі, інтерв’ю та аналітика. Все важливе про Ужгород в одному місці, зручно з телефону та комп’ютера.
A cozy swissotel Kolasin for mountain lovers. Ski slopes, trekking trails, and local cuisine are nearby. Rooms are equipped with amenities, Wi-Fi, parking, and friendly staff are available to help you plan your vacation.
Сравнительный анализ объясняет кракен тор или кракен ссылка разницу между клир доменами с автоматическим редиректом и полными онион адресами работающими только в Tor сети.
Проверенные форумы публикуют актуальная кракен ссылка с обязательной PGP верификацией от администрации и fingerprint публичного ключа для криптографической проверки подлинности.
Casino utan registrering https://casino-utan-registrering.se bygger pa en snabbare ide: du hoppar over kontoskapandet och gar direkt in via din bank-ID-verifiering. Systemet ordnar uppgifter och transaktioner i bakgrunden, sa anvandaren mots av en mer stromlinjeformad start. Det gor att hela upplevelsen far ett mer direkt, tekniskt och friktionsfritt upplagg utan extra formular.
I casino crypto https://crypto-casino-it.com sono piattaforme online che utilizzano valute digitali per transazioni rapide e sicure. Permettono di vedere in pratica i vantaggi della blockchain: trasparenza dei processi, assenza di intermediari, trasferimenti internazionali agevoli e un’interfaccia moderna, pensata per un’esperienza tecnologica degli utenti.
Casino utan svensk licens https://casinos-utan-licens.se ar onlineplattformar som drivs av operatorer med licens fran andra europeiska jurisdiktioner. De erbjuder ofta ett bredare utbud av tjanster och anvander egna regler for registrering och betalningar. For spelare innebar detta andra rutiner for sakerhet, verifiering och ansvarsfullt spelande.
Free Online Jigsaw Puzzle https://addons.mozilla.org/ka/firefox/user/13330707/ play anytime, anywhere. Huge gallery of scenic photos, art and animals, customizable number of pieces, autosave and full-screen mode. No registration required – just open the site and start solving.
Explore hyperliquid hyperevm and gain unlimited access to a modern, decentralized market. Trade derivatives, manage your portfolio, utilize analytics, and initiate trades in a next-generation ecosystem.
Choose hyperliquid hyperevm as a convenient tool for trading and investing. The platform offers speed, reliability, advanced features, and fair pricing for cryptocurrency trading.
Use hyperliquid app for stable and efficient trading. The platform combines security, high liquidity, advanced solutions, and user-friendly functionality suitable for both beginners and professional traders.
Discover trade on hyperliquid a platform for fast and secure trading without intermediaries. Gain access to innovative tools, low fees, deep liquidity, and a transparent ecosystem for working with digital assets.
Choose hyperliquid arbitrage finder — a platform for traders who demand speed and control: over 100 pairs per transaction, flexible orders, HL token staking, and risk management tools. Support for algorithmic strategies and advanced analytics.
Check out hypertrade, a modern DEX with its own L1: minimal fees, instant order execution, and on-chain transparency. Ideal for those who want the speed of a CEX and the benefits of decentralization.
Открываешь бизнес? открытие бизнеса в оаэ полный пакет услуг: консультация по структуре, подготовка и подача документов, получение коммерческой лицензии, оформление рабочих виз, помощь в открытии корпоративного счета, налоговое планирование и пострегистрационная поддержка. Гарантия конфиденциальности.
Хотите открыть компанию оаэ? Предоставим полный комплекс услуг: выбор free zone, регистрация компании, лицензирование, визовая поддержка, банковский счет и бухгалтерия. Прозрачные условия, быстрые сроки и сопровождение до полного запуска бизнеса.
Предлагаем учреждение холдингов оаэ для международного бизнеса: подбор free zone или mainland, разработка структуры владения, подготовка учредительных документов, лицензирование, банковское сопровождение и поддержка по налогам. Конфиденциальность и прозрачные условия работы.
Профессиональное учреждение семейных офисов оаэ: от разработки стратегии управления семейным капиталом и выбора юрисдикции до регистрации, комплаенса, настройки банковских отношений и сопровождения инвестиционных проектов. Полная конфиденциальность и защита интересов семьи.
Хочешь фонд? личные фонды оаэ — безопасный инструмент для защиты активов и наследственного планирования. Помогаем выбрать структуру, подготовить документы, зарегистрировать фонд, обеспечить конфиденциальность, управление и соответствие международным требованиям.
Хотите открыть счёт? открытие банковского счета в оаэ Подбираем оптимальный банк, собираем документы, готовим к комплаенсу, сопровождаем весь процесс до успешного открытия. Поддерживаем предпринимателей, инвесторов и резидентов с учётом всех требований.
Нужна виза инвестора в оаэ? Подберём оптимальный вариант — через бизнес, долю в компании или недвижимость. Готовим документы, сопровождаем на всех этапах, обеспечиваем корректное прохождение комплаенса и получение резидентского статуса.
Комплексные бухгалтерский учет в оаэ: финансовая отчётность, налоговые декларации, управление первичными документами, аудит, VAT и corporate tax. Обеспечиваем точность, своевременность и полное соответствие законодательству для стабильной работы вашего бизнеса.
Профессиональное налоговое консультирование оаэ: разбираем вашу ситуацию, подбираем оптимальную корпоративную и личную структуру, помогаем учесть требования местного законодательства, корпоративного налога и substance. Сопровождаем бизнес и инвестиции на постоянной основе.
Оформление золотая виза оаэ под ключ: анализ вашей ситуации, подбор оптимальной категории (инвестор, бизнес, квалифицированный специалист), подготовка документов, сопровождение подачи и продления статуса. Удобный формат взаимодействия и конфиденциальный сервис.
Профессиональная легализация документов в оаэ: нотариальное заверение, Минюст, МИД, консульства, сертифицированные переводы. Сопровождаем весь процесс от проверки документов до финального подтверждения. Подходит для компаний, инвесторов и частных клиентов.
Профессиональное консульское сопровождение оаэ для частных лиц и бизнеса: консультации по визовым и миграционным вопросам, подготовка обращений, запись в консульство, помощь при подаче документов и получении решений. Минимизируем риски отказов и задержек.
Помогаем открыть брокерский счет в оаэ: подбор надёжного брокера, подготовка документов, прохождение KYC, сопровождение подачи и активации. Подходит для частных инвесторов, семейных офисов и компаний. Доступ к мировым рынкам и комфортные условия работы с капиталом.
Предлагаем корпоративные услуги в оаэ для действующих и новых компаний: регистрация и перерегистрация, выпуск и передача долей, протоколы собраний, обновление лицензий, KYC и комплаенс. Обеспечиваем порядок в документах и соответствие требованиям регуляторов.
Нужна поддержка по трудовым вопросам оаэ? Консультируем по трудовым договорам, рабочим визам, оформлению сотрудников, переработкам, отпускам и увольнениям. Готовим рекомендации, помогаем минимизировать риски штрафов и конфликтов между работодателем и работником.
Разрабатываем опционные планы в оаэ под ключ: анализ корпоративной структуры, выбор модели vesting, подготовка опционных соглашений, настройка механики выхода и выкупа долей. Помогаем выстроить прозрачную и понятную систему долгосрочной мотивации команды.
Corporate corporate bank account opening in dubai made simple: we help choose the right bank, prepare documents, meet compliance requirements, arrange interviews and support the entire onboarding process. Reliable assistance for startups, SMEs, holding companies and international businesses.
Разработка соглашения об управлении оаэ: фиксируем правила принятия решений, распределение ролей, отчётность и контроль результатов. Учитываем особенности вашей компании, отрасли и требований регуляторов. Помогаем выстроить устойчивую систему корпоративного управления.
Get your golden visa uae with full support: we analyse your profile, select the right category (investor, business owner, specialist), prepare a compliant file, submit the application and follow up with authorities. Transparent process, clear requirements and reliable guidance.
Professional business setup uae: advisory on jurisdiction and licence type, company registration, visa processing, corporate bank account opening and ongoing compliance. Transparent costs, clear timelines and tailored solutions for your project.
Comprehensive consular support uae: embassy and consulate liaison, legalisation and attestation of documents, visa assistance, translations and filings with local authorities. Reliable, confidential service for expatriates, investors and corporate clients.
Comprehensive tax consultant dubai: advisory on corporate tax, VAT, group restructuring, profit allocation, substance and reporting obligations. We provide practical strategies to optimise taxation and ensure accurate, compliant financial management.
Trusted accounting firm dubai providing bookkeeping, financial reporting, VAT filing, corporate tax compliance, audits and payroll services. We support free zone and mainland companies with accurate records, transparent processes and full regulatory compliance.
End-to-end corporate setup uae: company formation, trade licence, corporate documentation, visa processing, bank account assistance and compliance checks. We streamline incorporation and help establish a strong operational foundation in the UAE.
Launch your fund setup uae with end-to-end support: structuring, legal documentation, licensing, AML/KYC compliance, corporate setup and administration. We help create flexible investment vehicles for global investors and family wealth platforms.
Need document legalization uae? We manage the entire process — review, notarisation, ministry approvals, embassy attestation and translation. Suitable for business setup, visas, employment, education and property transactions. Efficient and hassle-free.
Comprehensive family office setup uae: from choosing the right jurisdiction and legal structure to incorporation, banking, policies, reporting and ongoing administration. Tailored solutions for families consolidating wealth, protecting assets and planning succession.
Set up a holding company in uae with full legal and corporate support. We help select the right jurisdiction, prepare documents, register the entity, coordinate banking and ensure compliance with substance, tax and reporting rules for international groups.
Need a power of attorney uae? We draft POA documents, organise notary appointments, handle MOFA attestation, embassy legalisation and certified translations. Ideal for delegating authority for banking, business, real estate and legal procedures.
Open a brokerage account uae with full support. We review your goals, recommend regulated platforms, guide you through compliance, handle documentation and assist with activation. Ideal for stock, ETF, bond and multi-asset trading from a trusted jurisdiction.
Complete uae work visa support: from eligibility check and document preparation to work permit approval, medical tests and residence visa issuance. Ideal for professionals moving to Dubai, Abu Dhabi and other emirates for long-term employment.
Авиабилеты в Китай https://chinaavia.com по выгодным ценам: удобный поиск рейсов, сравнение тарифов, прямые и стыковочные перелёты, актуальные расписания. Бронируйте билеты в Пекин, Шанхай, Гуанчжоу и другие города онлайн. Надёжная оплата и мгновенная выдача электронного билета.
Need a will in uae? We help structure inheritances, appoint executors and guardians, cover local and foreign assets and prepare documents in line with UAE requirements. Step-by-step guidance from first consultation to registration and safe storage of your will.
Автоматический сайт марокетплейс аккаунтов приветствует вебмастеров в нашем ассортименте расходников. Главная фишка этого шопа — заключается в наличие эксклюзивной библиотеки, в которой опубликованы свежие гайды по арбитражу. Тут доступны аккаунты FB, Insta, TG, Discord под любые цели: от авторегов до фармленными профилями с друзьями. Переходите в наше комьюнити, изучайте обучающие материалы, делитесь опытом и делайте профит вместе с нами прямо сейчас.
Descubre juegos exclusivos de casino: tragamonedas clasicas y de video, juegos de mesa, video poker y jackpots en una interfaz intuitiva. Bonos de bienvenida, ofertas de recarga y recompensas de fidelidad, ademas de depositos y retiros rapidos y un atento servicio de atencion al cliente. Solo para adultos. Mayores de 18 anos.
знакомства для девушек Любовь флирт милые барышни деляться своими впечатляющими достижениями в отношении мужчин, опыт как говорится, мудрость ценнее всего на свете.
Platforma internetowa mostbet casino: zaklady przedmeczowe i na zywo, wysokie kursy, akumulatory, zaklady na sumy i handicapy, a takze popularne sloty i kasyno na zywo. Bonus powitalny, regularne promocje, szybkie wyplaty na karty i portfele.
Prodej reziva https://www.kup-drevo.cz v Ceske republice: siroky vyber reziva, stavebniho a dokoncovaciho reziva, tramu, prken a stepky. Dodavame soukromym klientum i firmam stalou kvalitu, konkurenceschopne ceny a dodavky po cele Ceske republice.
Professional automatic backup secure, efficient, fast and privacy-focused reliable FTP Backup storage in Europe. 100% Dropbox European alternative. Protection on storage account. Choose European Backup Storage for peace of mind, security, and reliable 24x7x365 data management service.
Вызов электрика https://vash-elektrik24.ru на дом в Москве: оперативный выезд, поиск и устранение неисправностей, установка розеток и выключателей, подключение техники, ремонт проводки. Квалифицированные мастера, точные цены, гарантия на работы и удобное время приезда.
Хочешь сдать авто? выкуп авто спб быстро и безопасно: моментальная оценка, выезд специалиста, оформление сделки и мгновенная выплата наличными или на карту. Покупаем автомобили всех марок и годов, включая битые и после ДТП. Работаем без скрытых комиссий.
Все современные специальности ВГУ им. Машерова в одном разделе: список факультетов, направления подготовки, краткие описания программ, длительность обучения, квалификация выпускника и основные дисциплины. Помогаем абитуриентам выбрать подходящую профессию и траекторию обучения.
High-quality platform marketplace accounts invites you to our huge inventory of marketing tools. What sets us apart of our shop is the availability of an exclusive wiki section, featuring working strategies regarding ad campaigns. Discover how to warm up accounts securely and how to avoid checkpoints while running social networks. Our inventory features accounts for Twitter, Discord, LinkedIn for any purpose: from freshly registered to aged profiles with activity.
Cryptocasino reviews https://crypto-casinos-canada.com in Canada – If you’re looking for fast BTC/ETH transactions and clear terms, cryptocasino reviews will help you evaluate which platforms offer transparent bonuses and consistent payouts.
BankID-fria kasinon https://casinos-utan-bankid.com Manga spelare forbiser hur mycket uttagsgranser och verifieringskrav varierar, men BankID-fria kasinon hjalper dig att jamfora bonusar, betalningsmetoder och tillforlitlighet.
Casinos, die Paysafecard https://paysefcard-casino-de.info akzeptieren: Viele Spieler in Deutschland mochten ihr Konto aufladen, ohne ihre Bankdaten anzugeben. Casinos, die Paysafecard akzeptieren, ermoglichen sichere Prepaid-Einzahlungen mit einem festen Guthaben. So behalten Sie die volle Kontrolle uber Ihre Ausgaben und konnen weiterhin Spielautomaten und Live-Dealer-Spiele spielen.
Проблемы с алкоголем? вывод из запоя с выездом цена: анонимная помощь, круглосуточный выезд врача, детоксикация, капельницы, стабилизация состояния и поддержка. Индивидуальный подход, современные методы и контроль здоровья. Конфиденциально и безопасно.
Current recommendations: https://www.bnbaccess.eu
Recommended reading: https://fleuriste-toulouse.fr
Go for details: http://planeur-condom.fr
bukmacher internetowy mostbet casino oferuje szeroki wybor zakladow sportowych, zakladow na zywo i slotow od czolowych dostawcow. Oferuje szybka rejestracje, bonusy dla nowych graczy, przyjazna dla uzytkownika aplikacje mobilna, natychmiastowe wyplaty i calodobowa obsluge klienta.
View details: https://luxe.tv
Most Interesting: https://ahpunaises.fr
Just published: http://www.rando-cretes.fr
Главные новости сегодня: https://efaflex.ru
Женский портал https://forthenaturalwoman.com о жизни, красоте и вдохновении: мода, уход за собой, здоровье, отношения, карьера и личные финансы. Полезные статьи, честные обзоры, советы экспертов и истории реальных женщин. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу и находите идеи для себя каждый день.
Главные новости https://mynewsmonitor.com онлайн: самые важные события дня в сжатом и понятном формате. Политика, экономика, общество, мир, наука и культура. Краткие сводки, развёрнутые статьи, мнения экспертов и удобная лента, которая обновляется в режиме реального времени.
Актуальные и главные https://allnews.in.ua новости: короткие заметки о срочных событиях и развёрнутые аналитические материалы. Помогаем понять, что произошло, почему это важно и к чему может привести. Лента обновляется в течение дня, чтобы вы не упустили ничего значимого.
Главные новости https://newsline.in.ua онлайн: от срочных сообщений до глубоких обзоров и экспертных комментариев. Политика, экономика, безопасность, технологии и культура. Только проверенные факты и удобная лента, чтобы быстро ориентироваться во всём, что происходит.
Главные новости https://ukrnews.in.ua сегодня: политика, экономика, международные события, наука, культура и общественные темы. Оперативные сводки, анализ и подробные статьи. Полная картина дня, собранная в одном месте для удобного и быстрого чтения.
Все главные https://ua-news.com.ua новости в одном потоке: актуальные события, важные решения, прогнозы, мнения и аналитика. Помогаем понять, что стоит за заголовками, как события связаны между собой и почему они значимы. Обновления в режиме реального времени.
Новостной портал https://ua-today.com.ua с акцентом на достоверность: только проверенные источники, факты, комментарии экспертов и глубокая аналитика. Удобная лента событий, фильтры по темам, архив материалов и быстрый доступ к главному за день.
Современный авто https://cargurus.com.ua портал: свежие новости, премьеры, обзоры новых и подержанных автомобилей, тест-драйвы, советы по эксплуатации и страхованию. Удобный поиск по маркам и моделям, рейтинги, подборки и полезные материалы для автолюбителей любого уровня.
Онлайн авто https://autoindustriya.com.ua портал: всё об автомобилях и автожизни. Обзоры и сравнения моделей, тест-драйвы, лайфхаки по ремонту и обслуживанию, информация о кредитах и лизинге, новости рынка. Помогаем выбрать машину, понять тонкости владения и сэкономить на содержании.
Женский портал https://womanblog.com.ua с актуальными темами: тренды моды и макияжа, здоровье, фитнес, питание, саморазвитие и вдохновляющие истории. Ежедневные обновления, рекомендации специалистов и подборки идей для повседневной жизни, карьеры и личного счастья.
Современный новостной https://arguments.com.ua портал: главные новости дня, поясняющая аналитика, мнения экспертов и репортажи с мест событий. Лента в реальном времени, тематические рубрики, фото и видео. Помогаем разобраться в том, что происходит в стране и мире.
Современный женский https://womanstyle.com.ua портал для тех, кто хочет успевать всё: стиль и красота, психология и отношения, материнство, дом, путешествия и работа. Практичные лайфхаки, чек-листы, подборки и мотивационные материалы, которые помогают заботиться о себе и жить в балансе.
Авто портал https://automotive-news.com.ua для тех, кто живёт автомобилями: новости автопрома, обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору и обслуживанию, сравнение моделей и подбор авто по параметрам. Фото, видео, мнения экспертов и реальные отзывы владельцев в одном месте.
Портал о ремонте https://remont-sam.com и строительстве: от подготовки проекта и сметы до отделки и декора. Подробные инструкции, обзоры инструментов, рейтинги материалов, фото-примеры и лайфхаки. Удобная навигация по темам помогает быстро найти нужное решение для вашего объекта.
Строительный портал https://garden-story.com для профессионалов и частных мастеров: статьи и инструкции по ремонту, отделке и строительству, обзоры материалов и инструментов, калькуляторы, сметы, фото-примеры и советы экспертов. Всё, чтобы грамотно спланировать и выполнить работы.
Портал о строительстве https://stroyline.com и ремонте: пошаговые инструкции, обзоры материалов, калькуляторы, идеи планировок и дизайна, советы мастеров и реальные примеры. Помогаем спланировать работы, избежать типичных ошибок и сэкономить время и бюджет.
Строительный портал https://sovetremont.com с практическими советами: ремонт квартир, строительство домов, инженерные системы, отделка, фасады, кровля и благоустройство. Руководства, видео, расчёты и рекомендации экспертов, которые помогают экономить время и деньги.
Онлайн-портал https://stroyinfo.com о строительстве и ремонте для владельцев квартир, домов и дач: полезные статьи, схемы, чек-листы, подбор материалов и техники, советы по отделке и инженерным системам. Всё, чтобы сделать ремонт своими руками или грамотно контролировать подрядчиков.
Свежие новости https://ukrportal.com.ua Украины и мира: политика, экономика, общество, происшествия, аналитика и авторские материалы. Оперативные обновления 24/7, проверенные факты и объективная подача. Следите за ключевыми событиями, которые формируют будущее страны и всего мира.
Новости Украины https://ukrinfo24.com.ua и мира: оперативная информация, разбор ключевых событий, интервью, репортажи и аналитика. Только проверенные источники и объективная подача. Будьте в курсе того, что происходит в стране и на международной арене прямо сейчас.
Актуальные новости https://ukrmedia24.com.ua Украины и мира в одном месте: главные события дня, обзоры, комментарии экспертов, репортажи и эксклюзивные материалы. Политика, экономика, технологии, культура и спорт. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для ежедневного чтения.
Лента новостей https://uavesti.com.ua Украины и мира: самые важные события дня, актуальные темы, экспертные оценки и глубокая аналитика. Удобный формат, быстрые обновления, проверенные данные. Политика, общество, экономика, культура и мировые тенденции — всё на одной платформе.
Все новости https://uanews24.com.ua Украины и мира — быстро, достоверно и понятно: события в политике, экономике, науке, культуре и спорте. Подробные обзоры, интервью и аналитика помогают увидеть полную картину происходящего. Ежедневные обновления и удобная навигация.
Сайт для женщин https://golosiyiv.kiev.ua которые ценят себя и своё время: полезные статьи о моде и уходе, психологии, детях, отношениях, работе и хобби. Подборки идей, гайды, чек-листы и вдохновляющие истории. Помогаем находить баланс между заботой о других и заботой о себе.
Онлайн женский https://womenclub.kr.ua портал для девушек и женщин любого возраста: статьи про красоту и уход, отношения, семью, детей, карьеру и хобби. Удобная навигация по разделам, полезные советы, тесты и подборки, которые помогают находить ответы на важные вопросы.
Сайт для женщин https://e-times.com.ua о жизни, красоте и вдохновении: мода, макияж, уход за собой, здоровье, отношения, семья и карьера. Практичные советы, обзоры, чек-листы и личные истории. Помогаем заботиться о себе, развиваться и находить новые идеи каждый день.
Онлайн-сайт https://funtura.com.ua для женщин любого возраста: тренды моды и макияжа, здоровый образ жизни, питание, фитнес, отношения и саморазвитие. Регулярные обновления, советы экспертов и вдохновляющие материалы, которые помогают чувствовать себя увереннее каждый день.
Журнал о животных https://zoo-park.com дикая природа и домашние питомцы. Познавательные материалы, фотоистории, редкие виды, повадки, экология и ответственное содержание. Понятные гайды по уходу, выбору питомца и безопасному общению с животными.
Журнал о животных https://myzoofriend.com советы по уходу за питомцами, здоровье, питание, воспитание и поведение. Обзоры кормов и аксессуаров, рекомендации ветеринаров, истории спасения и интересные факты о кошках, собаках и дикой природе.
Новостной портал https://infonews.com.ua с полным охватом событий: оперативная лента, большие тексты, интервью и аналитика. Политика, экономика, общество, технологии, культура и спорт. Обновления в режиме реального времени и удобная структура разделов для ежедневного чтения.
Авто портал https://just-forum.com с полным набором разделов: новости, обзоры, тесты, подержанные авто, советы по покупке, эксплуатации и продаже автомобиля. Честные мнения экспертов, реальные отзывы, подборки лучших моделей и удобная навигация по маркам и классам.
Портал о даче https://sovetyogorod.com саде и огороде: статьи и гайды по уходу за почвой, посадке, обрезке, мульчированию и борьбе с болезнями растений. Обзоры инструментов, идеи для теплиц и компостеров, ландшафтные решения и полезные советы для урожая.
Женский портал https://dreamywoman.com о стиле жизни: красота и уход, мода, здоровье, психология, отношения, семья и карьера. Полезные статьи, подборки, чек-листы и вдохновляющие истории. Всё, чтобы заботиться о себе, развиваться и находить идеи на каждый день.
Новостной портал https://ua24news.com.ua Украины: оперативные события дня, политика, экономика, общество, происшествия и международная повестка. Проверенные факты, аналитика, интервью и репортажи. Узнавайте главное о жизни страны и мира в удобном формате 24/7.
Современный женский https://nova-woman.com сайт для девушек и женщин: тренды моды и макияжа, питание, фитнес, эмоциональное здоровье, отношения и саморазвитие. Понятные советы, обзоры, тесты и подборки, которые помогают чувствовать себя увереннее и счастливее.
Онлайн-новостной https://novosti24online.com.ua портал Украины: лента новостей, авторские колонки, интервью, обзоры и аналитика. Политика, социальные вопросы, экономика, международные события — всё оперативно, достоверно и понятно каждому читателю.
Главные новости https://smi24.com.ua Украины в одном месте: актуальные события, мнения аналитиков, расследования, репортажи и эксклюзивные материалы. Наш новостной портал помогает понимать, что происходит в стране и как события влияют на жизнь людей.
Новостной портал https://mediasfera.com.ua Украины для тех, кто хочет быть в курсе: свежие публикации, разбор ключевых событий, экспертные оценки и подробные материалы о политике, экономике и обществе. Быстрые обновления, удобная навигация и проверенная информация.
Новости Украины https://mediaportal.com.ua в удобном формате: лента последних событий, разделы по темам, авторские колонки и аналитика. Освещаем политику, экономику, безопасность, социальные вопросы и международные отношения. Портал для тех, кто хочет получать полную картину дня.
Женский сайт https://loveliness.kyiv.ua с практичным контентом: уход за кожей и волосами, стильные образы, дом и уют, дети, работа и финансы. Полезные рекомендации, экспертные материалы и вдохновение без лишней «воды». Удобная навигация по рубрикам и регулярные обновления.
Универсальный авто https://kolesnitsa.com.ua портал для водителей и будущих владельцев: обзоры автомобилей, сравнение комплектаций, тест-драйвы, советы по ТО и ремонту, подбор шин и аксессуаров. Актуальные новости, аналитика рынка и материалы, которые помогают делать осознанный выбор.
Онлайн женский https://lugor.org.ua сайт для тех, кто ценит своё время: гайды по красоте и стилю, психологические советы, идеи для дома, отношения, материнство и карьерные цели. Подборки, чек-листы, истории и советы, которые реально работают в повседневной жизни.
Украинский новостной https://mediacentr.com.ua портал с акцентом на объективность и факты: свежие новости, аналитические статьи, интервью и спецпроекты. Освещаем жизнь страны, реформы, фронт, дипломатию и повседневные истории людей. Всё важное — на одной площадке.
Новостной портал https://infosmi.com.ua Украины: главные события дня, оперативная лента, аналитика и мнения экспертов. Политика, экономика, общество, война и международные новости. Чёткая подача, удобная структура разделов и регулярные обновления в режиме 24/7.
Украинский новостной https://medicalanswers.com.ua портал: главные новости, расширенные обзоры, разбор решений власти, ситуации на фронте и жизни граждан. Фото, видео, инфографика и мнения экспертов помогают глубже понять происходящее в Украине и вокруг неё.
Онлайн новостной https://expressnews.com.ua портал для тех, кто хочет быть в курсе: свежие новости, обзоры, спецпроекты и авторские материалы. Политика, бизнес, общество, наука, культура и спорт — всё в одном месте, с понятной подачей и регулярными обновлениями 24/7.
Портал смачних ідей https://mallinaproject.com.ua прості рецепти на щодень, святкові страви, десерти, випічка та корисні перекуси. Покрокові інструкції, поради, підбірки меню й лайфхаки для кухні. Готуйте швидко, смачно та з натхненням разом із нами.
Портал о технологиях https://technocom.dp.ua новости IT и гаджетов, обзоры смартфонов и ноутбуков, сравнения, тесты, инструкции и лайфхаки. Искусственный интеллект, кибербезопасность, софт, цифровые сервисы и тренды — простым языком и с пользой для читателя.
Надёжный эвакуатор Дмитров — помощь на дороге 24 часа. Эвакуация легковых и коммерческих авто, кроссоверов и мотоциклов. Современная техника, фиксированная стоимость, быстрый выезд по городу и области.
Мужской портал https://phizmat.org.ua о стиле, здоровье, отношениях и деньгах. Свежие новости, честные обзоры гаджетов и авто, тренировки и питание, подборки фильмов и игр, лайфхаки для работы и отдыха — без воды и кликбейта. Советы, инструкции и тесты каждый день.
Туристический портал https://prostokarta.com.ua о путешествиях по России и миру: маршруты, города и страны, советы туристам, визы и перелёты, отели и жильё, обзоры курортов, идеи для отдыха, лайфхаки, личный опыт и актуальные новости туризма.
Срочный эвакуатор Дмитров: оперативный выезд, подача от 20 минут. Перевозка автомобилей после ДТП и поломок, межгород, бережная транспортировка. Работаем круглосуточно, без скрытых доплат, принимаем заявки в любое время.
Женский журнал https://eternaltown.com.ua о стиле, красоте и здоровье. Мода и тренды, уход за кожей и волосами, отношения и психология, дом и семья, карьера и саморазвитие. Полезные советы, подборки, интервью и вдохновение каждый день.
Нужно межевание? стоимость межевания земельного участка профессиональное межевание участка для оформления и регистрации прав. Геодезические измерения, уточнение границ, межевой план, сопровождение в Росреестре. Опытные кадастровые инженеры, точность и прозрачная стоимость.
Профессиональное агентство интернет маркетинга для малого и среднего бизнеса. Настройка рекламы, продвижение сайтов, рост заявок и продаж. Аналитика, оптимизация и постоянный контроль эффективности рекламных кампаний.
Продажа тяговых аккумуляторных https://e-battery.ru батарей для вилочных погрузчиков – надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники. Подбор АКБ по параметрам, доставка, установка, долгий ресурс и высокая производительность для интенсивной эксплуатации
Нужен аккумулятор? https://bestakbspb.ru/ подбор АКБ по марке и модели авто, большой выбор ёмкости и пускового тока. Доставка, самовывоз, выгодные условия и помощь в установке.
Skip to details: https://vds05058.ambien-blog.com/45627413/try-instant-load-puzzle-games-online
Курсы арабского языка https://shams-arab.ru блог с полезными статьями, упражнениями и примерами. Разбираем грамматику, лексику, диалоги и особенности языка. Делимся советами по обучению, мотивации и выбору формата занятий.
Сервис помощи https://students-helper.ru студентам с учебными работами. Курсовые, контрольные, рефераты, отчёты и презентации. Индивидуальный подход, соблюдение сроков, доработки по требованиям преподавателя и конфиденциальность.
Школа БПЛА https://obucheniebpla.ru обучение управлению беспилотными летательными аппаратами с нуля и для продвинутых. Практика полётов, основы безопасности, навигация, аэрофотосъёмка и подготовка операторов дронов по современным стандартам.
Образовательный блог https://za-obrazovanie.ru о методиках обучения и развитии навыков. Статьи о преподавании, педагогике, оценивании, мотивации и работе с детьми и взрослыми. Практика, кейсы и полезные материалы.
Обучение родителей https://mother-massage.ru массажу и гимнастике для детей от рождения до года. Практические занятия, безопасные техники, развитие моторики и укрепление здоровья малыша. Поддержка специалиста, пошаговые рекомендации и уверенность родителей.
La plateforme 1xbet burkina faso: paris sportifs en ligne, matchs de football, evenements en direct et statistiques. Description du service, marches disponibles, cotes et principales fonctionnalites du site.
Site web 1xbet rdc – paris sportifs en ligne sur le football et autres sports. Propose des paris en direct et a l’avance, des cotes, des resultats et des tournois. Description detaillee du service, des fonctionnalites du compte et de son utilisation au Congo.
Site web de parifoot rd congo: paris sportifs, championnats de football, resultats des matchs et cotes. Informations detaillees sur la plateforme, les conditions d’utilisation, les fonctionnalites et les evenements sportifs disponibles.
La plateforme en ligne xbet burkina: paris sportifs en ligne, matchs de football, evenements en direct et statistiques. Description du service, marches disponibles, cotes et principales fonctionnalites du site.
Application mobile xbet burkina. Paris sportifs en ligne, football et tournois populaires, evenements en direct et statistiques. Presentation de l’application et de ses principales fonctionnalites.
Профессиональные инъекционная косметология обучение теория, практика, безопасность и современные подходы к эстетическим процедурам. Помогаем получить уверенные навыки и системные знания для работы.
Образовательный блог https://educationruss.ru об обучении за границей. Университеты и колледжи, языковые курсы, условия поступления, стоимость, документы и жизнь студентов. Полезные статьи и рекомендации для абитуриентов и родителей.
Школа блогеров https://vdskill.ru и видеотехнологий для авторов и предпринимателей. Создание видео, сторителлинг, монтаж и продвижение. Практические занятия, поддержка наставников и актуальные инструменты для роста.
Блог Елены Беляевой https://bestyleacademy.ru профессионального стилиста. Разборы гардероба, капсульные коллекции, советы по стилю и актуальным трендам. Практика, вдохновение и понятные рекомендации для женщин и мужчин.
Профессиональное плазмолифтинг курс. Осваиваем современные техники, стандарты безопасности и нюансы работы с пациентами. Теория, практика и поддержка на всех этапах обучения.
Neironica https://neironica.ru онлайн?платформа с ИИ?инструментами для создания Контент-завода, и автоматизации публикации статей, постов и видео во все соцсети
Neironica https://neironica.ru онлайн?платформа с ИИ?инструментами для создания Контент-завода, и автоматизации публикации статей, постов и видео во все соцсети
Learn More: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bqwc15lwl1ui0tpfpsgcdeoqiis4jhdm?usp=sharing
Современная Стоматология в Воронеже лечение кариеса, протезирование, имплантация, профессиональная гигиена и эстетика улыбки. Квалифицированные специалисты, точная диагностика и забота о пациентах.
Любишь играть? игры в интернете – ваш путеводитель в мире популярных онлайн игр. Мы собрали для вас актуальную информацию из мира онлайн игр на каждый день. На сайте вы сможете найти самые последние новости об играх, свежие обзоры и видео топовых игр, увлекательные истории и литературу по различным игровым вселенным и персонажам, а также почитать гайды по вашей любимой онлайн игре.
Читать расширенную версию: УЗИ полового члена: Показания, методика и важность исследования
Telecharger 1xbet 1xbet rdc
1xbet maintenant telecharger 1xbet
Site web officiel 1xbet 1xbet rdc telecharger
Центр печатных услуг «Копирыч» https://kopirych.by предоставляет комплексные услуги нанесения печати на бумагу, а также ткани. Дополнительно мы специализируемся на изготовлении продукции для рекламы и бизнеса. Использование современного технического оборудования и безопасных материалов обеспечивает не только быстрый но и качественный заказ.
Главные новости Пензы https://inpenza.ru оперативно и достоверно. Мы освещаем все значимые события, происходящие в Пензе и Пензенской области. Важные объявления, афиша, полезная информация для каждого жителя. Ваш надежный источник новостей.
Журнал о строительстве https://prostostroy.com Ваш гид в мире стройки и ремонта. Актуальные тренды, экспертные советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. От фундамента до крыши – все, что нужно знать для успешного проекта.
Все о медицине https://zapisnapriemrostov.ru и здоровье в одном месте! Получите доступ к достоверным статьям, рекомендациям специалистов и полезным лайфхакам для поддержания отличного самочувствия. Будьте в курсе и живите полной жизнью!
Строительство и ремонт https://ctoday.ru всё, что нужно знать. Планируете стройку или обновление? Наш сайт – ваш надежный помощник. Актуальная информация о материалах, технологиях, дизайне и юридических аспектах. С нами ремонт станет проще и приятнее!
Тюмень сегодня https://kfaktiv.ru главные события города! Узнайте о последних новостях, которые формируют жизнь Тюмени. От городских инициатив до культурных событий и важных объявлений – будьте в курсе всего, что происходит в нашем любимом городе. Ваша порция актуальной информации!
Сияющая кожа https://omaske.ru и роскошные локоны – легко! Откройте секреты природы для красоты. Наши домашние маски для лица и волос подарят вам натуральный уход, глубокое питание и видимый результат. Забудьте о химии, почувствуйте силу трав и фруктов!
Всё о секретах ПО https://software-expert.ru ваш гид. Откройте для себя мир скрытых возможностей, эффективных стратегий и неочевидных лайфхаков в разработке программного обеспечения. Поймите, как создавать и использовать ПО на новом уровне.
Все о провайдерах https://providers.by Беларуси! Актуальные новости, честные отзывы пользователей и детальные обзоры тарифов. Поможем выбрать лучшего интернет-провайдера, анализируем рынок и тенденции. Будьте в курсе всех изменений!
Рейтинг казино https://casinos.ceo онлайн 2025 — актуальный обзор платформ с лицензией, играми и условиями. Сравнение бонусов, способов оплаты, скорости выплат и поддержки. Помогаем выбрать надёжное казино на основе фактов и критериев.
Ремонт своими руками https://pic4you.ru портал с понятными инструкциями и советами. Этапы работ, выбор инструментов и материалов, расчёты и примеры. Помогаем сделать качественный ремонт без лишних затрат.
Красивый интерьер https://moidomiks.ru своими руками — идеи, советы и пошаговые инструкции для дома и квартиры. Декор, отделка, планировка и сочетание цветов. Помогаем создать уютное и стильное пространство без лишних затрат.
All details at the link: https://theweekly-horoscope.com/horoscope-for-people-born-on-february-2/
проститутки владимиров шлюхи челябинск
Szukasz kasyna? kasyno online blik sprawdzamy licencje, metody platnosci, czas realizacji transakcji i dostepnosc gier. Praktyczne informacje o kasynach z platnoscia BLIK.
Нужен клининг? рейтинг клининговых компаний в москве оцениваем услуги, цены, опыт, отзывы клиентов и качество уборки. Помогаем выбрать надёжную клининговую компанию для дома или бизнеса.
Real-time boost when you buy tiktok live likes improves discovery. Active engagement during broadcasts elevates streams in trending live feeds attracting spontaneous organic viewership.
Квартиры в Москве https://kvartira-spb-pokupka.ru для покупки — большой выбор объектов в разных районах города. Новостройки и вторичный рынок, помощь с ипотекой, юридическое сопровождение и актуальные предложения от собственников и застройщиков.
Квартиры в рассрочку https://kupikvartiru-piter.ru удобный способ покупки жилья без ипотеки. Новостройки и готовые объекты, прозрачные условия, фиксированная цена и помощь в оформлении документов. Подбор вариантов под ваши возможности.
Недорогие квартиры https://kvartira-umetro.ru для покупки: актуальные предложения, удобный поиск по цене, району и метражу. Подбор бюджетных вариантов, консультации специалистов и сопровождение сделки.
Квартиры от застройщика https://kvartiravgorod.ru покупка напрямую без переплат. Новостройки на разных стадиях готовности, современные планировки, помощь с ипотекой и сопровождение сделки от выбора до получения ключей.
Однокомнатные квартиры https://kvartiradlyazhizni.ru в Москве для покупки. Большой выбор вариантов в разных районах города, удобный поиск по цене и планировке. Консультации специалистов, помощь с ипотекой и безопасное оформление сделки.
Paris sportifs pronostic foot gratuit : matchs, tournois, cotes et resultats, lignes de paris et evenements en direct. Presentation detaillee des fonctionnalites et du fonctionnement du service.
Envie de parier? Related Site Service de paris sportifs et footballistiques. Presentation des evenements disponibles, des cotes, du mode direct et des principales fonctionnalites de la plateforme. Informations utiles pour les utilisateurs.
Квартиры от застройщика https://kvartirav-vygodno.ru напрямую — актуальные цены и выбор новостроек. Подбор по параметрам, помощь с документами, ипотекой и рассрочкой. Прозрачные условия и сопровождение сделки.
Plateforme en ligne Get the facts paris sportifs, matchs de football, evenements en direct et statistiques. Decouvrez les fonctionnalites du service, les marches disponibles et comment l’utiliser.
Квартиры от застройщика https://tltdomik.ru покупка в новостройках на прозрачных условиях. Современные планировки, разные стадии готовности, помощь с ипотекой и рассрочкой. Сопровождаем сделку от выбора до получения ключей.
Квартиры в новостройках https://tltnewflat24.ru и на вторичном рынке — широкий выбор объектов. Анализ плюсов и минусов, подбор под ваши задачи, консультации специалистов и юридическое сопровождение покупки.
Geely Кунцево https://geely-kuntsevo.ru официальный дилер автомобилей Geely в Москве. Продажа новых моделей, тест-драйвы, выгодные условия покупки, кредит и трейд-ин. Сервисное обслуживание, оригинальные запчасти и консультации специалистов.
Платформа мостбет для ставок на спорт онлайн. Футбольные матчи, live-режим, коэффициенты и результаты. Описание функционала сервиса и основных инструментов для пользователей.
Портал о медицине https://zapisnapriemrostov.ru и здоровье человека. Заболевания и их профилактика, современные методы лечения, рекомендации специалистов, здоровье взрослых и детей. Полезные материалы для заботы о самочувствии каждый день.
Портал о провайдерах https://providers.by Беларуси: свежие новости рынка, отзывы абонентов и сравнение тарифов. Помогаем выбрать интернет-провайдера по скорости, цене и качеству обслуживания.
Нейросеть-раздеватор — это алгоритм искусственного интеллекта, которая анализирует изображения.
Она опирается на обученные модели для изменения внешнего вида на снимках.
Функционирование подобных решений основана на распознавании форм.
Подобные нейросети вызывают интерес в контексте современных цифровых технологий.
тг чтобы раздевать
При этом важно учитывать границы допустимого и права человека.
Использование таких технологий требует ответственного подхода.
Многие эксперты подчёркивают, что ИИ должен применяться законно.
В целом, нейросеть-раздеватор является примером возможностей ИИ, который вызывает дискуссии.
Информационный портал https://software-expert.ru о секретах ПО. Скрытые возможности программ, настройки, оптимизация, безопасность и обновления. Практичные советы и разборы для повседневного и профессионального использования.
Онлайн-портал https://ctoday.ru о строительстве и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, расчёты, выбор материалов и оборудования. Полезные материалы для частного строительства, ремонта и обустройства помещений.
Домашние маски https://omaske.ru для лица и волос — натуральные рецепты для ухода за кожей и волосами. Питание, увлажнение и восстановление с доступными ингредиентами. Советы по применению, типам кожи и волос.
Просто Строй https://prostostroy.com онлайн-журнал о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве дома. Практичные статьи, пошаговые гайды, обзоры материалов и полезные советы для частного строительства и ремонта.
High-Quality Direct Black Vsf Factories, Manufacturers
Standard Q Series High Precision Single Row Gear Ball Slewing Bearing Ring For Crane Excavator
garden-green.pl
cheap louis vuitton men
Vietnam High Quality Extension stainless Steel Compression Spring coiled Torsion Springs made in China
Standard HS Series Single Row 4 Point Contact Ball Slewing Bearing For Crane Excavator
cheap louis vuitton men belt
cheap louis vuitton men bags
High-Quality Auramine O Suppliers
cheap louis vuitton man bag
High-Quality Cold Water Fiber Reactive Dye Factory
Made in Vietnam Rear Caliper Return stainless Steel Compression Spring coiled Torsion Springs for wholesales
cheap louis vuitton material
Best Dye Acid Blue Factories
High-Quality Acid Azo Dyes Manufacturer
Made in Vietnam Stainless Steel stretch Tension extension Spring with CE certificate
Новости Тюмени https://kfaktiv.ru и области онлайн: общество, экономика, политика, происшествия и городские события. Оперативные публикации, фото и комментарии. Следите за жизнью региона ежедневно.
Красивый интерьер https://moidomiks.ru своими руками: вдохновение, мастер-классы и полезные советы. Оформление комнат, декор, текстиль и освещение. Простые идеи для обновления интерьера и создания гармоничной атмосферы.
скачать азино мобайл azino
нужна заклепка? заклепка вытяжная нержавеющая надёжный крепёж для прочных и долговечных соединений. Устойчива к коррозии, влаге и перепадам температур. Подходит для металла, строительства, машиностроения и наружных работ.
Проблемы с алкоголем? прокапать от алкоголя на дому Томск выезд врача-нарколога на дом и приём в клинике 24/7 (Томск и область) без ожидания. Осмотр, детоксикация, капельница, контроль давления и самочувствия. Анонимно, бережно, с рекомендациями на восстановление и поддержкой семьи.
Хочешь просить пить? нарколог на дом Хабаровск быстрое прибытие, медицинский осмотр, капельница для снятия интоксикации, контроль пульса и давления. Анонимная помощь взрослым, внимательное отношение, поддержка после процедуры и советы, как избежать срыва.
Есть зависимости? прокапаться Томск вывод из запоя и детоксикация под наблюдением врача. Приём и выезд на дом 24/7, индивидуальный подбор препаратов, контроль самочувствия, конфиденциальность. Помогаем стабилизировать состояние и организовать дальнейшее лечение.
Нужен юрист? юрист Новосибирск разберём ситуацию, оценим риски и предложим стратегию. Составим иск, претензию, договор, жалобу, защитим в суде. Для граждан и компаний. Первичная консультация онлайн/по телефону. Прозрачные условия.
Мед-Омск: https://med-omsk.ru Многопрофильный медицинский центр в Омске. Широкий спектр диагностических и лечебных услуг для всей семьи.
МСМ-Медимпэкс: https://msm-medical.ru Ооснащение онкологических центров оборудованием для лучевой терапии и ядерной медицины. Инновационные решения для медицины.
Камышинская ЦГБ: https://cgbkam.ru Центральная городская больница Камышина. Полный комплекс стационарной и амбулаторной помощи, диагностика и профилактика заболеваний.
Баунтовская ЦРБ: https://crbbaunt.ru Официальный сайт районной больницы в Бурятии. Доступная медицинская помощь и актуальная информация для пациентов региона.
Наш Малыш: https://malish-nash.ru Интернет-магазин товаров для детей и новорожденных. Все необходимое для комфортного роста и развития вашего ребенка.
Сайт Вінниця https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua новини Вінниці та області. Огляди, транспорт, місця та багато корисного.
Антарес-МЕД: https://antares-med.ru Центр пластической хирургии и косметологии в Санкт-Петербурге. Эстетическая медицина, коррекция фигуры и программы омоложения.
Стоматик СПб: https://stomatic-spb.ru Семейная стоматология в Санкт-Петербурге. Профессиональное лечение зубов, включая услуги для детей и лечение под наркозом.
Проблемы в авто? автоэлектрик с выездом в санкт петербурге диагностика на месте, запуск двигателя, поиск короткого замыкания, ремонт проводки, замена предохранителей и реле, настройка сигнализации. Приедем быстро по городу и области. Честная цена, гарантия, без лишних работ.
Проблемы с зубами? https://www.stomatologiya-v-bare.com лечение кариеса и каналов, восстановление формы и цвета зуба, замена старых пломб. Индивидуальный подход, современные технологии, стерильность. Запишитесь на консультацию и получите план лечения.
Стоматология в Калуге https://albakaluga.ru Альбадент — имплантация и протезирование зубов с гарантией эстетики. Виниры, костная пластика и реставрация улыбки по индивидуальному плану лечения.
Российский изготовитель реализует https://www.sportprof.su по доступным ценам от производителя. Ассортимент включает штанги, резиновые диски, эллипсоиды. Всегда имеются надежные силовые тренажеры и комплектующие для реализации спортивных задач. Приобретайте онлайн тренажер Смита, тягу верхнего блока, скамью для бицепса, Дельта машину, станок Гаккеншмидта, конструкции для работы с собственным весом, гиперэкстензию, а также сопутствующие снаряды.
Don’t miss it here: https://www.forumdaily.com/ky/the-surprising-benefits-of-solving-jigsaw-puzzles-for-all-ages/
Центр охраны труда https://www.unitalm.ru “Юнитал-М” проводит обучение по охране труда более чем по 350-ти программам, в том числе по электробезопасности и пожарной безопасности. А также оказывает услуги освидетельствования и испытаний оборудования и аутсорсинга охраны труда.
Нужны заклепки? заклепки вытяжные нержавеющие гост для прочного соединения листового металла и профиля. Стойкость к коррозии, аккуратная головка, надежная фиксация даже при вибрациях. Подбор размеров и типа борта, быстрая отгрузка и доставка.
Нужен эвакуатор? эвакуатор спб быстрый выезд по Санкт-Петербургу и области. Аккуратно погрузим легковое авто, кроссовер, мотоцикл. Перевозка после ДТП и поломок, помощь с запуском/колесом. Прозрачная цена, без навязываний.
Новости Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua на сайте КиевИнфо. Читайте о последних событиях в столице и области.
Рейтинг казино https://casinos.autos онлайн 2025 для осознанного выбора: критерии безопасности, репутации, бонусной политики, выплат и сервиса. Таблицы по странам и форматам игр, реальные условия акций, плюсы/минусы, FAQ и ссылки на правила. 18+
Лучшие подборки для вас: Продать фотоаппарат Xiaomi за деньги — скупка рядом со мной
Нужны заклепки? заклепки нержавеющие вытяжные купить 4.8 для прочного соединения листового металла и профиля. Стойкость к коррозии, аккуратная головка, надежная фиксация даже при вибрациях. Подбор размеров и типа борта, быстрая отгрузка и доставка.
Нужен эвакуатор? вызов эвакуатора цена быстрый выезд по Санкт-Петербургу и области. Аккуратно погрузим легковое авто, кроссовер, мотоцикл. Перевозка после ДТП и поломок, помощь с запуском/колесом. Прозрачная цена, без навязываний.
Расширенная статья здесь: Продать товары для зимнего спорта за деньги — круглосуточная скупка у метро
Хочешь продвинуть сайт? seo продвижение сайтов яндекс наша компания предлагает профессиональные услуги по SEO?продвижению (Search Engine Optimization) — мы поможем вывести ресурс в топ?3 поисковых систем Google и Яндекс всего за месяц. Сотрудничество строится на прозрачной основе: все договорённости фиксируются в официальном договоре, что гарантирует чёткость взаимодействия и уверенность в достижении результата.
шлюхи самара мама шлюха
любительское порно порно инцест
Центр охраны труда https://unitalm.ru “Юнитал-М” проводит обучение по охране труда более чем по 350-ти программам, в том числе по электробезопасности и пожарной безопасности. А также оказывает услуги освидетельствования и испытаний оборудования и аутсорсинга охраны труда.
Продаешь антиквариат? Скупка антиквариата в Москве — выгодно продать старинные вещи оценка и выкуп старинных вещей с понятными условиями. Принимаем фарфор, бронзу, серебро, иконы, монеты, часы, книги, мебель и предметы искусства. Возможен выезд и оценка по фото. Оплата сразу, конфиденциальность.
Стоматология в Калуге https://albakaluga.ru Альбадент — имплантация и протезирование зубов с гарантией эстетики. Виниры, костная пластика и реставрация улыбки по индивидуальному плану лечения.
Стоматология в Калуге https://albakaluga.ru Альбадент — имплантация и протезирование зубов с гарантией эстетики. Виниры, костная пластика и реставрация улыбки по индивидуальному плану лечения.
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae/ под ключ: продажа новых и б/у автомобилей, диагностика перед покупкой, регистрация и страховка. Прокат на сутки и долгосрок, включая премиум. VIP номерные знаки — подбор вариантов, торг, оформление передачи и сопровождение на русском.
Центр охраны труда https://unitalm.ru “Юнитал-М” проводит обучение по охране труда более чем по 350-ти программам, в том числе по электробезопасности и пожарной безопасности. А также оказывает услуги освидетельствования и испытаний оборудования и аутсорсинга охраны труда.
Нужен эвакуатор? вызвать эвакуатор машина быстрый выезд по Санкт-Петербургу и области. Аккуратно погрузим легковое авто, кроссовер, мотоцикл. Перевозка после ДТП и поломок, помощь с запуском/колесом. Прозрачная цена, без навязываний.
Продаешь антиквариат? Скупка антиквариата в Москве — выгодно продать старинные вещи оценка и выкуп старинных вещей с понятными условиями. Принимаем фарфор, бронзу, серебро, иконы, монеты, часы, книги, мебель и предметы искусства. Возможен выезд и оценка по фото. Оплата сразу, конфиденциальность.
Житомир новости https://faine-misto.zt.ua на сайте Файне мисто. События, обзоры и много полезного.
Новости Хмельницкий https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua на сайте у мисти. Последние события в городе и области. Авторские обзоры, транспорт и много полезного.
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae/showrooms/all/ под ключ: продажа новых и б/у автомобилей, диагностика перед покупкой, регистрация и страховка. Прокат на сутки и долгосрок, включая премиум. VIP номерные знаки — подбор вариантов, торг, оформление передачи и сопровождение на русском.
События Львова https://u-misti.lviv.ua на сайте у мисти. Последние новости в городе и области. Транспорт, обзоры заведений, блоги и много полезного.
Любишь азарт? https://everumonline.ru игры от популярных провайдеров, live-казино, бонусы и турниры. Проверяйте лицензию и правила, лимиты и комиссии вывода перед игрой. Подбор способов оплаты, поддержка и обзоры условий.
Любишь азарт? https://riobetmobile.ru бонусы, слоты и live-игры, турниры, платежные методы, верификация, лимиты и правила. Даем вывод, кому подходит, и чек-лист, на что обратить внимание перед пополнением и игрой. Актуально на 2025.
Киев новости https://u-misti.kyiv.ua на сайте у мисти. События, обзоры, полезное и интресное.
Новостной портал Одессы https://u-misti.odesa.ua поможет вам быть в курсе последних новостей города и области. Интересные обзоры мест, компании, адреса, информация о транспорте. Все про Одессу на одном сайте.
Одесса новости на https://faine-misto.od.ua читайте о последних событиях на портале Файне Одесса. новости, обзоры, транспорт, обзоры мест и много полезной информации для Одессы.
Автогид https://avtogid.in.ua портал для автовладельцев. Обзоры и рейтинги, новости автомобильной индустрии, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию машины.
Хочешь бонусы? https://casinobezdeposita.ru бонусы за регистрацию, фриспины, промокоды. Сравниваем условия отыгрыша, лимит вывода, сроки, верификацию и поддержку. Обновления и фильтры по методам оплаты.
ООО «ТрастСервис» https://www.trustsol.ru московская IT-компания с более чем 15-летним опытом в разработке, внедрении и сопровождении IT-систем для бизнеса. Компания предлагает комплексный IT-аутсорсинг, администрирование серверов и рабочих станций, безопасность, телефонию, облачные решения и разработку ПО. ТрастСервис обслуживает малые, средние и крупные организации, помогает оптимизировать инфраструктуру, снизить издержки и обеспечить стабильную работу IT-среды.
Delicious – here: https://deogiricollege.org/pag/are-online-casino-games-really-fair.html
Pastory https://pastory.app is a revolutionary educational app for kids that takes a proactive approach to entertainment. Instead of blocking content, it intelligently transforms YouTube and TikTok feeds into productive learning journeys. By using this AI-powered learning tool, parents can finally turn mindless scrolling into an enriching experience without the constant struggle over screen time.
Partnering with a specialized https://aiiimpact.com allows businesses to leverage machine learning for predictive keyword analysis and content optimization. By integrating professional ai seo services, companies can scale their organic reach faster than ever before. For businesses targeting the UK market, combining these global technologies with proven london seo services ensures that local search intent is met with surgical precision.
Черкассы новости https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua на городском портале у мисти. Последние события, обзоры, транспорт, много полезного и интересного
Experience Brainy https://askbrainy.com the free & open-source AI assistant. Get real-time web search, deep research, and voice message support directly on Telegram and the web. No subscriptions, just powerful answers.
Сдаешь экзамен? помощь студентам тусур готовим к экзаменам по билету и практике, объясняем сложные темы, даём подборку задач и решений, тренируем устный ответ. Проверим конспекты, поможем оформить лабы и отчёты.
Учишься в вузе? студенческие работы на заказ Разберём методичку, составим план, поможем с введением, целями и выводами, оформим список литературы, проверим ошибки и оформление. Конфиденциально, быстро, по шагам.
Блог Жiнка https://zhinka.in.ua полезные статьи на каждый день. Мода, уход, женское здоровье. воспитание детей, отношения. Тысячи советов на все случаи жизни.
FarbWood https://farbwood.by команда, включающая конструкторов, менеджеров и мастеров строительных специальностей. Каждый член нашего коллектива имеет за плечами собственный солидный опыт работы в своей сфере от 9 лет. Объединив общие знания и навыки, мы постарались создать компанию, которая сможет предоставить качественные услуги частным и корпоративным заказчикам.
Строительство и ремонт https://colorprofi.ru без сюрпризов: пошаговые инструкции, советы мастеров, сравнение материалов, схемы, частые ошибки и способы сэкономить. От фундамента и стен до плитки, пола, потолков и инженерки. Обновляемые статьи и ответы на вопросы.
Бесплатные программы https://soft-sng.ru для компьютера: офис, браузер, антивирус, архиватор, PDF, плееры, монтаж видео и фото, утилиты для системы. Скачивание с официальных сайтов, краткие обзоры, плюсы/минусы и аналоги. Подбор по Windows/macOS/Linux, подборки и инструкции.
Мировые новости https://lratvakan.com сегодня: свежая информация из разных стран, важные заявления, международная политика, рынки и тренды. Оперативные обновления, проверенные источники и понятные обзоры событий каждого дня.
Портал о строительстве https://strojdvor.ru ремонте и инженерных системах: от фундамента до отделки и коммуникаций. Пошаговые инструкции, сравнение материалов, расчёты, советы экспертов и типовые ошибки. Помогаем сделать надёжно и без переплат.
Новости Москвы https://moskva-news.com и Московской области: политика, экономика, общество, происшествия, транспорт, ЖКХ и погода. Оперативные репортажи, комментарии экспертов, официальные заявления и фото. Главное за день — быстро, точно, без лишнего.
Последние события Винницы https://u-misti.vinnica.ua на портале у мисти. Следите за новостями Винницы и области, полезные обзоры, справочники и много интересного из жизни города.
Полезные советы https://vashesamodelkino.ru для дома и быта: практичные идеи на каждый день — от уборки и готовки до хранения вещей и мелкого ремонта. Понятные инструкции, бытовые лайфхаки и решения, которые реально работают и упрощают жизнь.
Всё о ремонте https://svoimi-rukamy.net своими руками: понятные гайды, схемы, расчёты и лайфхаки для квартиры и дома. Черновые и чистовые работы, отделка, мелкий ремонт и обновление интерьера. Практично, доступно и без лишней теории.
Новости K-POP https://www.iloveasia.su из Кореи: айдол-группы, соло-артисты, камбэки, скандалы, концерты и шоу. Актуальные обновления, переводы корейских источников, фото и видео. Следите за любимыми артистами и трендами индустрии каждый день.
Expanded article here: site link
Premium selection: https://kangcoding.com/?p=4323
The best is in one place: https://atkell.com/blogs/250119/psychologie-du-tilt-comment-garder-le-controle-et-eviter-la
Нужна косметика? корейская косметика крем большой выбор оригинальных средств K-beauty. Уход для всех типов кожи, новинки и хиты продаж. Поможем подобрать продукты, выгодные цены, акции и оперативная доставка по Алматы.
Read the extended version: https://promotionaumaroc.com/wp-content/articles/?how-vip-programs-reward-loyal-players.html
Житомир новости https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua на сайте у місті. Актуальные события и происшествия в Житомире и области. Авторские обзоры, расписание транспорта, мета и много полезного.
вакансии специалист вакансии без опыта
Товар дня – обзоры товаров https://hotgoods.com.ua
Стоимость аренды автобуса https://gortransauto.ru
Новости Днепр https://u-misti.dp.ua последние события Днепра и области. Транспорт, обзоры, все о Днепре на одном сайте
Experience Brainy https://askbrainy.com the free & open-source AI assistant. Get real-time web search, deep research, and voice message support directly on Telegram and the web. No subscriptions, just powerful answers.
кейсы кс скины кс 2 кейсы
News about Poltava on https://u-misti.poltava.ua covers the main and interesting events in Poltava and the surrounding region. The site features transport updates, blogs, and local events.
Looking for a casino? elon-casino-top.com/: slots, live casino, bonus offers, and tournaments. We cover the rules, wagering requirements, withdrawals, and account security. Please review the terms and conditions before playing.
Looking for a casino? elon-casino-top.com: slots, live casino, bonus offers, and tournaments. We cover the rules, wagering requirements, withdrawals, and account security. Please review the terms and conditions before playing.
Experience Brainy https://askbrainy.com the free & open-source AI assistant. Get real-time web search, deep research, and voice message support directly on Telegram and the web. No subscriptions, just powerful answers.
News about Chernivtsi on https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua covers the latest events in Chernivtsi and the surrounding region. The site U Misti features local news, transport updates, blogs, and city events.
Пенсионерам https://pensioneram.in.ua украинский портал для людей на пенсии. Начисления, права, выплаты, много полезного.
Солоха женский сайт https://soloha.in.ua о моде, красоте, уходе. Полезные советы, рецепты, сонник и гороскопы.
Нужен сайт или продвижение? стоимость разработки сайта дизайн, разработка, SEO, контекст и аналитика. Делаем быстрые, удобные сайты с понятной структурой, настраиваем продвижение и приводим целевой трафик. Прозрачные этапы, измеримый результат, рост заявок.
Блог обо всём https://drimtim.ru полезные статьи, новости, советы, идеи и обзоры на самые разные темы. Дом и быт, технологии, путешествия, здоровье, финансы и повседневная жизнь. Просто, интересно и по делу — читайте каждый день.
Всё о столярном деле https://derevoblog.ru в видеоформате: обучающие ролики, мастер-классы, обзоры оборудования и проектов из дерева. Понятные инструкции, практические советы и вдохновение для создания мебели и изделий своими руками.
http://www.girobots.ru
China Zipper Coin Pouch Keychain Suppliers
Wholesale Blank Metal Keychains Bulk
China Leather Jacket Keychain Manufacturer
China Garage Door Opener On Keychain Manufacturer Factories
China Vintage Bottle Opener Keychain Supplier Manufacturer
Сделать тату в Сочи: опытные тату-мастера, авторские эскизы и аккуратная работа. Современное оборудование, одноразовые расходники, соблюдение санитарных норм. Поможем выбрать стиль и размер, проконсультируем по уходу после сеанса.
Нужен дизайн? https://paradis-ekb.ru/ создаём стильные и функциональные пространства для квартир, домов и коммерческих объектов. Концепция, планировки, 3D-визуализация, подбор материалов и авторский надзор. Работаем под бюджет и задачи клиента.
Нужна недвижимость? доска объявлений недвижимость Томск выгодно купить квартиру, дом или коммерческий объект. Работаем с жилой и коммерческой недвижимостью. Экономим время и защищаем ваши интересы.
All the Details: https://mcdmenumy.com/mcdonalds-halloween-menu/
Сломалась стиралка? ремонт стиральных машин Нижний Новгород всех марок и моделей. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка электроники. Работаем без выходных, выезд в день обращения, прозрачная стоимость и гарантия на выполненные работы.
Ищешь квартиру? район новостройка Томск квартиры от студий до просторных семейных вариантов. Подбор по цене, району и срокам сдачи, проверка застройщика и документов. Поможем купить квартиру без рисков и переплат.
Нужна гостиница? гостиница мытищи комфортные номера для отдыха и командировок. Удобное расположение, чистые номера, Wi-Fi, парковка и круглосуточная стойка. Подходит для краткосрочного и длительного проживания, выгодные цены и удобное бронирование.
Нужен отель? отель площадь ильича спокойное проживание рядом с метро и ключевыми районами Москвы. Современные номера, Wi-Fi, круглосуточная стойка. Подходит для краткосрочного и длительного размещения.
Хочешь отдохнуть? почасовой отель предлагаем почасовое размещение в комфортных номерах. Удобные кровати, кондиционер, Wi-Fi, душ. Быстрое бронирование, конфиденциальность и выгодные тарифы для краткосрочного пребывания.
softdsp.com
Comprar Sistema De Clasificación Proveedor Empresas
Mejor Máquina De Alimentación Empresas Fábricas
Comprar Prensa De Vapor Para Ropa Fábricas Empresas
Mejor Máquina De Carga De Ropa Proveedores Fábricas
Comprar Equipos De Clasificación Empresas Fábrica
дизайн квартиры сделать дизайн проект квартиры
Play at https://elon-casino-top.com online: slots from popular providers, live dealers, promotions, and tournaments. Learn about the bonus policy, wagering requirements, payment methods, and withdrawal times. Information for adult players. 18+. Gambling requires supervision.
Play online at https://elonbet-casino-game.com: slots, live casino, and special offers. We explain the rules, limits, verification, and payments to avoid any surprises. This material is for informational purposes only.
Play online at https://elonbet-casino-game.com: slots, live casino, and special offers. We explain the rules, limits, verification, and payments to avoid any surprises. This material is for informational purposes only.
сделать дизайн проект квартиры дизайн интерьера студии петербурга
Dental problems? dental clinic Full-service dental care: painless dental treatment, implants, prosthetics, orthodontics, and cosmetic dentistry. Modern equipment, experienced doctors, sterile hygiene, and a personalized approach. Consultation and treatment plan included.
квартира в гродно на сутки https://newgrodno.ru
открытие кейсов кс cs кейсы
A professional https://www.family-dentist-near-me-in-montenegro.com: therapy, surgery, orthopedics, and orthodontics all in one location. Individualized treatment plans, modern equipment, and strict sterility standards. We help you maintain long-lasting dental health.
CortexLab AI https://cortexlab.app a 2025 guide to visual transformation tools: capabilities, use cases, limitations, and risks. We explain how to evaluate quality, ethics, and safety, select application scenarios, and work responsibly with AI.
обучение рабочих на высоте https://obucheniye-okhrana-truda.ru
Купить Apple в Москве https://rznonline.ru/stati/item/top-5-prichin-kupit-iphone/ с гарантией: смартфоны, ноутбуки, планшеты, часы и аксессуары. Актуальные модели, честные цены, акции и поддержка после покупки. Самовывоз или курьерская доставка в удобное время.
iPhone 17 Pro Max https://www.cloudav.ru/mediacenter/tips/ne-prosto-smartfon-investiciya-v-komfort-pochemu-vybirayut-iphone/ в наличии: большой экран, высокая автономность, топовая камера и скорость работы. Поможем выбрать конфигурацию памяти, проверим подлинность и организуем быструю доставку. Гарантия и поддержка после покупки.
iPhone 17 Pro Max giport.ru премиальный смартфон с крупным дисплеем, продвинутой камерой и высокой скоростью работы. Отличный выбор для пользователей, которым важны качество фото и видео, мощность и комфорт в использовании.
Купить iPhone https://www.c-inform.info/news/id/111609 большой выбор моделей, памяти и цветов. Только оригинальная техника Apple, гарантия, прозрачные цены и рассрочка. Консультации, перенос данных и быстрая доставка в удобное время.
Apple iPhone 17 Pro https://x-true.info/136496-iphone-17-pro-flagman-innovacij-v-mire-smartfonov.html сочетание компактности и максимальных возможностей. Чёткий дисплей, быстрый чип, улучшенная камера и стабильная работа системы. Подходит для съёмки контента, игр и повседневных задач.
iPhone 17 Pro Max https://satom.ru/articles/iphone-17-pro-max-vs-iphone-16-serii-stoit-li-perehodit-na-novinku/ премиальный смартфон с большим дисплеем, мощным процессором и улучшенными фото- и видеовозможностями. Отличный выбор для пользователей, которым важны производительность, качество и автономность.
Нужна газификация? газгольдер под ключ: проектирование, согласования, подвод газа, монтаж оборудования и пусконаладка. Работаем по нормам, помогаем с документами, подбираем котёл и комплектующие. Прозрачная смета, сроки и гарантия.
Нужен переезд офиса? переезд офиса Обеспечим упаковку, разборку мебели, перенос и расстановку рабочих мест. Работаем оперативно и аккуратно, подстраиваемся под график компании. Понятная смета и соблюдение сроков.
Сфера недропользования — это совокупность процессов, связанный с изучением и использованием недр.
Оно включает добычу минерального сырья и их рациональное использование.
Недропользование регулируется установленными правилами, направленными на сохранение природного баланса.
Ответственное ведение работ в недропользовании способствует экономическому росту.
общество экспертов России по недропользованию
Современный горнолыжный курорт для активного отдыха: подготовленные склоны, снежные парки, школы катания и сервис. Комфортная инфраструктура, рестораны, спа и развлечения apres-ski. Идеальное место для зимнего отпуска.
Нужен трафик и лиды? разработка сайтов в казани SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
квартира посуточно гродно https://newgrodno.ru
Ищешь казино? melbet casino: слоты от топ-провайдеров, live-дилеры, турниры и акции. Объясняем условия бонусов, вейджер, депозиты и вывод средств, требования к верификации. Информация для взрослых игроков.
Лучшее казино куш казино промокод: слоты от популярных провайдеров, live-дилеры, акции и турниры. Разбираем бонусную политику, вейджер, платежи и сроки выплат, требования к верификации. Материал носит информационный характер.
Онлайн казино https://catcasino-origin.ru слоты, live-казино и специальные предложения. Подробно о регистрации, бонусах, выводе средств и безопасности аккаунта. Перед началом игры рекомендуем изучить правила.
Любишь азарт? казино комета играть играть онлайн в слоты и live-казино. Разбор регистрации, бонусов, правил игры, лимитов и способов вывода средств.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
High-Quality Candy Hearts Factory Suppliers
status.gaucbc.org
Best Candy Hearts Companies Suppliers
SIMIS Candy Hearts Manufacturer Supplier
ODM Candy Hearts Manufacturer Supplier
OEM Candy Hearts Suppliers Factory
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Современный горнолыжный курорт для зимнего отпуска: подготовленные склоны, снежные парки, школы катания и развитая инфраструктура. Комфортные отели, рестораны и развлечения apres-ski для всей семьи.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
All details at the link: https://medicalmedium.ru/effektivnye-inekczii-dlya-lecheniya-zashhemleniya-sedalishhnogo-nerva-chto-nuzhno-znat/
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Нужен трафик и лиды? веб студия avigroup в казани SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Онлайн-кинотеатр https://rosseriaall.net/ предлагает бесплатный просмотр российских сериалов в высоком качестве без регистрации. База содержит мелодраматические ленты, детективные расследования, криминал, военную тематику, комедийные и триллерные сериалы, фантастические и семейные картины с простой навигацией по категориям и периодам выпуска. Доступны как классические сериалы прошлых лет, так и новинки 2025 года. Регулярное обновление контента и интуитивный интерфейс позволяют быстро найти интересующий проект и начать просмотр в любое время.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Нужен трафик и лиды? сайт студии avigroup SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
В сфере автотюнинга московская студия “Individual Design” позиционирует себя как ведущий специалист в оклейке машин пленкой, от защитных антигравийных покрытий до ярких цветовых изменений с премиальными материалами типа LLumar, SunTek и 3M. В этой студии опытные специалисты за часы преображают стандартный кузов в художественный объект, давая не просто визуальный апгрейд, но и крепкую оборону от повреждений, идеально для жесткого климата Москвы; пленка виниловая или полиуретановая просто клеится и удаляется без остатка, превосходя покраску в удобстве, с ценами, радующими гибкостью и бонусами для лояльных посетителей. Если нужен топовый детейлинг в Лефортово, в паре минут от третьего кольца, загляните на https://individual-design.ru/ – там детальный прайс, фото работ и легкая запись, где каждый проект обретает статус персонального шедевра.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Looking for skid plates for enduro, trials, and motocross motorcycles? Visit https://hardglide.com/ where you’ll find high-quality skid plates, suspension arm guards, engine guards, and other accessories. HardGlide products ship worldwide. Learn more on the website.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
興味深いブログ https://nazenazeblog.com/ をご覧ください。最新のエンターテイメントに関する記事を掲載しています。きっと楽しい時間をお過ごしいただけます!ブログの様々なカテゴリーは、当サイトを訪れるすべての人にとって興味深いものとなり、きっと常連読者になっていただけるでしょう。
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Нужен трафик и лиды? https://avigroup.pro/kazan/kontekstnaya-reklama/ SEO-оптимизация, продвижение сайтов и реклама в Яндекс Директ: приводим целевой трафик и заявки. Аудит, семантика, контент, техническое SEO, настройка и ведение рекламы. Работаем на результат — рост лидов, продаж и позиций.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
?Necesitas mudarte? https://trasladoavalencia.es ?Necesitas una mudanza rapida, segura y sin complicaciones en Valencia? Ofrecemos servicios profesionales de transporte y mudanzas para particulares y empresas. ?Solicita un presupuesto gratuito y disfruta de nuestro servicio de calidad!
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Нужны услуги грузчиков? квартирный переезд в новосибирске с грузчиками Предоставим крепких и аккуратных работников для любых задач — переезд, склад, доставка, подъем мебели. Быстрый выезд, почасовая оплата, гибкий график и ответственность за сохранность вашего имущества.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Предприятие «Трубпром» присутствует в сфере металлопроката с 2005 года и реализует стальные трубы по оптовой стоимости. В каталоге представлены бесшовные, электросварные, нержавеющие, котельные и магистральные трубы всех диаметров. Продукция соответствует ГОСТ 8732-78, 10705-80, 10704-91 и другим стандартам качества. Покупателям доступны трубы из различных марок стали: 09г2с, 20, 3сп, 17Г1С, 13ХФА. Ищете купить магистральных труб? Подробный ассортимент размещен на сайте http://www.trub-prom.com с актуальными ценами и техническими характеристиками. Организация осуществляет транспортировку товаров по территории России.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Маска для осознанных сновидений DreamStalker Expert четвертого поколения от российского производителя оснащена Wi-Fi управлением, двумя датчиками движения глаз, RGB-светодиодами и OLED-дисплеем. Устройство доступно на https://claps.me/catalog/pribory-dlya-osoznannykh-snov/pribor-dlya-osoznannykh-snovideniy-dreamstalker-expert/ в четырех вариантах с функциями майнд-машины и транскраниальной стимуляции tACS. Прибор предлагает автоматическую запись сновидений, голосовые подсказки и возможность докупки лицензий на дополнительные функции.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Медицинский центр “Киндер Дент” в Люберцах предоставляет стоматологические услуги для детей и взрослых с опцией безболезненного лечения во сне. https://kinder-dent-lyubertsy.ru/ предлагает полный спектр услуг: от профессиональной гигиены и лечения кариеса до имплантации, протезирования и ортодонтии. Центр располагает новейшей техникой, в том числе системой Vector для пародонтологических процедур. Прием ведут врачи экспертного уровня, работающие даже со сложными случаями. Выполняются услуги по осветлению эмали, монтажу керамических накладок, различные виды протезных конструкций, костная пластика и комплексная имплантация на четырех или шести опорах.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
directionenergizesgrowth.bond – Really helpful info, I’ll be coming back to read more soon.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
momentummakers – Engaging text and clear structure help deliver the main ideas efficiently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
clarityleadsmovement.bond – Nice layout and simple flow, made it easy to find what I needed.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Progress Experience – Everything flows nicely and the message is easy to grasp.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
guidedprogresshub – Helpful recommendations are easy to follow and implement.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
forwardmotionactivatednow.bond – Great work on this site, feels polished and surprisingly easy to navigate.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Momentum Focus Online – Easy-to-read format with information that feels relevant.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
growthinsights – Inspiring content, concepts for growth are described with clarity.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
goalclaritycenter – Structured advice helps maintain steady focus throughout tasks.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Недалеко от Москвы, в городе Клин, функционирует питомник “Всё Своё”, с широким спектром саженцев плодовых и декоративных растений, оптимально подходящих для подмосковных условий. Здесь вы найдёте яблони, груши, вишни, сливы, а также экзотические варианты вроде многосортовых гибридов и колоновидных форм, все зимостойкие и готовые к богатому урожаю. Не забыты кустарники: малина, смородина, голубика, жимолость, плюс эстетичные гортензии, розы, хвойные и пионы, всего за 500 наименований от верифицированных российских источников. Профессионалы дают консультации, организуют доставку и посадку, обеспечивая крепкие растения по выгодным ценам. Посетите https://sadovodklin.ru/ чтобы ознакомиться с каталогом, акциями и форумом, где делятся советами по уходу за садом в суровых условиях севера России, и сделайте заказ прямо онлайн или по телефону для самовывоза.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritysetsdirection.bond – Pretty solid content, I enjoyed reading through the pages today.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Official Action Driven Site – Simple presentation that quickly explains the purpose without confusion.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
clarity driven ideas – Helpful perspective, ideas are communicated cleanly.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
forwardbuilder – Motivating tips, helps maintain a steady pace while achieving goals.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
momentumtracker – Very helpful, clear steps ensure projects maintain steady progress.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Планируешь перевозку? квартирный переезд удобное решение для переездов и доставки. Погрузка, транспортировка и разгрузка в одном сервисе. Работаем аккуратно и оперативно, подбираем машину под объём груза. Почасовая оплата, без переплат.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
futurefocushub – Practical advice supports planning with confidence.
directionshapesoutcomes.bond – Smooth experience overall, pages are organized and load without any lag.
clarityinmotion – Engaging text paired with logical layout enhances readability.
purpose based growth – Strong message, growth ideas are easy to understand.
ideasmomentum – Practical tips, ideas shared create real momentum in daily tasks.
dailyfocusguide – Excellent tips, prioritizing focus drives steady progress every day.
actionableclarity – Useful notes, clarity makes taking action simpler and more effective.
forwarddirectionstream – Advice is concise and helps the team stay coordinated.
energizedirection – Very insightful, these tips really energize movement toward achieving goals.
ideaimpulse – Great tips, interpreting signals properly keeps ideas progressing smoothly.
goalpath – Clear steps today create smoother results.
aligned movement – Thoughtful advice, direction helps momentum stay strong.
progressmovespurposefully.bond – Interesting site, the structure makes sense and keeps things straightforward.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Clarity Initiative – The flow feels natural and the presentation stays focused.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritydrive – Insightful tips, clarity of purpose improves the pace and quality of progress.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
consistentgrowth – Great guidance, steady actions make achieving goals feel realistic and doable.
pathmomentum – Inspiring ideas, keeps my planning momentum high throughout the day.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritygrowthhub – Helpful tips, makes following growth strategies much easier.
goalbeacon – Signals provide a clear path for moving projects forward effectively.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
directionlens – Helpful notes, clear focus shapes decisions and sets direction confidently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
futurethinking – Great content, activates strategic thinking and keeps insights clear.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritybeacon – Maintaining focus enhances results and helps achieve objectives effectively.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
conceptdrive – Very useful, proper use of signals ensures ideas progress steadily over time.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
planmomentum – Thoughtful steps help ideas grow and influence outcomes.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
clear focus wins – Well explained, focused effort improves movement toward goals.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Студия детейлинга Individual Design предлагает профессиональную оклейку автомобилей современными защитными и декоративными пленками в Москве. Расположенная в районе Лефортово, всего в пяти минутах от Третьего транспортного кольца, студия специализируется на работе с полиуретановыми и виниловыми материалами высочайшего качества. Технология оклейки позволяет преобразить внешний вид автомобиля за несколько часов без повреждения заводского лакокрасочного покрытия. Подробнее об услугах тонировки, шумоизоляции и защитной оклейки можно узнать на https://individual-design.ru/ где представлены примеры выполненных работ. Профессиональные мастера помогут воплотить любые дизайнерские идеи для вашего автомобиля.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
successsignalstream – Content is concise and organized for quick reading.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
directionactivatesprogress.bond – Clean design and clear message, it actually feels trustworthy to browse.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
alignmentforgrowth – Practical advice, aligning daily actions ensures growth feels achievable.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
signalboost – Useful reminders, the content helps prioritize growth initiatives effectively.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Нужны грузчики? грузоперевозки чехов : переезды, доставка мебели и техники, погрузка и разгрузка. Подберём транспорт под объём груза, обеспечим аккуратную работу и соблюдение сроков. Прозрачные тарифы и удобный заказ.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
structuredstepsguide – Recommendations are logical and easy to follow for consistent results.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
smartdecisions – Helpful tips, following clarity in decisions improves outcomes quickly.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionigniter – Practical advice, taking steps methodically keeps momentum strong.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionbeacon – Maintaining attention increases results and drives progress efficiently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
energyfocus – Inspiring insights, focused energy here keeps projects moving effectively.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
alliancenetworkcircle – Excellent, the network promotes strong, transparent partnerships across regions.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
networkleaders – Compelling idea, the network positioning feels confident and worldwide.
planwise – Smart planning keeps your projects on track and productive.
momentumbeacon – Clear signals make it easier to maintain steady progress.
idea driven motion – Well written, the focus on action makes ideas feel achievable.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
bondednetwork – Trusted relationships designed to support ongoing collaboration.
signalstreamline – Visual design supports comprehension and keeps readers engaged.
alliancehub – Join a network designed to foster reliable connections and mutual success.
clarityprogresshub – Practical suggestions make completing tasks easier and more structured.
nextstepforward – Encouraging content, the guidance inspires me to take the next steps confidently.
guidedprogress – Great advice, signals here make completing tasks feel organized and smooth.
innovationpathstream – Clear guidance helps turn concepts into actionable steps.
growthpathsignal – Useful insights, following these signals makes moving forward in growth clear and simple.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionmovesforwardclean.bond – Good read, I found a couple sections that were genuinely useful.
activatedmindset – Very helpful, content encourages forward thinking while keeping it simple.
momentumbeacon – Very useful, signals guide workflow and sustain consistent project momentum.
progresspathway – Inspiring insights, moving forward in small, natural increments keeps momentum steady.
businessunitycircle – Helpful guidance, uniting members produces structured results that are easy to track.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
efficiencycompass – Forward momentum keeps work moving efficiently without wasted effort.
directional focus tips – Well framed, focus guides progress naturally.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Ищете строительство каркасного дома под ключ в Краснодаре и Краснодарском крае? Посетите сайт https://masterim-novostroy.ru/ – посмотрите наши проекты и сможете собрать теплый дом за 2 недели! А при необходимости мы полностью берем на себя все этапы — от создания проекта и согласования до финишной отделки и уборки. Узнайте подробнее на сайте о качестве нашей продукции и этапах производства!
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
focusedactionpath – Useful tips, focusing direction properly makes action steps efficient and achievable.
takeactiongainconfidence – Practical reminder, confidence grows best when actions are taken consistently.
Growth Flow Online – Pages load efficiently and the message is easy to grasp.
forwardmotionstream – Guidance is concise and helps maintain steady focus throughout the day.
intentionalgrowth – Very practical, choosing growth deliberately makes progress more predictable today.
collaborationcircle – Join trusted relationships that encourage teamwork and shared success.
taskbeacon – Accuracy and structure in growth planning ensure smooth execution.
movementinsights – Useful pointers, consistently acting keeps projects moving forward.
clarityplanninghub – Guidance helps organize steps and maintain focus efficiently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
teamhub – Practical tools to help professionals collaborate effectively and achieve shared goals.
signalcreatesalignment.bond – Looks great on mobile too, everything feels quick and nicely put together.
momentumbuilder – Inspiring content, this guide shows how consistent effort builds momentum quickly.
ideahub – Implementing ideas consistently supports growth and positive results.
Компания «Трубпром» работает на рынке металлопроката с 2005 года и предлагает купить стальные трубы любых диаметров по ценам производителя. В каталоге https://www.trub-prom.com/ представлен широкий ассортимент продукции: бесшовные, электросварные, нержавеющие, котельные трубы различных марок стали и типоразмеров. Организация ведет оптово-розничную торговлю со склада в столице с транспортировкой в любой регион РФ, обеспечивая соответствие стандартам и высокое качество продукции.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
trustedgrowthnetwork – Excellent advice, trust-driven strategies create meaningful and consistent development.
flowdrivenaction – Helpful insights, taking steps regularly generates steady momentum naturally.
alliancetrustcircle – Helpful tips, the alliance builds on trust while promoting forward-thinking ideas.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
growth planning clarity – Insightful guidance, clarity strengthens long-term growth decisions.
pathofspeed – Very practical, following the right path increases project speed without stress.
nextstepguide – Great suggestions, signals here clarify what to tackle first.
momentumdirectionhub – Navigation through the guidance feels smooth and intuitive.
actiontracker – Useful content, monitoring and taking action consistently accelerates results.
forwardthinkgrowth – Great content, growth ideas feel fresh and immediately useful.
Focus Movement Network – Strong structure that keeps the concept easy to follow.
networkinghubonline – Practical, hub resources support productive networking and relationship growth.
claritytractionstream – Recommendations are actionable and help prioritize important tasks.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
momentumideas – Very practical, acting on ideas consistently helps them gain real momentum quickly.
ventureallies – Form partnerships that maximize growth and mutual benefits.
successalliancenetwork – Helpful insight, alliances here encourage collective progress and dependable results.
forwardengine – Applying direction properly generates leverage, keeping work on track and moving forward.
progressengine – Signals feed action, ensuring tasks move forward reliably and efficiently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
momentumengine – Sustained energy today accelerates long-term results.
workflowsignals – Very insightful, keeps progress on track step by step.
designedsuccess – Great guidance, carefully thought-out actions improve consistency in achieving goals.
engineofmotion – Inspiring read, the way motion works is broken down nicely.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
activemomentumcenter – Tips are logical and encourage timely execution of tasks.
forwardaction – Nice tips, taking meaningful action consistently shapes results effectively.
progresspathway – Very useful, gives a clear sense of direction for completing steps.
practicalclarity – Useful tips, well-explained ideas make following through simple and effective.
sharedgrowthnetwork – Very practical, this network encourages reciprocal growth and lasting collaboration.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
workflowcompass – Focused guidance improves daily efficiency.
solidfoundationfund – Strong long-term strategies that foster dependable outcomes.
clarityengine – Practical signals create smooth flow and keep progress on track consistently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
actionprogressguide – Tips are simple, making it easy to take real steps forward.
enterpriseconnect – Connect with enterprises and individuals to create meaningful collaborations.
clear growth flow – Enjoyed reading this, growth strategies feel organized and clean.
focusforprogress – Useful advice, directing attention correctly keeps progress steady and visible.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
trustedpartnershiphub – Excellent view, reliability and commitment are highlighted clearly.
growthmotion – Clear strategies, staying focused helps implement growth steps easily.
directionbyaction – Very helpful, deliberate actions guide direction and make progress smoother.
directionpilot – Proper guidance makes workflow more organized and effective.
continuousprogress – Excellent tips, slow and steady approaches really work in practice.
Ищете лучший авто сервис в Киеве? Посетите сайт https://bs-service.com.ua/ – там вы найдете только профессиональные услуги по ремонту амортизаторов, а также на перепрошивку автомобилей. Узнайте наши привлекательные цены на сайте, также полезные советы от специалистов BS Service.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
forwardframework – Helpful content, a structured forward framework makes tackling goals easier.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
visionaryalliancenetwork – Practical, alliance messaging positions the club as both inspiring and approachable.
goalnavigator – Focused direction turns abstract ideas into actionable steps.
planbeacon – Helpful clarity allows projects to advance steadily without confusion or delay.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
intent based growth – Useful tips, intentional actions strengthen growth momentum.
forwardgrowthtips – Great insights, following structured growth paths feels manageable and easy.
synergypowercircle – Helpful, working with strong collaborative teams creates synergy and accelerates project outcomes.
jointventureshub – Supports coordinated efforts and strategic partnerships that thrive.
motionchannelhub – Clear advice, focuses effort on the most important actions.
channelledfocus – Great advice, proper focus channels energy for better productivity.
progressclarity – Very helpful, logical steps connect ideas to actionable forward motion.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
futureflow – Useful insights, clear strategies guide forward-thinking without feeling overwhelming.
unitedgoalscircle – Useful, shared goals tied to vision create clarity and coordinated action.
claritysignal – Clear signals make complex tasks much easier to handle.
goalbeacon – Organized approaches make achieving milestones smoother and faster.
signalfocus – Very practical, signals highlight what matters most for consistent progress.
forwardengine – Energy produced by focus powers tasks and keeps projects advancing consistently.
trustedconnections – Positive alliance tone, relationships seem built on shared benefit.
ideas2results – Great guidance, actionable steps make moving from idea to result easier.
alliancenetworkcircle – Strong, collaborative circles provide structure for partnerships to thrive and expand.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Game-Lands https://game-lands.ru/ – это сайт с подробными гайдами и прохождениями для новичков и опытных игроков. Здесь вы найдете лучшие советы, топовые билды и сборки, точное расположение предметов, секретов, пасхалок, и исправление багов на релизах. Узнаете, как получить редкие достижения, что делать в сложных моментах и с чего начать в новых играх. Всё, чтобы повысить скилл и раскрыть все возможности игровых механик.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritydrivenpath – Inspiring tips, clear focus helps keep projects moving consistently.
growthallies – Reliable guidance to strengthen professional ties and improve outcomes.
velocityhubcenter – Clear explanation, concepts of movement and focus are simple to grasp.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
networkofleadersbond – Practical perspective, the network builds credibility and fosters collaborative solutions.
progressbuilder – Practical advice, consistent movement ensures a forward path emerges clearly.
momentumbeacon – Proper direction fuels progress, boosting productivity and efficiency.
workflowbeacon – Turning creative concepts into progress is simplified with clear guidance.
guidedpath – Inspiring guidance, signals provide subtle directions that enhance progress and planning.
Планируешь перевозку? грузоперевозки цена удобное решение для переездов и доставки. Погрузка, транспортировка и разгрузка в одном сервисе. Работаем аккуратно и оперативно, подбираем машину под объём груза. Почасовая оплата, без переплат.
futurefocuscircle – Strong advice, circle messaging encourages proactive planning and strategic foresight.
progressstrategycircle – Practical, well-structured growth strategies ensure steady progress and tangible results.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
?Necesitas mudarte? https://trasladoavalencia.es ?Necesitas una mudanza rapida, segura y sin complicaciones en Valencia? Ofrecemos servicios profesionales de transporte y mudanzas para particulares y empresas. ?Solicita un presupuesto gratuito y disfruta de nuestro servicio de calidad!
networkalliance – Strengthen partnerships for improved collaboration and tangible outcomes.
energyflowcenter – Very motivating, helps maintain momentum on important tasks.
actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
momentumengine – Taking repeated steps helps projects gain momentum and move forward smoothly.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
alignedpartnerships – Clear intent, relationships are positioned with strategic care.
worldpartnershiphub – Strong network focus, this hub emphasizes cooperation and shared success globally.
trustnetwork – Reliable connections that foster professional credibility and long-term success.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
momentumbeacon – Keeping attention sharp accelerates progress and maintains momentum.
proskillhub – Develop your expertise and expand your professional opportunities effectively.
Collaborative Growth Platform – Suggests real potential for partnership-driven success worldwide.
directionenergizesgrowth.bond – Really helpful info, I’ll be coming back to read more soon.
energydirectionhub – Easy to follow, focus techniques support efficient progress.
growthbeacon – Clear direction energizes growth, helping projects move forward more effectively.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
AllianceVisionHub – Logical structure, key messages are presented clearly.
Ищешь грузчиков? грузчики цена помощь при переезде, доставке и монтаже. Аккуратная работа с мебелью и техникой, подъем на этаж, разборка и сборка. Гибкий график, быстрый выезд и понятная стоимость.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Современный интерьер требует не только эстетичных, но и практичных решений, особенно когда речь идет о помещениях с повышенной влажностью или необходимостью скрыть коммуникации. Реечные потолки из алюминия и стали завоевали популярность благодаря долговечности, устойчивости к коррозии и разнообразию дизайнерских вариантов — от классических до современных стилей с различной цветовой гаммой. Нижегородская компания предлагает готовые комплекты потолочных систем брендов Бард и Cesal, включающие все необходимые элементы для самостоятельной установки без привлечения специалистов. На сайте https://potolki-52.ru/ доступен удобный калькулятор для расчета стоимости под конкретные размеры помещения, а также подробное описание комплектующих и вариантов монтажа. Возможность регулировки высоты от пяти до десяти сантиметров позволяет адаптировать конструкцию под любые технические условия квартиры или предбанника.
GTA World – Clear headings and organized layout improve readability.
clarityleadsmovement.bond – Nice layout and simple flow, made it easy to find what I needed.
ideaexchange – Share knowledge and discover fresh concepts with an interactive community.
Каталог мини-приложений https://tgram.link и ботов Telegram 2026: кликеры, TON-игры, AI-сервисы и крипто-инструменты. Обзоры, рейтинги, инструкции и обновления. Подбор по категориям, безопасности и реальной пользе — всё в одном месте.
FutureGrowthConnect – Simple design, content feels intentional and credible.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
futurealliance – Thoughtful concept, partnerships are aligned with growth and forward momentum.
alliancecircle – Join a network that fosters collaboration and meaningful achievements.
progresscompass – A reliable system keeps motion organized and results predictable.
BondedConnectionsHub – Smooth navigation, I quickly found the resources I was looking for.
ideasdrivemovement – Practical advice, ideas here promote active steps toward goals.
AnchorAllianceCenter – Guides are clear and helpful, concepts are easy to grasp quickly.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
forwardmotionactivatednow.bond – Great work on this site, feels polished and surprisingly easy to navigate.
Business Funding Bonds – Simple formatting helps the main concept stand out.
BondedHubNetwork – Step-by-step guides that are easy to follow, very helpful overall.
UnityProNetwork – Logical and easy to read, platform communicates focus effectively.
Компания ПрофПруд предлагает комплексные решения для создания искусственных водоемов на загородных участках. В ассортименте https://profprud.ru/ представлено более 250 наименований: пленка ПВХ и бутилкаучуковая резина, готовые пластиковые пруды собственного производства, профессиональные фильтры, насосы, скиммеры, фонтанное оборудование и декоративные элементы. Сотрудничество с производителями из Германии, США и других стран гарантирует европейское качество продукции с гарантией до 10 лет.
BlueChipNetworkPortal – Smooth navigation, tips are clear and easy to understand.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
networkpros – Build a network of dependable partners for shared achievements.
SummitConnectionsPortal – Quick to navigate, resources are presented logically for easy learning.
growthpartners – Collaborate with trusted individuals to achieve tangible results and impact.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
BondTrustResources – Helpful explanations and tips, I learned key bond strategies efficiently.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
NetworkSteadfast – Clean layout, content is approachable and easy to implement.
TrustHeritageLink – Helpful content with step-by-step guidance, I absorbed the information fast.
claritygrowthstream – Helpful insights provide direction and simplify decision-making.
Principles Bond Center – Helpful insights presented in a simple, easy-to-follow format.
taskbeacon – Directional anchors make project movement predictable and steady.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
claritysetsdirection.bond – Pretty solid content, I enjoyed reading through the pages today.
CoreInsightPortal – Informative articles, I quickly learned several useful strategies.
GlobalTrustedLeaders – Professional tone, ideas are presented in a straightforward way.
ProfessionalUnityLink – Organized and minimal, ideas are easy to follow and trust builds naturally.
UnityBondHub – Very informative lessons, content is easy to navigate and understand.
relationalcore – Clear intent, the approach highlights trust at every level.
StrengthHubBonded – Informative and concise, learning was simple and effective.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
BTPortal – Easy-to-follow guides, I discovered multiple strategies efficiently.
В мире современного дизайна интерьеров компания Glassway уверенно занимает лидирующие позиции как производитель высококачественных подвесных потолков, алюминиевых перегородок и светодиодных светильников, предлагая решения для офисов, торговых центров и промышленных объектов. Обладая опытом свыше 10 лет, компания гарантирует весь процесс от дизайна до установки, применяя передовые технологии и материалы, отвечающие нормам безопасности. Среди популярных продуктов – кубообразные и реечные потолки, стеклянные перегородки с смарт-стеклом, а также энергоэффективные светильники, которые уже украсили такие проекты, как ВДНХ и торговую галерею Seasons. Ищете стеклянные перегородки купить? Посетите glassway.group, чтобы ознакомиться с каталогом и заказать персонализированные решения с гарантией качества и оперативной доставкой по всей России. Покупатели выделяют стабильность и оперативность работ, подкрепляя статус Glassway как ведущего поставщика в сфере строительства.
BondHubSecure – Informative and easy to navigate, everything loads quickly.
EverBondLink – Easy-to-follow guides with concise explanations, learning bonds felt simple today.
Capital Trust Center – Organized, approachable resources make learning fast and intuitive.
BondedStrategyNetwork – Helpful guides and step-by-step tutorials, I absorbed several important points.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
directionshapesoutcomes.bond – Smooth experience overall, pages are organized and load without any lag.
GrowthVisionHub – Professional presentation, ideas of growth come across naturally.
BondedValueCenterHub – Well-laid-out tutorials, content is simple and practical.
SuccessCircleHub – Simple layout, platform makes finding details very intuitive.
goalbeacon – Acting deliberately helps visions become achievable milestones.
NetworkBondedVisions – Straightforward presentation, makes navigation and learning quick.
Крымский полуостров представляет собой уникальное сочетание живописных ландшафтов, богатого исторического наследия и целебного климата, притягивающее миллионы путешественников ежегодно. От античных руин Херсонеса до величественных дворцов Южного берега, от горных троп Ай-Петри до уединенных бухт мыса Фиолент — каждый уголок полуострова хранит свои тайны. Блог https://crimea-trip.ru/ собрал полезную информацию о курортах, пляжах, туристических маршрутах и гастрономических особенностях региона, помогая спланировать незабываемое путешествие с учетом бюджета. Здесь вы найдете советы по выбору жилья, описания экскурсионных программ и рекомендации по оздоровительным процедурам, доступным благодаря уникальным природным факторам крымского побережья и целительному воздуху горных районов.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
SolidBondHub – Very clear layout and easy navigation, understanding networking concepts was straightforward.
Capital Unity Insights – Smooth interface with practical advice for everyday use.
UnityResourcesHub – Smooth layout and concise instructions, makes learning effective and simple.
Stability Bond Resource Center – Easy-to-navigate layout and concise tutorials accelerate learning.
HarmonyBondNetwork – Easy-to-follow tutorials, made learning practical strategies simple.
strategicnetwork – Clear messaging, the circle emphasizes collaboration in a practical way.
progressmovespurposefully.bond – Interesting site, the structure makes sense and keeps things straightforward.
StrengthNetworkPortal – Guides are well-laid-out, concepts are simple to grasp and apply.
UnityNetworkPro – Concise and professional, content communicates its purpose well.
GlobalPartnerTrust – Easy-to-navigate layout, collaboration ideas are front and center.
LongTermAllianceNetwork – Easy to navigate, everything loads seamlessly and is clear.
TrustGroupNetwork – Well-organized articles, everything loads fast and learning is simple.
BondedProsperityLink – Concise lessons and practical examples, I absorbed key strategies easily.
PrimeBridge – Clean design, learning steps are straightforward and intuitive.
CollectiveTrust Academy – Friendly layout and stepwise lessons helped me grasp concepts quickly.
Prime Capital Center – Smooth layout paired with helpful guidance improves the experience.
Please visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions
TrustedHarborNetwork – Very helpful articles and guides, everything makes sense immediately.
Trust Summit Central – Clear navigation and useful resources help users explore efficiently.
EverTrust Study Hub – Step-by-step instructions with useful tips make browsing smooth.
UnityPathInfo – Clear guidance and practical resources, I learned important concepts fast.
directionactivatesprogress.bond – Clean design and clear message, it actually feels trustworthy to browse.
UnitedGrowthLink – Clean layout, site makes objectives easy to understand quickly.
BridgeOfUnity – Guides are straightforward, makes learning simple and effective.
BCPNetwork – Friendly resources and insights, I learned several important strategies.
bondedalliancehub.bond – Useful guides and clear instructions, navigating and learning is effortless.
Flow Trust Hub – Engaging and useful articles that provide solid guidance every time.
capitaltrustline center – Well-organized content allowed me to grasp information quickly.
SolidTrustPortal – Easy to navigate, information is concise and highly practical.
Integrity Bond Learning Hub – Helpful advice delivered in a friendly, concise manner.
Capital Resources Hub – Easy navigation and informative pages helped me get results efficiently.
UnifiedNetworkInsights – Well-laid-out tutorials, everything was easy to comprehend quickly.
worldalliance – Consistent message, partnerships emphasize cooperation beyond borders.
BondedNetworkLink – Well-organized content, understanding difficult concepts was much easier today.
GrandUnity Knowledge Hub – Practical tutorials and well-organized pages simplified studying complex material.
actionmovesforwardclean.bond – Good read, I found a couple sections that were genuinely useful.
GlobalSmartAlliance – Clean and organized, content supports group objectives effectively.
Bonding Knowledge Center – Organized articles and intuitive layout make browsing efficient.
BondedEverHub – Smooth tutorials and practical guides, I quickly learned important methods.
CornerstoneVisionBond – Informative and concise, content feels trustworthy and professional.
Мобильный гейминг давно превратился из развлечения в серьезное увлечение миллионов людей по всему миру. Производители смартфонов активно развивают игровые возможности устройств, предлагая специализированные линейки с мощными процессорами и улучшенным охлаждением. Портал GameBox подготовил обстоятельную подборку игровых смартфонов для разных бюджетов – от доступных моделей до флагманских решений типа Black Shark и Asus ROG. Эксперты проанализировали производительность в популярных играх вроде PUBG Mobile и Genshin Impact. Ознакомиться с детальным обзором можно по адресу https://gamebox.biz/podborka-igrovyh-smartfonov/1000028296/ где представлены технические характеристики и рекомендации по выбору оптимального устройства для мобильного гейминга.
BondCapitalCenter – Smooth navigation and clear explanations, learning bond basics was easy.
HeritageHub – Everything is easy to read, resources are structured logically.
Lineage Insights Hub – Well-organized pages and clear instructions make it simple to revisit.
Value Bond Knowledge Base – Concise instructions with smooth navigation help users learn quickly.
trustforge.bond tips – Simple layout and helpful advice make studying fast and efficient.
trustaxis reference center – Smooth navigation and practical tutorials make complex topics easy to follow.
TrustLinePathway – Easy-to-read tutorials with clear examples, I learned several strategies quickly.
CapitalBondNetwork – Practical guides, navigation is effortless and learning was fast.
trustbridgegroup.bond – Simple layout and clear guides made learning bonds fast and effective today.
signalcreatesalignment.bond – Looks great on mobile too, everything feels quick and nicely put together.
BusinessAllianceGlobal – Well-structured design, ideas feel deliberate and business-oriented.
BondUnityPortal – Informative articles presented clearly, I found resources efficiently today.
IroncladPartnerSphere – Well-organized content, navigation is smooth and intuitive.
CircleBond Tips & Tricks – Fast, user-friendly pages with reliable advice for beginners and experts alike.
Bonded Growth Tips – Clear examples and intuitive navigation make understanding quick and simple.
Partners Keystone Central – Clear messaging keeps everything easy to digest.
TrustHub – Concise tutorials, very beginner-friendly and clear.
TrustedAllied Portal – Organized content and quick-loading pages make finding tips easy.
SynergyResourceHub – Practical tips and guidance, everything is well organized for quick learning.
https://mixtum.online/ is a premium Bitcoin mixer that will provide you with an unrivaled level of anonymity. Learn more about all our advantages on our website and try out our new mixing mode with unique processing parameters. We offer a free trial and no registration required.
HorizonsBondResourcesHub – Easy navigation, tutorials are clear and provide valuable insights.
integrityaxis.bond reference – Clear structure and practical guides help me learn about bonds smoothly today.
strategicunity – Professional feel throughout, alliances seem intentional and strong.
bondedtrustcore guides – Informative content and smooth navigation help grasp concepts fast.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Very reliable content with an efficient, quick-loading layout, everything works smoothly.
ReliableTrustCircle – Smooth presentation, platform feels dependable and approachable.
ProsperityBondHub – Helpful tips and clear strategies, learning was straightforward.
PartnershipsBondedNetwork – Practical and easy-to-follow tips, helps improve collaboration strategies.
LegacyTrustLink – Informative lessons with practical advice, I found it very helpful.
Secure Unity Knowledge – Clear structure and readable content improve understanding.
NobleCircleHub – Clean layout, explanations are clear and easy to understand.
LongView Alliance Tutorials – Practical examples and clear instructions helped me learn fast.
Growth Circle Learning Hub – Organized lessons and actionable tips made exploring information easy.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
HorizonHub – Clear and concise guides, very easy to follow for beginners.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
BondedEnduranceLink – Very practical resources, easy to follow and understand.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
Специализированный магазин https://tvoyprud.ru/ предлагает комплексные решения для обустройства искусственных водоемов: бутилкаучуковые и ПВХ пленки, готовые пластиковые пруды, насосы для фонтанов и водопадов ведущих брендов OASE, Jebao, Messner, системы фильтрации и аэрации. Профессиональные консультации, широкий ассортимент оборудования и аксессуаров для монтажа помогут создать идеальный декоративный пруд любой сложности.
Visit https://bestbuyingideas.com/ for informed buying decisions.
bondedpillars.bond articles – Organized content with real-world examples, easy to apply immediately.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Fast website performance and clear information, everything loads quickly without a hitch.
trustfoundry center – Concise tutorials combined with clear examples improved my learning experience.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
GrowthBondNetwork – Smooth flow, platform feels trustworthy and approachable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
SolidarityResources – Friendly layout with helpful examples, understanding came fast.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
MutualCapitalResources – Practical guides and concise tutorials, understanding concepts became easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CapitalBondHub – Straightforward instructions, content is easy to apply.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Bonded Collective Knowledge Hub – Well-laid-out content makes learning concepts efficient and smooth.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Bond Hub Knowledge – Stepwise instructions provide clear guidance for beginners and pros alike.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CapitalStrategy – Very useful information, steps and examples are clearly explained.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
UnitedBondCenter – Guides are straightforward and informative, very beginner-friendly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Bonded Legacy Guides – Step-by-step explanations and smooth navigation make browsing easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
HeritageBondHub – Clear and organized content, very easy for beginners to follow.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Bonded Learning Portal – Organized pages and concise instructions make navigation easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondedStrength Learning – Clear sections and reliable explanations make learning easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Secure Path Hub – Well-organized instructions suitable for beginners and experts alike.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
unitystronghold.bond center hub – Friendly explanations and structured resources improve understanding quickly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CollectiveBond Tips – Practical advice and organized content make understanding effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
bondednexus knowledge hub – Fast-loading pages and practical advice make studying straightforward.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Foundation Academy Hub – Stepwise guides and well-laid-out content make learning simple.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Alliance Bond Resources – Straight to the point content with advice that feels solid.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Fast website performance and clear information, everything loads quickly without a hitch.
unitybondcraft.bond lessons – Easy-to-follow content and helpful guides make studying efficient.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
bondedvaluechain tutorials – Practical examples and clear steps help users grasp ideas efficiently.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Partners Covenant Resources – Well-written content gives the site a credible feel.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Enduring Resource Portal – Concise guides and clear instructions help grasp strategies quickly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Prime Bond Guides – Smooth navigation and actionable content make learning efficient.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
unitykeystone.bond walkthroughs – Reliable tutorials and simple navigation allow quick understanding.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
bondedtrustway hub center – Informative resources and smooth pages make learning fast and easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Trust Circle Guide – Easy-to-read material that supports thinking ahead.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Среди игроков рынка автомобильного стайлинга “Individual Design” в Москве стоит особняком как профи по нанесению пленки на авто, включая антигравийку и стильные цветные варианты на базе топовых брендов LLumar, SunTek и 3M. Мастера с солидным стажем здесь за короткое время делают из простого кузова арт-объект, предлагая эстетический upgrade плюс стойкую защиту от сколов, что ценно в московской реальности; такая пленка наносится и снимается без проблем, выигрывая у покраски в практичности, а расценки впечатляют гибкостью и скидками для завсегдатаев. Если нужен топовый детейлинг в Лефортово, в паре минут от третьего кольца, загляните на https://individual-design.ru/ – там детальный прайс, фото работ и легкая запись, где каждый проект обретает статус персонального шедевра.
CoreAlliant Hub – Clear and practical guides make learning easy and fast today.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Future Bond Knowledge – Step-by-step explanations help users explore concepts efficiently.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
capitalties.bond tips – Informative content and structured lessons helped me grasp new ideas quickly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
capitalbondline tips – Clear explanations and concise examples helped me understand topics efficiently.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Capital Insights Center – Friendly navigation and concise guides help users learn efficiently.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Trusted Insights Hub – Friendly layout and smooth navigation support confident use.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Business Alignment Hub – Shows potential as a meeting point for strategic partners.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
TA Works – Pages are straightforward and explanations are easy to understand.
trustcontinuity.bond – Clear layout and practical guides make learning straightforward today.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
unitycatalyst walkthrough hub – Easy navigation and actionable lessons make the material easy to absorb.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Unity Learning Center – Smooth navigation and structured tips make understanding effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
VisionSphere – Easy-to-read, ideas are communicated effectively and feel current.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
trustlineage.bond strategies – Structured lessons and easy-to-follow content improve knowledge efficiently.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
unitybondworks reference – Step-by-step examples and concise content made comprehension easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Unity Online – Simple design, and the site is easy to navigate.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PartnerLinkAlliance – Clear layout, professional tone conveys strategic goals.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Онлайн-кинотеатр https://rosseriaall.net/ предлагает бесплатный просмотр российских сериалов в высоком качестве без регистрации. База содержит мелодраматические ленты, детективные расследования, криминал, военную тематику, комедийные и триллерные сериалы, фантастические и семейные картины с простой навигацией по категориям и периодам выпуска. Представлены популярные проекты минувших сезонов и свежие премьеры текущего года. Постоянное пополнение библиотеки и удобная система поиска дают возможность мгновенно обнаружить нужный сериал и запустить его круглосуточно.
UnitySphere – Information is clear, everything is easy to follow.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
bondedcontinuum overview – Simple layout, fast response times, and content that feels authentic.
Круиз подарил возможность увидеть новые места без постоянных переездов, комфорт лайнера делает путешествие легким: https://kruizy-po-persidskomu-zalivu.ru/
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
DirectionLine – Clean structure and easy access to content.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
VisionPathway – Well-structured pages and helpful tips, very easy to browse.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Harvest Central – Clicked on this link randomly, but the information was engaging.
DreamEdge – Unique ideas and user-friendly design make browsing creative content easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PathDock – Practical layout and guidance, navigation feels smooth and effortless.
FocusAndClarity – Smooth reading experience with well-organized insights.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
ChannelVision – Easy-to-follow layout with practical content makes browsing enjoyable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PixelPlayground – Interface is intuitive, design ideas are clear.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
steadfastlink hub – Content is laid out cleanly and the messaging is straightforward.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
IdeaStream – User-friendly design, reviewing content is effortless and enjoyable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
TaskTracker – User-friendly design makes it simple to manage multiple tasks.
MapCompass – Well-laid-out content, made searching much quicker.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
ClarityFlow – Friendly interface, navigating content feels natural and smooth.
VisionDeskPro – Clear layout and helpful tips make navigating ideas effortless.
ChicCorner – Friendly design, content is easy to access and navigate quickly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
DirectionHub – Organized layout, exploring concepts feels effortless and enjoyable.
Purposeful Steps – Well-structured guides help strategies click quickly and easily.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
MotionPathway – Helpful guides with clean design, finding information is easy today.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
VectorTrack – Practical advice and smooth layout make exploring content easy.
TrendIdeas – Browsing through the ideas was genuinely enjoyable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
AlignProgress – Clear guides, navigating the site feels fast and effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
BrightDesk – Practical guides and friendly interface make learning quick and easy.
VisionDrive – Clear navigation, site makes generating ideas quick and easy.
visit bonded core group – Navigation is clear and the site comes across as reliable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Insight Path – Straightforward layout helps users move quickly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CraftedPath – Easy-to-use interface, understanding strategies feels quick and natural.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
VisionStrategy – Clear layout, providing actionable insights for strategy planning.
CircleVision – Friendly menus and clear instructions, applying strategies is straightforward.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
ModernTrack – Always current, makes checking back worthwhile.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
WayMotion – Organized interface, exploring ideas is effortless and efficient.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
LinkPathway – Friendly interface with clear guidance, following strategies feels easy and quick.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PlanetLoop – Practical guides and clear navigation make exploring effortless.
ActivationStation – Clear layout, site makes following strategies simple and quick.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
SkillBoost – Clear guides, learning concepts is smooth and effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondCore – Friendly layout with helpful hints, understanding strategies feels fast and easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
Momentum Blueprint – Helpful insights and a welcoming interface make strategy browsing quick.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CoreHaven – Clear pages with useful hints, understanding ideas is quick and straightforward.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
UnityPath – Clear pointers and structured design help visitors explore ideas efficiently.
strategicbonding main site – The information flows well and stays concise.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
SecurePath – Well-organized content ensures learning strategies is smooth and intuitive.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
ResourceLink – Smooth interface, connecting ideas is easy and straightforward today.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
TaskVault – User-friendly design and features make managing work seamless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
FocusCreates – Friendly layout and clear instructions, navigating content is easy.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PathFirst – User-friendly interface, exploring resources is easy and straightforward.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
FocusFlow – Information is laid out clearly, moving around feels effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondCore – Friendly interface with practical tips, browsing content is simple and fast.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
GrowthTrack – Practical steps and clear instructions make strategy learning fast.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
PathwayDesign – Smooth interface, discovering ideas feels natural and efficient.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondNest – Well-laid menus with practical tips, browsing content is natural and effortless.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
DreamForge – Intuitive layout, understanding strategies feels effortless and natural.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
CapitalLink – Stepwise tips and organized layout improve site exploration.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
TrustTrack – Easy-to-follow steps let users navigate content effortlessly.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
IgnitionPoint – Very intuitive site, exploring content and ideas is fast and enjoyable.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
LaunchSphere – Smooth design and straightforward steps simplify launching projects.
For Informed Buying Decision – visit https://topbuyingidea.com/
MomentumPath – Organized content, understanding steps is fast and straightforward.
TrendFlow – Smooth navigation and concise content, discovering insights is easy.
UnityBridgeHub – Friendly design with practical tips, generating ideas is smooth and enjoyable.
WealthNetwork – Well-organized steps ensure exploring topics is easy.
PathNavigator – Plenty of useful material and a layout that feels effortless to use.
BrainZone – Well-organized content, site makes learning strategies easy today.
Компания Noblelift Equipment JSC Ltd. зарекомендовала себя как мировой лидер по производству складской техники с полным модельным рядом оборудования для логистических задач. Российское представительство https://nobleliftrussia.ru реализует широкий ассортимент погрузчиков, штабелеров, тележек и уборочной техники с расширенной гарантией до 36 месяцев. Продукция сертифицирована по стандартам EAC, CE и ISO 9001, успешно эксплуатируется более чем в 100 странах мира, что подтверждает высочайшее качество техники.
MapLoop – Easy-to-follow guides with engaging content make learning smooth.
NextMomentum – Informative design, browsing guides and tips is fast and intuitive.
capital bond network – Branding aligns well throughout and the content reads smoothly.
Concept Blueprint – Clear presentation helps information sink in fast.
TrustNest – Well-laid pages and practical advice, navigating content is intuitive today.
Nomad Cars https://nomadcars.net/ — ваш надежный партнер в импорте авто из Китая. Поставляем автомобили напрямую с заводов и аукционов в любую точку мира! Прозрачные условия, честные цены и полное сопровождение сделки.
TrustBridge – Step-by-step guidance makes browsing strategies effortless.
ActionRoute – Friendly interface with practical tips, following instructions feels effortless.
UnityCore – Structured guides and intuitive interface make understanding concepts easy.
TaskLoop – Navigation is simple and all features are very easy to understand.
ActionPoint – Friendly interface, exploring strategies is simple and straightforward.
InsightHub – Clean layout with practical tips, understanding strategies feels natural.
ExecutionBridge – Well-laid menus and clear instructions, applying ideas is smooth and easy.
CapitalPath – Friendly design and helpful guides, browsing content is straightforward and effortless.
FocusConcepts – Helpful advice that made learning feel natural.
TrustLink – Friendly interface and practical guidance simplify navigating concepts quickly.
MotionHubPlus – Organized guides and easy layout make exploring content fast and simple.
InsightPath – Organized content, exploring ideas feels quick and straightforward.
Action Learning Lane – Clear direction and organization boost understanding.
StrongholdPath – Clean interface and practical hints, navigating strategies feels natural.
CapitalTrust – Step-by-step guidance ensures strategies are simple to follow.
Среди подмосковных ландшафтов, в Клину, развивается садовый комплекс “Всё Своё”, предлагающий разнообразные саженцы деревьев и кустов, адаптированные к местной погоде. Здесь вы найдёте яблони, груши, вишни, сливы, а также экзотические варианты вроде многосортовых гибридов и колоновидных форм, все зимостойкие и готовые к богатому урожаю. Внимание уделено и кустам: малина, смородина, голубика, жимолость, включая декоративные гортензии, розы, хвойные и пионы, более 500 позиций от проверенных поставщиков из России. Специалисты с опытом проводят консультации, услуги доставки и высадки, предоставляя здоровые растения по привлекательным ценам. Посетите https://sadovodklin.ru/ чтобы ознакомиться с каталогом, акциями и форумом, где делятся советами по уходу за садом в суровых условиях севера России, и сделайте заказ прямо онлайн или по телефону для самовывоза.
ProgressPilot – Smooth design and easy-to-follow content, learning and applying ideas is fast.
visit anchorunity – Navigation is smooth and the content doesn’t feel overwhelming.
TrailClarity – Friendly design, navigating concepts feels straightforward and simple.
NexusHub – Smooth layout and practical guidance, exploring concepts is easy and fast.
PlanHub – Clear guidance and a layout that makes strategy planning simple.
InsightVision – Friendly layout and clear instructions, exploring knowledge feels natural.
ProgressRoute – Smooth experience with content that’s updated often.
CapitalCrew – Practical guides with smooth layout make exploring strategies simple.
Innovation Space – Clear menus and engaging content make exploring easy.
GrowthChain – Friendly design, exploring ideas feels straightforward and easy.
ClarityVision – Practical tools and readable steps make understanding tasks quick.
TrustBridgeFlow – Step-by-step guidance simplifies exploring ideas.
BondPath – Practical guidance and intuitive layout simplify understanding strategies.
EliteAdvisor – Friendly site design, understanding resources is fast and intuitive.
LegacyTrackHub – Friendly layout with helpful advice, learning content feels effortless.
VibeNotes – Intuitive layout, browsing and learning feels natural and easy.
PlanProgress – Informative resources, site layout helps understanding concepts quickly.
UnityTrack – Intuitive menus and clear instructions, browsing content feels natural.
EngineDock – Smooth and clear navigation makes finding information easy and effective.
SecureVision – Organized structure with helpful guides, exploring ideas feels effortless.
ProgressPath – Helpful guides and clean design, navigating ideas is fast and straightforward.
bonded growth directory – Clean visuals and responsive pages make browsing easy.
ConnectAxis – User-friendly interface, browsing ideas feels smooth and straightforward.
FlowWorks – Helpful content and easy-to-read structure make exploring fast and straightforward.
BondedCore – Clear guidance and friendly layout simplify understanding ideas.
BondedLeaf – Friendly layout and clear tips, learning strategies is effortless today.
IntentionalEdge – Practical content and smooth navigation, understanding methods is fast.
UnityCrest – Informative content, smooth layout, understanding concepts feels fast and effortless today. UnityNetwork – Practical guidance and clean design help users create and explore effectively.
FlowProgress – Practical layout, site makes planning and learning simple and intuitive.
FusionVision – Clear interface and helpful hints, learning strategies feels simple and intuitive.
FutureLine – Well-organized pages and concise tips, exploring strategies is easy.
FlowTracker – Smooth interface, and organizing steps feels natural.
Стоматологическая клиника “Киндер Дент” в Люберцах специализируется на детской и взрослой стоматологии с возможностью лечения под наркозом. https://kinder-dent-lyubertsy.ru/ предлагает полный спектр услуг: от профессиональной гигиены и лечения кариеса до имплантации, протезирования и ортодонтии. Клиника оснащена современным оборудованием, включая аппарат Vector для лечения десен. Пациентов консультируют высококвалифицированные специалисты, справляющиеся с нестандартными ситуациями. Выполняются услуги по осветлению эмали, монтажу керамических накладок, различные виды протезных конструкций, костная пластика и комплексная имплантация на четырех или шести опорах.
UnityConnect – Friendly design with clear instructions, navigating resources is fast.
GrowthHub – Clear layout and helpful guides, navigating concepts is simple and quick.
Понравилось сочетание азиатского колорита и международного уровня обслуживания https://kruizy-iz-kataya.ru/
BondedNetwork – User-friendly tips and structured layout simplify browsing.
ForceVision – Clear navigation, learning new ideas is simple and intuitive.
GlobalVision – User-friendly interface with well-laid-out resources makes finding info simple.
PathSignal – Smooth layout, useful content helps keep progress organized and clear.
StyleFlow – Clean and modern guides, navigating design tips is simple and fast.
FinanceFocus – User-friendly guides designed for fast content exploration.
HubBridge – Friendly interface with clear instructions, exploring ideas feels simple today.
UnityBondHub – Friendly interface, organized layout, navigating resources feels fast and effortless now.
NextFlow – Informative content, understanding steps is simple and natural.
MoneyNetwork – Concise steps and smooth design make exploring resources effortless.
BondedInsight – Clean interface with helpful hints, navigating ideas is effortless.
Direction Toolkit – Helpful resources with a polished interface aid understanding.
BondPath – Concise guidance ensures visitors explore topics efficiently.
TrustNest – Well-laid pages with concise guidance, exploring resources is easy.
SafeUnity – Easy guides and structured layout make navigation effortless.
BondFocus – Well-organized pages with clear tips, learning ideas is smooth and intuitive.
KeystoneBridge – Smooth interface and concise tips, navigating content is simple.
BondPath – Practical guidance and intuitive steps make exploring ideas easy.
CapitalPath – Clear steps and smooth interface make content easy to follow.
CapitalNest – Well-laid pages with practical hints, exploring content is simple.
AnchorTrack – Smooth structure with concise tips, exploring ideas is straightforward.
PartnersPath – Easy-to-follow guidance ensures users can explore strategies intuitively.
simple growth link – The site is neat, and content is easy to follow and understand.
unity harbor homepage – The platform is well-structured and appears credible.
WaypointHorizon – Smooth pages with practical tips, navigating ideas feels fast and simple.
PathForward – Intuitive interface, learning from guides feels smooth and simple.
CapitalPath – Concise guidance and clean design simplify exploring ideas.
capital bond portal – Navigation is smooth, and the explanations are beginner-friendly.
BondPathway – Smooth design with helpful guidance, learning strategies is simple and quick.
BondBridge – Friendly pointers and smooth layout simplify navigation.
official capital bridge – The design is clean and the information flows naturally.
check this platform – Information flows smoothly and makes the concept easy to grasp.
DesignStudio – Smooth navigation, finding new ideas feels natural and enjoyable.
official bond craft – Pages are easy to navigate and explanations make sense.
visit capital trust hub – Everything seems organized and easy to navigate.
official trust alignment – The layout is clear and explanations are straightforward.
ImpactPilot – Smooth interface, learning strategies and applying them feels quick.
helpful vision page – The content flows well and is easy to understand.
read full details – Layout is tidy and content is easy to comprehend.
trust craft site – First impression is positive, and the content seems well-structured.
BTB Connect — пространство деловых связей и новостей бизнеса https://btbconnect.ru/ – Запущена платформа для размещения и распространения пресс-релизов. Проект ориентирован на компании, которые ищут новые форматы делового сотрудничества, партнёров и медийное присутствие. BTB Connect объединяет бизнес и информационные площадки, создавая основу для дальнейшего роста и взаимодействия.
NextNavigator – Helpful tips and guides, learning new ideas is simple and fast.
progressmovesintelligently.bond – The site has a unique name, but the purpose is explained clearly.
TrustLine Hub – Everything is neatly arranged, making it simple to understand.
claritypowersmovement.bond – The design is simple, and the information is clear and easy to follow.
Waypoint Portal Pro – Clean sections and intuitive navigation make accessing information simple.
BizPower – Well-structured interface, learning new concepts feels effortless today.
Assurance Guide – Simple interface, everything is clear and accessible.
forward motion activated site – The layout loads quickly and information is straightforward.
Bridgeworth Center – Clean interface and practical layout help locate information efficiently.
Link Overview – Organized layout, pages are smooth and information is easy to scan.
Capital Alloy – I found their guides really clear and simple to understand.
Pillar Center – Information is organized logically, easy to follow and understand.
CH Insights – Quick and simple platform, helpful tutorials.
Trustline Portal – Content is straightforward, with no unnecessary clutter.
Capital Hub – Clear design and browsing feels effortless.
Trust Hub – Organized content, everything is clear and accessible.
Lynx Lab – Straightforward content, excellent for online learning.
Crest Insights – The design is sleek, and content sections are logically arranged.
CN Hub – Helpful tutorials, everything is easy to understand.
Axis Navigator – Easy-to-scan pages with clear and logical content flow.
Vertex Hub – Simple and professional, all sections are easy to navigate.
Centurion Bond page – Smooth navigation and helpful information throughout.
Official CoreMerge – User-friendly design with concise messaging throughout.
Bonded Connect Pro – Quick and organized pages, content is easy to follow.
Dependable Bond – Clean layout with easy navigation and clearly presented information.
стартовал наш новый https://utgardtv.com IPTV?сервис, созданный специально для зрителей из СНГ и Европы! более 2900+ телеканалов в высоком качестве (HD / UHD / 4K). Пакеты по регионам: Россия, Украина, Беларусь, Кавказ, Европа, Азия. Фильмы, Спорт, Музыка, Дети, Познавательные. Отдельный пакет 18+
Portfolio – Clean design, fast-loading pages, and easy to find details.
CW Insights – Helpful guides and resources, everything is easy to understand.
Careers – Job listings are readable, and applying is straightforward.
ClearPath site – Picked up some good info here, everything runs smoothly.
The HB Link – Interface is smooth, pages respond quickly, and reading is very straightforward.
Bonding guide – Easy-to-follow pages with helpful explanations.
Bonded Portal – Layout is tidy, content is concise and helpful.
IC Portal – Professional appearance, smooth navigation, and content is clear.
Dependable Capital – Smooth design and fast-loading pages with clear, useful content.
Bond Central – Layout is neat, browsing is smooth, and information is easy to read.
Central Hubspot – Easy to explore, information is concise and reliable.
Services – Content is straightforward, menus are intuitive, and pages look professional.
Careers – Job listings are simple to read, and the structure feels welcoming.
Optimum Space – Menus are intuitive, browsing is seamless, and content is easy to follow.
HC Hub Online – Clean layout, pages render fast, and information is well-arranged.
Official ClearView Bond – Informative pages that are simple to understand.
About – Pages are well-organized, menus are easy to use, and content reads naturally.
CoreWard Bond – Clean design and quick loading, content feels reliable.
Harbor Hub Online – Smooth navigation, polished layout, and content is simple to scan.
Mainline Online – Clean structure, responsive pages, and information is simple to follow.
Bonding platform – Pages are clear, and the information is presented logically.
Ищешь музыку? скачать бесплатно музыку 2026 популярные треки, новые релизы, плейлисты по жанрам и настроению. Удобный плеер, поиск по исполнителям и альбомам, стабильное качество звука. Включайте музыку в любое время.
Newsletter – Subscription process is simple, and formatting is clean and tidy.
Events – Simple pages, navigation is intuitive, and content feels organized.
OB Hub Online – Menus are clear, pages load quickly, and content is straightforward.
Community – Easy to explore, organized layout, and content is approachable.
HA Central – Structured layout, smooth navigation, and all information is easy to find.
Bond support site – Clean interface that makes usage effortless.
Bond platform – Clear design and fast-loading pages make browsing easy.
Partners – Professional layout, navigation is simple, and information is readable.
Login – Simple interface, quick loading, and instructions are easy to understand.
Bond Gateway – Well-laid-out pages, easy to browse, and content is presented logically.
Summit Knowledge – Smooth browsing, clean design, and information is well-organized and easy to read.
Bond support site – Pages are structured well, making information easy to follow.
The Keystone Hub – Pages render quickly, layout is tidy, and content is simple to follow.
Bond Online – Structured pages, fast navigation, and content is concise.
Services – Service details are simple to find, and browsing between sections is straightforward.
HS Central – Structured layout with intuitive navigation, content is easy to locate.
Login – Simple layout, fast pages, and instructions are easy to follow.
Trusted Horizon Navigator – Intuitive menus guide users efficiently through all pages.
Bond overview – Picked up useful knowledge without any hassle.
Downloads – Smooth pages, clearly arranged content, and easy to navigate.
Cornerstone Axis site – Pleasant layout and intuitive structure make finding info effortless.
need a video? film production company in italy offering full-cycle services: concept, scripting, filming, editing and post-production. Commercials, corporate videos, social media content and branded storytelling. Professional crew, modern equipment and a creative approach tailored to your goals.
The Mariner Hub – Pages load quickly, layout is neat, and content is simple to scan.
Summit Link – Pages respond quickly, and navigation feels effortless on every section.
Bond Info Center – Clean layout with content that’s simple to follow.
The PL Link – Navigation is smooth, design is tidy, and content is clear.
Products – Product details are clear, and browsing between items is smooth.
The IA Link – Polished interface, pages load fast, and reading through sections is straightforward.
Products – Pages load quickly, navigation works well, and content feels reliable.
Durable Link portal hub – Well-presented pages and professional design make information easy to access.
Documentation – Clean pages, fast navigation, and content is reliable.
Anchor reference – Well-functioning site with a friendly design.
Legacy Portal – Pages are well-organized, interface is intuitive, and content reads clearly.
Covenant portal hub – Clear, well-organized pages that are simple and informative to explore.
Trusted Legacy Access – Fast-loading pages with clear headings make locating information simple.
Trust Link – User-friendly design, clear structure, and browsing is effortless.
Contact – Easy-to-use interface, well-arranged pages, and smooth navigation.
PB Hub Online – Clean design, intuitive menus, and content is concise and helpful.
Trust Link – Easy navigation combined with a clear layout makes all content accessible.
Impact Online – Simple design, fast-loading pages, and content is easy to locate.
Team – Staff profiles are easy to read, and the page layout is organized.
Concord Bonding – Found the right info quickly, everything is explained clearly.
FAQ – Very informative and the interface is simple to use.
Contact – Simple interface, navigation flows smoothly, and content is approachable.
CrestLink portal – Information is presented clearly and the site is easy to use.
News – Crisp design, pages are fast, and content is clear and concise.
MA Connect – Layout is neat, navigation works well, and information is simple to follow.
Unified Anchor Insight – Navigation is natural and content is presented in a straightforward way.
Harbor Hub Online – Navigation is smooth, interface feels polished, and content is readable.
PB Connect – Smooth browsing, menus are logical, and content is concise.
Surefoot Connect – Information is easy to read and the site layout feels organized and reliable.
The Infinite Hub – Pages load quickly, layout is tidy, and content is easy to digest.
Resources – Neat structure, helpful information, and effortless browsing.
ZenPath Insights – Smooth browsing experience with simple navigation and readable content.
HB Online – Modern look with intuitive navigation, everything displays correctly.
Confluence Bond portal – Simple to browse, information is well organized and fast to access.
CrestPoint hub – Clean design and logical structure make exploring the site simple.
Events – Simple design, menus are intuitive, and content feels well-organized.
Login – Simple design, pages load quickly, and instructions are easy to follow.
BoldEdge – Current, well-laid-out content makes trend exploration seamless.
Pricing – Easy to compare options and the site feels polished.
check this page – Clean presentation overall, intuitive menus, and content flows naturally
Anchor Central – Well-organized sections, smooth navigation, and content is clear.
Unity Harbor Hub – Clear layout and concise content make browsing fast and simple.
PF Portal – Layout is organized, browsing is effortless, and content is concise and readable.
Community – Neat interface, smooth menus, and content is approachable.
Integra Corner – Interface is sleek, pages load quickly, and information is easy to read.
SurePath Portal – Pages load quickly, and content is structured for easy reading.
platform overview – Easy-to-follow idea, executed nicely, and encourages joint learning
The Heritage Link – Smooth navigation, well-organized sections, very easy to explore.
Visit Site – Layout is crisp, browsing is easy, and content feels trustworthy and clear.
MomentumSphere – Intuitive guides and organized design make managing tasks easy.
Bond platform – Easy-to-follow layout and smooth browsing experience.
Bonding portal – Interactive experience with clear instructions and helpful content.
AboutUs – Clear sections, professional design, and effortless browsing.
FAQ – Organized pages, navigation is simple, and explanations are easy to follow.
Events – Pages are well-structured and load instantly, very convenient.
Bond Hub Online – Layout is tidy, navigation works well, and information is readable.
zblog5 – Browsing is simple, pages respond quickly, and information is clear and reliable
The PC Link – Professional layout, intuitive navigation, and content is clear and easy to read.
Integrity Hub – Pages are organized, navigation is smooth, and content is easy to follow.
Synergy Base – Users can browse without confusion and locate important details easily.
Valor Bond Online – Professional design with readable content provides easy access.
web hub – Creative concepts are highlighted, pages are easy to scroll, inspiring thoughts along the way
Bond Hub Online – Sleek layout, responsive pages, and information is easy to digest.
Community – Neat design, smooth menus, and information is approachable.
Support Services – Smooth browsing, engaging features, and content is informative and accessible.
TrendVista – Layout is clean, trend guidance is simple to follow.
FAQ – Organized pages, smooth browsing, and explanations are easy to understand.
Bond reference – Practical content that loads fast and is easy to follow.
Bonding services – Clear, digestible information and well-laid-out pages improve usability.
Partners – Professional layout, smooth browsing, and information is clear.
Monument Corner – Pages render fast, design is clean, and content is easy to read.
Resources – Informative content, clean layout and simple to browse.
go to site – Clean visuals, simple navigation paths, and text is well structured
Tutorials – Clear instructions, tidy layout, and fast page response.
The IB Link – Polished pages, fast-loading design, and reading content is effortless.
Peakline Central Online – Well-laid-out pages, easy navigation, and information is concise and readable.
Talon Insight – Quick navigation with content that is concise and simple to understand.
Value Crest Hub – Simple design with well-structured content for effortless browsing.
main page – Nicely organized content, browsing is effortless and fun
Bond Central Hub – First impression is polished, pages load fast, and content is very easy to follow.
ActionCircle – Logical instructions and practical examples make following steps effortless.
Events – Crisp layout, navigation is easy, and content feels approachable.
Mutual Corner – Pages render quickly, menus are clear, and content is easy to digest.
online page – A clean presentation that supports smooth browsing and clear information
Partners – Professional design, smooth browsing, and information is readable.
Login – Quick access, simple design, and effortless navigation throughout.
PeakTrust Hub – Layout is neat, navigation is smooth, and content is easy to follow.
Home – Smooth navigation, fast-loading pages, and content is clear and reliable.
Talon Insight Hub – Pages are easy to move through, and content is immediately understandable.
Vantage Bond Base – Well-laid-out pages with smooth browsing make information easy to follow.
creative hub – Engaging concepts, smooth browsing, and ideas spark curiosity
CoreChoice – Smooth interface and clear sections make discovering options easy and fast.
Significant Works – Layout is neat, content is clear, and pages are easy to navigate.
page link – Navigation is intuitive, pages open fast, and details are trustworthy
Testimonials – Engaging layout, smooth interface, and information is easy to follow.
Events – Simple design, menus are intuitive, and content is organized.
Features – Organized structure, smooth navigation, and text is easy to follow.
True Harbor – Clean layout with well-organized content leaves a strong first impression.
online page – Items are easy to find, prices feel fair, and info is clearly presented
Portfolio – Neat visuals, structured content, and browsing is effortless.
Veracity Bond Guide – Well-laid-out pages with readable content make exploring simple and fast.
FocusWorksHub – Well-laid-out pages and practical guidance make using the site simple.
Features – Organized structure, navigation is smooth, and reading is effortless.
True Path Online – Clean structure and smooth browsing allow users to access essential content easily.
Documentation – Structured pages, fast loading, and content is reliable.
start exploring – Creative concepts flow naturally, pages inspire curiosity and imagination
Verifiable Bond Access – Pages load smoothly, content is straightforward, and navigation feels natural.
PlanMaster – Navigation is effortless, and the insights are actionable.
go to site – Layout is uncluttered, navigation is simple, and information is clear for users
RestoQ Hub – Pages load quickly, the interface is intuitive, and information is well-structured and trustworthy.
online page – Trendy collections easy to explore, navigation is smooth and inspiring
Посетите сайт https://priority-auto.ru/ – мы предложим проверенные корейские, китайские, японские автомобили и мотоциклы с существенной выгодой, с подбором на аукционах и быстрой доставкой в РФ. Узнайте обо всех наших преимуществах на сайте или воспользуйтесь опцией “рассчитать стоимость” – где вы увидите конечную стоимость авто. Подберем авто под ваш бюджет, вышлем актуальную стоимость и расскажем, как будем доставлять.
Veritas Capital Guide – Pages load smoothly, layout is simple, and content is easy to comprehend.
CoreAction – Logical layout and concise guidance make executing actions simple and fast.
Testimonials – Clear structure, navigation is effortless, and reading is simple.
homepage link – Browsing is effortless, layout remains simple, and content reads well
landing page – Layout feels lively, browsing is smooth, and content is easy to discover
Resources – Minimal design, smooth navigation, and information is clear.
web hub – Pages feel fast, layout is refined, and information is easy to navigate
Хочешь познакомится? https://znakomstva-blizko.ru удобный способ найти общение, дружбу или отношения. Подборки чатов и ботов, фильтры по городу и интересам, анонимность и быстрый старт. Общайтесь без лишних регистраций и сложных анкет.
online page – Trendy products featured clearly, site vibe is fresh and stylish
уроки вокала для начинающих с нуля https://uroki-vokala-moskva.ru
web hub – Navigation is straightforward, pages load clearly, and text is easy to follow
platform overview – Easy-to-follow idea, executed nicely, and encourages joint learning
плоская крыша под ключ цена москва https://ploskaya-krovlya-moskva.ru
CoreMerge portal hub – Layout is easy to understand and content is clear and organized.
Nicely organized store – Products are presented clearly and with care.
Friendly curated boutique – Products are arranged well, and navigation feels intuitive.
магазин рыбы и морепродуктов https://mor-produkt.ru
Golden Maple Market Finds – Site feels warm and inviting, items are easy to explore.
сайт про дачу https://dacha-ua.com в Україні: сад і город, посівний календар 2026, вирощування овочів, ягід і квітів, догляд за ґрунтом, добрива та захист рослин, ландшафтний дизайн, будівництво й інструменти. Практичні поради та інструкції.
trans porn
Visit 20Tekzader – Pages load quickly, layout feels organized, and information is easy to grasp.
CoreStead portal hub – Informative and accessible, making learning quick and easy.
Well-organized shop – The layout keeps everything easy to navigate and understand.
Нужна фотокнига? напечатать фотокнигу в москве недорого печать из ваших фотографий в высоком качестве. Разные форматы и обложки, плотная бумага, современный дизайн. Поможем с макетом, быстрая печать и доставка. Идеально для подарка и семейных архивов
Calm curated boutique – Items are displayed neatly, and exploring feels soothing.
Inviting Golden Rift Store – Finding items is simple, and browsing is relaxing.
Хочешь фотокнигу? заказ фотокниги индивидуальный дизайн, премиальная печать и аккуратная сборка. Большой выбор размеров и переплётов, помощь с версткой. Быстрое производство и доставка
CoreWard resource – Pages load quickly and the content is clearly written.
HollowCreek Finds – Fast-loading pages, items are clearly shown and browsing is enjoyable.
Quick-loading shop – The overall structure feels clean and easy to browse.
Ivory Branch Picks – Easy to browse and the selection is appealing.
Curated online Drift Pine – Products are neatly displayed, and exploration is effortless.
Chic Golden Shore Boutique – Layout is neat, and finding products is effortless.
Планируете отдых на Черноморском побережье и хотите свободно передвигаться по городу и окрестностям? Компания CarTrip предлагает широкий выбор автомобилей для комфортного путешествия по Анапе и Краснодарскому краю. В каталоге представлены модели на любой вкус и бюджет: от экономичных Datsun On-Do до стильных Skoda Rapid с автоматической коробкой передач. Все автомобили арендуются без залога, что делает процесс максимально простым и удобным. Посмотреть полный ассортимент можно на сайте https://auto-arenda-anapa.ru/nashi-avto/ где указаны актуальные цены и условия. Круглосуточная поддержка менеджеров поможет выбрать идеальный вариант для вашего отпуска.
Moonfall Boutique – Intuitive layout, pages load quickly, and items are appealing.
best ever free porn sex pictures
Bonding guide – Structured content with intuitive navigation throughout the site.
Partners – Professional design, smooth menus, and information is readable.
CHB-AC Connect – Simple design, responsive pages, and information is clear and professional.
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
Well-crafted selections – Browsing shows care, quality, and thoughtful presentation.
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Larkspur Boutique – Shopping is intuitive with clear product categories.
Hollow Ridge Online Store – Layout is intuitive, items are accessible and shopping feels effortless.
Tide Select Emporium – Browsing feels effortless, and products are nicely displayed.
MF Collection – Smooth pages, well-organized products, and simple navigation.
Driftstone Collective finds – The collection is unique, with clear photos and honest product details.
adult xxx video hot porn site
Official Cornerstone Axis – Clean layout, easy to browse, and information is well-presented.
LF Marketplace – Navigation is simple and products are easy to find.
MF Online Hub – Simple navigation with clear product presentation and enjoyable browsing.
The Golden Thread – Simple design, smooth browsing, and products feel thoughtfully curated.
Honey Fern Store – Enjoyable browsing, items look well curated and site navigation is smooth.
Boutique showcase – The products are displayed attractively, giving a positive browsing experience.
Driftwood Lane treasures – The store has a pleasant feel, and product discovery is smooth.
Covenant Bond – Informative and easy to read, content is clear without feeling heavy.
Omnigram https://omnigram.ru/ — CRM в Телеграме: собирает диалоги из WhatsApp, Avito, Telegram-ботов, Gmail и других каналов прямо в Telegram-группы с топиками по клиентам. Команда отвечает вместе, делает внутренние заметки, ставит статусы сделок командами (/paid, /closed), подключает ИИ-помощника и вебхуки/API. Старт — за пару минут (QR). Тариф от 1000 ?/мес: 5 000 сообщений и 1 бот; дальше — pay-as-you-go. Работает на любом устройстве, доступ можно разграничить.
Moonfall Shop – Simple browsing, fast pages, and products are visually appealing.
Lighthouse Finds Online – Pages load quickly and items are easy to locate.
Vein of Gold – Pleasant experience, pages load fast and shopping is effortless.
Edouard Chambost Official – Layout is tidy, navigation is smooth, and content is easy to read.
Indigo Harbor Store – Browsing was pleasant, items feel thoughtfully curated and the layout is smooth.
IndigoHarbor Goods Hub – Pages load fast, items are appealing and the site feels polished.
Coastal treasures shop – Browsing feels relaxed, and the content is easy to understand.
Ember Coast treasures online – Each item looks appealing, and navigation is effortless.
Bonding guide – Practical, clearly presented content with intuitive navigation.
MF Collection – Smooth pages, well-organized products, and simple navigation.
LinenWild Goods – Browsing is enjoyable and products feel naturally selected.
Harbor Market – Clean layout, items look carefully selected and pages load quickly.
Inked Meadow Goods – Clean interface, items appear high-quality and shopping is smooth.
Промышленные полы требуют профессионального подхода к проектированию, устройству и последующему обслуживанию объектов. Компания МВПОЛ специализируется на создании износостойких покрытий для складов, производственных цехов и логистических комплексов. Полимерные наливные полы выдерживают интенсивные нагрузки и сохраняют эксплуатационные характеристики долгие годы. Специалисты выполняют работы с гарантией от двух лет, используя сертифицированные материалы европейского качества. Подробнее об услугах и технологиях можно узнать на сайте https://mvpol.ru/ в разделе проектов. Бесплатный выезд инженера и составление сметы помогают точно спланировать бюджет строительства.
Friendly Emberfield finds – Layout is clean, and browsing flows naturally.
Shop smart deals – The store layout is clean, and prices look fair for the selection.
Bond overview – Well-laid-out pages with readable text and effortless navigation.
Moonfall Specials – Smooth experience, pages load quickly, and items are easy to find.
LunarBay Specials – Smooth navigation and a nicely curated product range.
Harvest Hub – Smooth browsing and products are displayed in a neat, appealing way.
grain supply hub – Wide range to pick from, pricing felt honest and shipping was smooth.
Explore Al-Brett – Simple layout, pages respond fast, and content is easy to digest.
Exeed в СПб у официального дилера ИАТ https://exeed-iat.ru/ – это выгодные цены и авто в наличии, а также профессиональный сервис. Узнайте на сайте модельный ряд, наши преимущества и предложения. Цены, комплектации и модельный ряд на сайте, а также специальные финансовые программы, трейд-ин, лизинг, скидки и акции, тест-драйв!
Iron Hollow Online Shop – Nice design, browsing is effortless and products feel thoughtfully arranged.
Charming Emberleaf online – The shop feels welcoming, and products are easy to explore.
a href=”https://moonpetalcollective.shop/” />moon petal curation – Smooth layout and an interesting collection made browsing fun.
Copper Petal selection – Products are well presented, and navigating the shop is smooth.
trend alert deals – Site navigation is smooth, found several stylish items.
unique value zone store – Good experience overall, checkout felt smooth and effortless.
Бутик-отель с бассейном и спа Gentalion https://gentalion.ru/ у метро Белорусская в центре Москвы – это отличные и комфортные номера, превосходный сервис и современное высококлассное оснащение! Наш отель близок к культурным сокровищницам столицы: музеям Кремля, Большому театру, Третьяковской галерее. Радушие, вежливость и забота о клиентах ожидают вас у нас в гостях!
MF Online Hub – Simple navigation with clear product presentation and enjoyable browsing.
Bond reference – Pages load quickly and content is organized for easy reading.
opalgrain deals – Pleasant shopping experience, items are well displayed and ordering is straightforward.
LunarCoast Hub – Easy navigation with products clearly displayed and shopping feels smooth.
Наш IT-портал https://nashkomp.ru/ – ваш навигатор в мире высоких технологий. Ежедневно публикуем актуальные новости из жизни индустрии, обзоры мощного железа и тесты новейших гаджетов. На сайте вы найдете аналитику рынка программного обеспечения, практические руководства по программированию и советы по кибербезопасности. Мы пишем просто о сложном: от архитектуры нейросетей до сборки игрового ПК. Наша цель — создать экспертное сообщество для профессионалов и энтузиастов. Будьте в курсе будущего сегодня вместе с нами!
Quiet Stone Online Shop – Items look genuine, layout is clean and exploring is effortless.
topbuyingidea.com
High Coast Boutique – Pages load quickly, browsing is simple, and items look curated.
hub for everyday tips – Casual style, useful tips easy to find, enjoyable experience.
Moonfall Boutique – Intuitive layout, pages load quickly, and items are appealing.
Moonfall Shop – Simple browsing, fast pages, and products are visually appealing.
modern thought click – Enjoyed the insights, navigation is simple and site is user-friendly.
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
Moonfall Boutique – Intuitive layout, pages load quickly, and items are appealing.
motivational clicks online – Positive vibe, smooth layout, and simple navigation.
плоская кровля цена https://ustrojstvo-ploskoj-krovli.ru
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Every Moment Matters – Positive energy throughout, easy navigation and encourages mindful thinking.
free live sex cams
lesbian sex
best free american porn sites
inspired ideas hub – Pages load quickly, content is insightful and easy to browse.
Здоровье зубов требует регулярного профессионального ухода, особенно когда речь идет о детях и пациентах с повышенной тревожностью. Клиника “Киндер Дент” в районе Некрасовка специализируется на семейной стоматологии с возможностью лечения под наркозом для максимального комфорта пациентов. Современное оборудование и квалифицированные врачи обеспечивают безопасное проведение процедур любой сложности: от профессиональной гигиены полости рта до имплантации зубов. Узнайте больше на сайте https://kinder-dent.ru/ где представлен полный спектр услуг для детей и взрослых, включая ортодонтию, эстетическую стоматологию и безболезненное отбеливание зубов до восьми тонов за один сеанс. Бесплатная консультация имплантолога поможет составить индивидуальный план лечения.
Купить iPhone 17 https://itcrumbs.ru/neochevidnye-pomoshhniki-10-skrytyh-funktsij-iphone-17-kotorye-sekonomyat-vam-vremya_105144 новая модель Apple с современным дизайном, высокой производительностью и улучшенной камерой. Оригинальная техника, гарантия, проверка серийного номера. Выбор конфигураций памяти, удобная оплата и быстрая доставка.
Аренда серверов https://ctrl.qckl.net/index.php?rp=/store/discount-server с гарантией стабильности: мощные конфигурации, высокая скорость сети и надёжное хранение данных. Масштабируемые решения, резервное копирование и поддержка 24/7. Оптимально для бизнеса и IT-проектов.
fresh fashion corner – Easy to browse, fun shopping experience, items are appealing.
Нужно авто? автомобили мурманск подбор по марке, бюджету и условиям эксплуатации, проверка юридической чистоты. Помощь с кредитом и обменом, быстро и удобно.
Официальная торговая платформа на кракен маркетплейс с escrow системой для защиты интересов покупателей и продавцов
раздел сохранности объекта культурного наследия https://razdel-osokn.ru
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Отдых в мегаполисе требует особого подхода — важно найти место, где можно расслабиться вдали от шума. Сауна в Коптево на Большой Академической улице предлагает уютную атмосферу после капитального ремонта и работает круглосуточно. Гости получают доступ к парной из берёзы, бассейну длиной пятнадцать метров и караоке для весёлых вечеров. Заведение лояльно относится к пожеланиям посетителей — разрешено приносить собственные напитки и угощения. Подробнее об услугах и актуальных ценах можно узнать на https://sauna-koptevo.ru/ перед бронированием времени. Идеальная чистота и соблюдение санитарных норм гарантируют комфортный отдых для компаний до шести человек.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Риобет казино https://riobetcasino-ytr.ru играть онлайн в слоты и live-казино. Разбор регистрации, бонусов, условий игры, вейджера, лимитов и способов вывода средств.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Посетите сайт https://strong.by/ и вы сможете купить новые и б/у запчасти с разбора в Минске. У нас большое новое поступление машин на разбор, так что вы без проблем найдете качественные запчасти по выгодной цене для своего авто у нас. Просто выбирайте марку авто, а мы покажем вам все варианты. Забирайте запчасти самостоятельно или воспользуйтесь доставкой день в день по Минску.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Сейчас всё больше игроков интересуются различными дополнениями, читами и скриптами для Roblox — с их помощью можно упростить геймплей, добавить новые функции и разнообразить игры. На одном игровом портале https://joyverse.ru/ регулярно публикуются свежие скрипты, коды и обзоры на игру Роблокс, которые могут пригодиться как новичкам, так и опытным игрокам.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Read More: https://astonwellltd.co.uk/about-ricky-casino-support-care-service/
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
УЗИ на дому https://vrachnadom-sev.ru
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Безопасный доступ через Tor на кракен onion вход с полной анонимностью и многоуровневым шифрованием трафика
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
focus-driven results – Highlights that concentrating effort leads to tangible growth outcomes.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
progressive traction tips – Encourages smart planning and steady action to achieve lasting results.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
signal clarity – Suggests clarity improves when progress follows reliable signals.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Самозанятые водители и индивидуальные предприниматели получают стабильный доход при подключении к парку AREON. Гибкий график работы позволяет самостоятельно планировать время выполнения заказов и выходные дни. Ежедневные выплаты через приложение Яндекс.Про обеспечивают финансовую предсказуемость и оперативный доступ к средствам. Для регистрации потребуется паспорт, водительские права категории B и разрешение на деятельность такси. Более подробная информация о тарифах и условиях размещена на https://parkareon.ru/ для всех желающих. Повышенные тарифы Комфорт+ и Бизнес доступны после прохождения специального тренинга и собеседования.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
forward movement guide – Shows that consistent effort accelerates results more than waiting for perfect planning.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
forward motion tips – Highlights that combining planning with action keeps projects on track.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Продажа тяговых ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Юридические вопросы требуют профессионального решения — ошибки в документах или процедурах могут стоить времени и денег. Команда опытных специалистов в Краснодаре предлагает бесплатную первичную консультацию по семейным, жилищным и автомобильным спорам. Адвокаты проводят детальный анализ ситуации и разрабатывают чёткий алгоритм дальнейших действий для клиента. Компания работает с делами любой сложности — от раздела имущества до оспаривания сделок с недвижимостью. Записаться на приём и получить помощь можно через https://yuridicheskaya-kompaniya-krasnodar.ru/ в удобное время по телефону. Более трёхсот человек ежемесячно получают квалифицированную поддержку и защиту своих интересов в судах всех инстанций.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
action tips hub – Encourages moving forward, which often opens new paths.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Ищете взлом вибер? xakerforum.com/threads/uslugi-xakera-vzlom-tajnaja-slezhka.282/page-6 — это тематический ресурс для тех, кто серьезно относится к кибербезопасности, анонимности и современным цифровым инструментам. Форум предлагает структурированные разделы по защите данных, тестированию на проникновение, изучению уязвимостей, обсуждению софта и методик, а также обмену практическим опытом между профессионалами и новичками. Живое сообщество, свежие гайды и подробные технические разборы позволяют участникам быстро получать сжатую, практическую информацию без лишней теории и давно неработающих методик. Здесь ценится конкретика, грамотный разбор кейсов и реальные рабочие решения.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
дайсон фен оригинал купить дайсон фен оригинал купить .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Ищете отель в центре Москвы? Обратите внимание на отель Тукан https://hoteltukan.ru/ – это удобное бронирование, комфортные номера, парковка и чистота. Посмотрите на сайте наши номера – они вам понравятся! А отель можете забронировать даже за час до заезда. Недорогие варианты в европейском стиле у нас, так есть и роскошные апартаменты для самых взыскательных и требовательных клиентов.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
цена стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками официальный сайт купит… цена стайлер дайсон для волос с насадками официальный сайт купит… .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Get Things Done – Motivates action while staying grounded in reality.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Бутик-отель с бассейном и спа Gentalion https://gentalion.ru/ у метро Белорусская в центре Москвы – это отличные и комфортные номера, превосходный сервис и современное высококлассное оснащение! Наш отель близок к культурным сокровищницам столицы: музеям Кремля, Большому театру, Третьяковской галерее. Радушие, вежливость и забота о клиентах ожидают вас у нас в гостях!
Omnigram https://omnigram.ru/ — CRM в Телеграме: собирает диалоги из WhatsApp, Avito, Telegram-ботов, Gmail и других каналов прямо в Telegram-группы с топиками по клиентам. Команда отвечает вместе, делает внутренние заметки, ставит статусы сделок командами (/paid, /closed), подключает ИИ-помощника и вебхуки/API. Старт — за пару минут (QR). Тариф от 1000 ?/мес: 5 000 сообщений и 1 бот; дальше — pay-as-you-go. Работает на любом устройстве, доступ можно разграничить.
фен купить dyson оригинал stajler-dsn-1.ru .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
кіно онлайн якості кримінальні серіали дивитися онлайн
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Looking for skid plates for enduro, trials, and motocross motorcycles? Visit https://hardglide.com/ where you’ll find high-quality skid plates, suspension arm guards, engine guards, and other accessories. HardGlide products ship worldwide. Learn more on the website.
GuidedGrowth – Practical structure and clean presentation help visitors implement advice easily.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
progress unlocked – Clear message, unlocking progress through focused growth feels achievable.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
ideas unleashed – Practical point, letting ideas loose generates momentum quickly and smoothly.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Клининговая компания Наша Белка https://nashabelka.ru/ оказывает услуги по уборке всех видов помещений – от генеральной уборки до мойки окон и витрин. Узнайте обо всех наших выгодных предложениях на сайте и видах работ которые мы предлагаем и профессионально оказываем. Поддерживайте свои помещения в чистоте по выгодным ценам!
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
motion synchronized – Insightful point, synchronized motion results when direction creates proper alignment.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
clarity engine – Thoughtful phrasing, clarity acts as an engine for forward progress and momentum.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
фен дайсон как отличить оригинал fen-dn-kupit-13.ru .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
купить стайлер дайсон новосибирск купить стайлер дайсон новосибирск .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
дайсон стайлер для волос цена с насадками официальный сайт купит… дайсон стайлер для волос цена с насадками официальный сайт купит… .
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
OutcomePathway – Clear, practical guidance paired with a structured layout supports effective action.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
clarity leverage point – Practical thought, identifying clarity points creates leverage that improves results.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
amplified momentum – Insightful idea, direction amplifies momentum and helps achieve goals faster.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Ищете женский журнал про здоровье, красоту, отношения? Посетите https://victoryhome.ru/ – это онлайн блог, у нас все о звездах, моде, красоте, любви, сексе, гороскопы, психология, дети, здоровье и многое другое. Записи в блоге появляются постоянно, что позволит вам получать интересную информацию каждый день. Подробнее на сайте.
For informed buying decision visit – https://bestbuyingideas.com/
Транспортная компания “Открытый Краснодар” более пяти лет обеспечивает качественные и безопасные перевозки пассажиров по городу и краю. Фирма специализируется на аренде автобусов, микроавтобусов и минивэнов с профессиональными водителями для корпоративных клиентов, туристических групп и организации свадебных кортежей. Особое внимание уделяется перевозке детей и вахтовым маршрутам с соблюдением всех норм безопасности. На странице https://krasnodar-transport.ru/ представлены тарифы и подробная информация об услугах компании. Своевременная подача транспорта, чистые салоны и честные цены – главные преимущества, за которые клиенты выбирают эту компанию.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
ActionInsights – Well-organized site with practical steps and a confident tone.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
creative unlock – Practical insight, releasing ideas enables consistent progress over time.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Промышленные полы требуют профессионального подхода к проектированию, устройству и последующему обслуживанию объектов. Компания МВПОЛ специализируется на создании износостойких покрытий для складов, производственных цехов и логистических комплексов. Полимерные наливные полы выдерживают интенсивные нагрузки и сохраняют эксплуатационные характеристики долгие годы. Специалисты выполняют работы с гарантией от двух лет, используя сертифицированные материалы европейского качества. Подробнее об услугах и технологиях можно узнать на сайте https://mvpol.ru/ в разделе проектов. Бесплатный выезд инженера и составление сметы помогают точно спланировать бюджет строительства.
clarity unlocks progress – Strong concept, clarity unlocks momentum and helps tasks move forward smoothly.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
priority setter – Strong concept, taking small steps naturally clarifies what matters most.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
energized ideas – Motivating point, energized ideas drive forward action and spark collaboration.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
path with clarity – Insightful point, clear thinking opens the path to actionable steps easily.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
smooth progress – Simple yet effective, growth moves cleanly when priorities are aligned properly.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
forward motion – Insightful note, steady steps in progress create lasting forward motion.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
direction shapes motion – Strong idea, shaping motion with clear direction makes processes smoother.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Отдых в мегаполисе требует особого подхода — важно найти место, где можно расслабиться вдали от шума. Сауна в Коптево на Большой Академической улице предлагает уютную атмосферу после капитального ремонта и работает круглосуточно. Гости получают доступ к парной из берёзы, бассейну длиной пятнадцать метров и караоке для весёлых вечеров. Заведение лояльно относится к пожеланиям посетителей — разрешено приносить собственные напитки и угощения. Подробнее об услугах и актуальных ценах можно узнать на https://sauna-koptevo.ru/ перед бронированием времени. Идеальная чистота и соблюдение санитарных норм гарантируют комфортный отдых для компаний до шести человек.
Самозанятые водители и индивидуальные предприниматели получают стабильный доход при подключении к парку AREON. Гибкий график работы позволяет самостоятельно планировать время выполнения заказов и выходные дни. Ежедневные выплаты через приложение Яндекс.Про обеспечивают финансовую предсказуемость и оперативный доступ к средствам. Для регистрации потребуется паспорт, водительские права категории B и разрешение на деятельность такси. Более подробная информация о тарифах и условиях размещена на https://parkareon.ru/ для всех желающих. Повышенные тарифы Комфорт+ и Бизнес доступны после прохождения специального тренинга и собеседования.
дивитися кіно онлайн серіали 2026 дивитися онлайн безкоштовно
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
ClickFactor Experts – Clear layout, site makes discovering details effortless and enjoyable
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Click to Win Hub – The site feels clean and easy to understand with smooth navigation
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
накрутка просмотров тт бесплатно
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Для квартиры после затопления сверху натяжной потолок часто спасает отделку и мебель также Для встроенной мебели важно отступить нужный зазор и не потерять высоту После монтажа уточните правила ухода лучше мягкая салфетка и нейтральное средство в итоге будет аккуратно и практично для ежедневной жизни: https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondAxis Resources – Smooth design, helps users quickly understand and access relevant content
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondVertex Source – Well-structured pages make browsing reliable and smooth
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Urban Market Spot – Clean layout with clear descriptions for all items
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Davin Chiri Zorve19 の基本ユーザーガイドをお探しですか?インストール、利用可能なアップデート、新機能に関する包括的な情報は https://motionworks.jp/ をご覧ください。初心者からプロまで、どなたでも楽しめる完全ガイドです!
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondAllied Access – Streamlined navigation keeps everything easy to reach
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Path to Progress – Simple design allows users to navigate personal growth tips effortlessly
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Натяжные потолки подходят и для квартиры, и для офиса, и для студии, бесшовное решение дает ровную плоскость, помогает быстро освежить отделку без демонтажа штукатурки; подбираются профили, обходы углов и аккуратные вставки по периметру: https://potolki-decarat.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Натяжные потолки подходят и для квартиры, и для офиса, и для студии, позволяет встроить треки, споты и подсветку, а скрытый карниз под шторы подчеркивает стиль; замер занимает около получаса, после чего готовится смета и договор – https://potolki-decarat.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Positive Growth Guide – Maintains an encouraging tone without information overload
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Ищете строительство каркасного дома под ключ в Краснодаре и Краснодарском крае? Посетите сайт https://masterim-novostroy.ru/ – посмотрите наши проекты и сможете собрать теплый дом за 2 недели! А при необходимости мы полностью берем на себя все этапы — от создания проекта и согласования до финишной отделки и уборки. Узнайте подробнее на сайте о качестве нашей продукции и этапах производства!
Business Collaboration Center – Intuitive interface, users can coordinate projects and communicate efficiently online
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
SmartBuy Hub – Navigation is smooth and helps make informed shopping choices
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
ClickSource Station – Clear interface makes discovering and creating content simple
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Shopping Comparison Site – Everything is presented in a way that saves time while browsing
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Создание функционального и эстетичного пространства требует профессионального подхода и качественных материалов. Компания Glassway специализируется на производстве подвесных потолков, алюминиевых перегородок, дверей и светодиодных светильников для офисов, торговых центров и промышленных объектов. Собственное производство позволяет предлагать продукцию по заводским ценам с гарантией качества и гибкими условиями сотрудничества. Посетите https://glassway.group/ чтобы ознакомиться с полным каталогом решений: от кассетных потолков и стеклянных перегородок до смарт-стекла и облицовочных панелей. Профессиональная команда выполнит монтажные работы любой сложности, воплотив в жизнь самые смелые дизайнерские проекты для вашего бизнеса.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Habit Builder – Engaging interface motivates users to improve daily routines
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Skill Academy – Organized site helps visitors explore topics and learn effectively
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
накрутка подписчиков в тгк без регистрации
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Premium Selection Site – Modern interface with effortless product discovery
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
DealFinder Online – User-friendly design that makes browsing a breeze
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
BondLegacy Gateway – Well-arranged content feels reliable and easy to explore
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Белорусская компания «РазВикТрейд» предлагает полный цикл производства пресс-форм и литья пластиковых изделий для бизнеса из России и Беларуси. Завод с 10-летней практикой реализует задачи различной сложности: от разработки 3D-проекта до старта массового выпуска. Подробнее о возможностях и кейсах компании можно узнать на https://press-forma.by/ – здесь представлены примеры работ, каталог готовой тары и условия сотрудничества. Клиенты получают гарантию соблюдения сроков, экономическую оптимизацию проекта и выгоду в 2-3 раза выше по сравнению с китайским производством.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
как набрать подписчиков в ТГ
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Universal Shopping Point – The variety makes it useful for quick online browsing
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Smart Shopper Hub – Easy-to-follow pages make finding solutions for purchases straightforward
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
ClickField Link – Organized design keeps content approachable and intuitive for all visitors
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
DealSpot Central – Smooth user experience and transparent listings
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Unique Artisan Spot – Friendly interface makes finding creative products simple
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Аренда NVMe VPS/VDS https://xhost24.com мощные виртуальные серверы с быстрыми SSD NVMe. Высокая производительность, стабильная сеть, защита и удобное управление. Подходит для e-commerce, API, CRM, игровых и веб-проектов любого масштаба.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
ModeFinder – Clear interface keeps online shopping fast and satisfying
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Натяжные потолки помогают быстро обновить интерьер: скрытый карниз под шторы помогает быстро освежить отделку без демонтажа штукатурки, в городе Москва, поэтому интерьер выглядит собранно; по итогу остается чистый потолок и аккуратные примыкания: https://potolki-decarat.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Forward Thinking – Smooth interface encourages discovering different paths and ideas
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Better Decision Hub – Provides sensible approaches that encourage smarter choices
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
дивитися серіали онлайн детективне кіно дивитися безкоштовно
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Think & Click – Well-organized site encourages exploring ideas and creative solutions
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
дайсон пылесос купить в москве оригинал dn-pylesos.ru .
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Маска для осознанных сновидений DreamStalker Expert четвертого поколения от российского производителя оснащена Wi-Fi управлением, двумя датчиками движения глаз, RGB-светодиодами и OLED-дисплеем. Устройство доступно на https://claps.me/catalog/pribory-dlya-osoznannykh-snov/pribor-dlya-osoznannykh-snovideniy-dreamstalker-expert/ в четырех вариантах с функциями майнд-машины и транскраниальной стимуляции tACS. Прибор предлагает автоматическую запись сновидений, голосовые подсказки и возможность докупки лицензий на дополнительные функции.
Reliable Picks Online – Smooth experience with clear product presentation
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Market Express – Clean interface, shopping is quick and hassle-free every visit
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
как получить подписчиков в Инстаграм бесплатно
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
кіно онлайн якості бойовики та трилери українською в HD
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
пылесос дайсон вертикальный беспроводной купить пылесос дайсон вертикальный беспроводной купить .
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
дивитись безкоштовно серіали кримінальні серіали дивитися онлайн
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
комедії онлайн безкоштовно онлайн кінотеатр ua-bay.net українською
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
В спальне натяжной потолок улучшает восприятие интерьера, особенно с мягким светом, выбирайте полупрозрачное полотно, оно хорошо сочетается с современными световыми линиями, попросите образцы при дневном и теплым вечерним светом, комната будет выглядеть дороже, особенно с правильной подсветкой https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
actionable insights hub – Offers practical advice that’s easy to understand and implement.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
https://alstrive.ru/blog/iphone-17-air-balans-stilja-i-proizvoditelnosti/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Натяжной потолок позволяет смело играть со световыми сценариями, позволяет встроить треки, споты и подсветку, а ПВХ полотно подчеркивает стиль; можно заранее спланировать скрытый карниз и подсветку по проекту: монтаж натяжных потолков в москве
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
пылесосы дайсон v11 купить dn-pylesos.ru .
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
insightful action center – Ideas are easy to implement and relevant to everyday decisions.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
Кастрационно-резистентный рак предстательной железы остается серьезным вызовом для онкологов, но инновационные препараты дают пациентам новую надежду. Энзалутамид представляет собой современный антиандрогенный препарат, который блокирует рецепторы мужских гормонов и тормозит рост опухолевых клеток. Клинические исследования показали увеличение общей выживаемости на 4,8 месяца и снижение риска смерти на 37%. Подробную информацию о механизме действия, дозировках и показаниях можно найти на https://indenza.com.ru/ — специализированном ресурсе для пациентов и врачей. Удобство приема — всего один раз в день стандартная доза 160 мг — делает терапию комфортной, а консультация специалиста помогает контролировать ход лечения.
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
As we can observe in the results of studies on humans, the use of dragon fruit can prevent or improve numerous risk factors for developing metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications, which are among the leading causes of death today. This can be observed in the reduction of glycemia, total cholesterol, LDL-c, improvement in blood pressure and total antioxidant status, and an increase in HDL-c levels. Jesus reveals in John 14:6, 14-24, 15:16, 16:24 that his children are to always call upon God in the name of his Son Jesus Christ, and that man must always appeal to Jesus (through his name – John 14:14-15) as the mediator between man and God the Holy Ghost (John 14:16, 1 Tim. 2:5). Lu, T.L.D. 2009. Heritage Management in Post-colonial Hong Kong. International Journal of Heritage Studies 15 (2–3): 258–272.
https://astera.co/2025/12/31/plinko-by-bgaming-the-ultimate-uk-player-review/
The Battlefield 6 launch is upon us, with one of the most anticipated games of 2025 dropping at 11am PDT… The Gates of Olympus slot game offers a unique twist with its tumble mechanic along with its scatter pay feature. You can play, significantly increasing your chance of winning. The Gates of Olympus slot is an exciting slot machine where the mechanics attract the attention of many players. The project was developed by Pragmatic and offers a standard 6×5 cell format with 30 symbols. The main task of the player is to spin the reels in the hope that at least eight identical symbols will appear on the screen. Each symbol has its own individual value. Iwild Casino 50 Free Spins Gates of Olympus Join the excitement of online casinos today and experience the thrill of winning big from the comfort of your own home Players can interact with others through chat functions, making the game more social and enjoyable When it comes to security, reputable online casino poker sites use state-of-the-art encryption technology to protect players’ personal and financial information Gametwist Slots Kostenlos Spielautomaten & Casino
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
https://mixtum.online/ is a premium Bitcoin mixer that will provide you with an unrivaled level of anonymity. Learn more about all our advantages on our website and try out our new mixing mode with unique processing parameters. We offer a free trial and no registration required.
В офисе или салоне натяжной потолок помогает быстро обновить интерьер без пыли плюс Сатиновая фактура выглядит мягко и добавляет глубины без зеркального эффекта В коммерческом помещении заложите ревизии чтобы обслуживать инженерку без демонтажа так вы заранее избегаете переделок и лишних расходов на финиш – https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
В коридоре натяжной потолок делает пространство опрятным и помогает спрятать кабели, выбирайте полупрозрачное полотно, оно хорошо сочетается с современными световыми линиями, согласуйте высоту потолка, чтобы двери и карнизы не упирались, интерьер станет современнее и свет распределится лучше https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva.ru/
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
купить беспроводный пылесос дайсон в москве dn-pylesos.ru .
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
купить выпрямитель дайсон оригинал купить выпрямитель дайсон оригинал .
For informed buying decisions, visit – https://topbuyingidea.com/
монтаж плоской крыши https://montazh-ploskoj-kryshi.ru
Натяжной потолок упрощает уход и экономит время на уборке, скрытый карниз под шторы помогает быстро освежить отделку без демонтажа штукатурки; по итогу остается чистый потолок и аккуратные примыкания, https://potolki-decarat.ru/
расчет зоны влияния нового строительства на существующую застройку https://ocenka-vliyaniya-stroitelstva.ru
Play Lightning Roulette Online on the official website https://lightningrouletteplay.com/en/ . Learn how to play Lightning online roulette, as well as how to register an account, make a deposit or withdrawal, and learn game strategies. And be sure to take advantage of our lucrative bonuses and promotions!
выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве [url=https://vypryamitel-dn-4.ru/]выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве[/url] .
The most interesting click: https://www.bonjouridee.com/en/the-power-of-puzzles-cognitive-benefits-game-types-and-digital-platforms/
Авто не на русском? русификация бортового компьютера авто комфортное управление без языкового барьера. Перевод мультимедийной системы, бортового компьютера и навигации. Подходит для новых и б/у авто. Профессиональная настройка, аккуратная установка и поддержка.
Нужны цветы купить цветы таиланд мы предлагаем свежие и невероятно красивые букеты, которые порадуют любого получателя. Наша служба обеспечивает оперативную доставку по всему острову, а в ассортименте вы найдёте цветы и композиции на самый взыскательный вкус. При этом мы гордимся тем, что сохраняем лучшие цены на острове — красота теперь доступна без переплат!
Нужен детейлинг leveldetailingcy.com специализированный детейлинг центр на Кипре в Лимассоле, где заботятся о безупречном состоянии автомобилей, предлагая клиентам полный комплекс услуг по уходу за транспортными средствами. Мастера студии с вниманием относятся к каждой детали: они не только выполняют оклейку кузова защитными материалами, но и проводят тщательную обработку салона, возвращая автомобилю первозданный вид.
Делаешь документы? конструктор трудового договора онлайн позволяет существенно ускорить работу: с его помощью вы сможете готовить необходимые документы в десять раз быстрее и при этом гарантированно избегать ошибок. Инструмент предельно прост в освоении — специальное обучение не требуется. Все ваши данные надёжно защищены, а настройка индивидуальных шаблонов выполняется оперативно и без сложностей.
Do you want bonuses? CSGOFAST Code deposit bonuses, free cases, terms and conditions. A quick activation guide, FAQ, and the latest updates.
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: аудит, стратегия, семантика, техоптимизация, контент и ссылки. Улучшаем позиции в Google/Яндекс, увеличиваем трафик и заявки. Прозрачная отчетность, понятные KPI и работа на результат — от старта до стабильного роста.
growth insights portal – Focus on lasting results with clear guidance for planning ahead.
дайсон стайлер купить выпрямитель дайсон стайлер купить выпрямитель .
Rebricek najlepsich kasin https://betrating.sk/casino-hry/automaty-online/wild-o-tron-3000/ na Slovensku: bezpecni prevadzkovatelia, lukrativne bonusy, hracie automaty a zive kasina, pohodlne platby a zakaznicka podpora. Cestne recenzie a aktualizovane zoznamy pre pohodlne online hranie.
corporatepartnershipportal – Feels credible and structured, suitable for strategic business alliances.
Najlepsie online kasina https://betrating.sk/online-kasina/golden-star/ na Slovensku – porovnajte licencie, bonusy, RTP, vyplaty a mobilne verzie. Pomozeme vam vybrat spolahlive kasino pre hru o skutocne peniaze a demo. Pravidelne aktualizujeme nase hodnotenia a propagacne akcie.
Компания ПрофПруд предлагает комплексные решения для создания искусственных водоемов на загородных участках. На сайте https://profprud.ru/ вы найдете широкий выбор товаров: от пленочных материалов и готовых форм до систем фильтрации, насосного оборудования, скиммеров и элементов декора для водоемов. Сотрудничество с производителями из Германии, США и других стран гарантирует европейское качество продукции с гарантией до 10 лет.
explore steady progress – Offers easy-to-understand guidance on long-term success and growth planning.
Продвижение сайтов https://team-black-top.ru под ключ: аудит, стратегия, семантика, техоптимизация, контент и ссылки. Улучшаем позиции в Google/Яндекс, увеличиваем трафик и заявки. Прозрачная отчетность, понятные KPI и работа на результат — от старта до стабильного роста.
SEO-продвижение сайта https://seo-topteam.ru в Москве с запуском от 1 дня. Экспресс-анализ, приоритетные правки, оптимизация под ключевые запросы и регион. Работаем на рост позиций, трафика и лидов. Подходит для бизнеса и услуг.
future commerce hub – Shows a modern approach, perfect for businesses aiming at long-term market planning.
Организация яркого и запоминающегося детского праздника требует профессионального подхода и творческой фантазии. Агентство “Ириска-Шоу” в Краснодаре специализируется на проведении праздников под ключ с участием любимых персонажей детей. В арсенале компании более пятидесяти программ: от классических аниматоров-клоунов до современных героев TikTok-вечеринок и персонажей популярных мультфильмов. Профессиональные ведущие создадут атмосферу волшебства на дне рождения, выпускном в детском саду или новогоднем празднике. Узнать больше о программах и заказать праздник можно на сайте https://iriska-show.ru/ где представлен полный каталог услуг с описанием и ценами.
Тяговые аккумуляторные https://ab-resurs.ru батареи для складской техники: погрузчики, ричтраки, электротележки, штабелеры. Новые АКБ с гарантией, помощь в подборе, совместимость с популярными моделями, доставка и сервисное сопровождение.
где купить оригинал фен выпрямителя дайсон vypryamitel-dn-4.ru .
Продажа тяговых АКБ https://faamru.com для складской техники любого типа: вилочные погрузчики, ричтраки, электрические тележки и штабелеры. Качественные аккумуляторные батареи, долгий срок службы, гарантия и профессиональный подбор.
value deals hub – Shopping feels safe, and pages load quickly with intuitive design.
dealguardian – Appears well organized, makes trading safer for users.
daily shopping hub – Checkout and browsing are simple, making regular purchases quick.
safeshophub – Gives a sense of security, perfect for buyers looking for reliability.
Тяговые аккумуляторные https://ab-resurs.ru батареи для складской техники: погрузчики, ричтраки, электротележки, штабелеры. Новые АКБ с гарантией, помощь в подборе, совместимость с популярными моделями, доставка и сервисное сопровождение.
Продажа тяговых АКБ https://faamru.com для складской техники любого типа: вилочные погрузчики, ричтраки, электрические тележки и штабелеры. Качественные аккумуляторные батареи, долгий срок службы, гарантия и профессиональный подбор.
discover insights portal – Offers content that challenges assumptions and inspires new ideas.
alliancebondsolutions – Organized approach conveys professionalism and practical corporate utility.
Здоровье зубов требует регулярного профессионального ухода, особенно когда речь идет о детях и пациентах с повышенной тревожностью. Клиника “Киндер Дент” в районе Некрасовка специализируется на семейной стоматологии с возможностью лечения под наркозом для максимального комфорта пациентов. Современное оборудование и квалифицированные врачи обеспечивают безопасное проведение процедур любой сложности: от профессиональной гигиены полости рта до имплантации зубов. Узнайте больше на сайте https://kinder-dent.ru/ где представлен полный спектр услуг для детей и взрослых, включая ортодонтию, эстетическую стоматологию и безболезненное отбеливание зубов до восьми тонов за один сеанс. Бесплатная консультация имплантолога поможет составить индивидуальный план лечения.
様々なトピックの医学レビューをお探しですか?https://ropc.jp/ をご覧ください。ほぼあらゆる医学トピックのレビューが見つかります。記事や専門家の意見は、アマチュアの方にも専門家の方にも興味深いものとなるでしょう。また、様々な診断に関する情報も掲載しています。
trusted business network – Messaging communicates reliability, which is attractive for professional collaborations.
reliable shopping center – Deals are dependable, and navigating the site feels intuitive and simple.
дивитися фільми турецькі серіали українською мовою
дивитися фільми безкоштовно онлайн трансляція фільмів uakino.lu
shopsecureconnect – Highlights security, making online purchases feel worry-free and smooth.
business networking hub – Information is clearly presented, giving users confidence in navigating the platform.
dyson фен выпрямитель купить dyson фен выпрямитель купить .
Любите качественное кино с захватывающими сюжетами и яркими персонажами? Портал Rosseriaall предлагает обширную коллекцию российских сериалов для комфортного онлайн-просмотра в любое удобное время. Каталог включает новинки 2025 года и проверенные временем проекты, структурированные по жанрам: мелодрамы, детективы, криминальные истории, военные драмы, комедии и семейные сериалы. На сайте https://rosseriaall.net/ вы найдете как популярные многосезонные проекты вроде “Тайны следствия”, так и свежие премьеры текущего года. Удобная навигация позволяет быстро подобрать контент по настроению, а регулярные обновления гарантируют доступ к самым актуальным релизам отечественного телевидения.
safeshophub – Gives a sense of security, perfect for buyers looking for reliability.
value shopping network – Organized categories and intuitive checkout improve the user experience.
Сервис https://seoprofi.org/ специализируется на безопасной накрутке просмотров для Rutube и VK Видео, а также увеличении трафика на веб-сайты с естественным распределением показателей. Платформа обеспечивает удержание аудитории на уровне 50-80%, запускает кампании за 1-3 часа и предлагает тарифы от 1200 рублей за 1000 единиц трафика. Методика учитывает алгоритмы рекомендаций площадок, исключает резкие скачки статистики и помогает выводить контент в топ без рисков блокировки при круглосуточной поддержке.
Техническое обслуживание грузовых и коммерческих автомобилей и спецтехники. Снабжение и поставки комплектующих для грузовых автомобилей, легкового коммерческого транспорта на бортовой платформе ВИС lada: https://ukinvest02.ru/
international business hub – Highlights global connections, great for expanding business networks worldwide.
фен выпрямитель дайсон купить в сургуте vypryamitel-dn-kupit-4.ru .
global bonds guide – Helpful breakdown of concepts makes enterprise bonds easy to understand.
Онлайн курсы психологии https://ilmacademy.com.ua удобный формат обучения для тех, кто хочет освоить профессию психолога, получить практические навыки и пройти профессиональное обучение дистанционно. Курсы подойдут для начинающих и специалистов, ориентированных на практику.
Нужна тара? https://mkr-big-bag.ru Компания “МКР-Биг-Бэг” — производство и продажа биг-бэгов (МКР) оптом. Широкий ассортимент мягких контейнеров для сыпучих материалов. Индивидуальные заказы, доставка по России. Надежно, быстро, выгодно!
Белое SEO https://seomgroup.ru работает. Спустя год работ с уверенностью это говорю. Главное найти спецов, которые не обещают золотые горы за месяц. Нормальные результаты, это минимум 3-4 месяца работы. Зато теперь получаем стабильный органический трафик, не как с рекламы, где бюджет кончился и все.
verifiedshopnetwork – Feels credible, ideal for users wanting safe and verified transactions.
Комиссионный центр https://skypka.tv специализируется на скупке самой разной техники — от смартфонов и телевизоров до фотоаппаратов и игровой электроники, так что выгодно избавиться можно практически от любых лишних устройств.
Свежие новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua Украины и мира: события в Киеве и регионах, экономика, общество, происшествия, спорт, технологии и культура. Оперативная лента 24/7, аналитика, комментарии, фото и видео.
Новостной портал https://dailynews.kyiv.ua Украины с проверкой фактов: важные заявления, решения властей, бизнес и финансы, жизнь городов и областей, погода, транспорт, культура. Удобные рубрики и поиск, обновления каждый час, коротко и по делу.
Компания выполняет комплексную разработку электронных устройств под ключ, начиная с проектирования схем и печатных плат. Параллельно создается встроенное и прикладное программное обеспечение для управления устройством. Прототипы изготавливаются и тестируются на функциональность и надежность. После успешной проверки выполняется сборка и монтаж плат. Предоставляется мелкосерийное и серийное производство изделий для разных объемов заказов. Разрабатываются корпуса с учетом эргономики и защиты компонентов. Проводится промышленный дизайн для удобства использования и визуального восприятия. При необходимости выполняется реверс-инжиниринг существующих решений. Используются 3D-моделирование и 3D-печать для ускорения создания прототипов. Все изделия сопровождаются документацией и технической поддержкой. Заказчик получает готовый продукт http://polyamory.wiki/index.php?title=%D0%A1%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9%20%D1%8D%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8.
sonabet app login download
выпрямитель дайсон оригинал выпрямитель дайсон оригинал .
Посетите сайт https://priority-auto.ru/ – мы предложим проверенные корейские, китайские, японские автомобили и мотоциклы с существенной выгодой, с подбором на аукционах и быстрой доставкой в РФ. Узнайте обо всех наших преимуществах на сайте или воспользуйтесь опцией “рассчитать стоимость” – где вы увидите конечную стоимость авто. Подберем авто под ваш бюджет, вышлем актуальную стоимость и расскажем, как будем доставлять.
https://sonabet.pro/
RavionCore Point – Pages load quickly, layout tidy and finding information straightforward.
handy page – Fast pages, intuitive layout, information feels natural and concise
directionpowersmovement link – Efficient layout, content is accessible, and navigation is straightforward
online retail hub – Feels updated and suited to current consumer purchasing behavior.
Строительный портал https://domtut.com.ua с практикой: проекты, чертежи, СНиП и ГОСТ, инструменты, ошибки и решения. Ремонт квартир, строительство домов, инженерные системы и благоустройство. Понятно, по делу и с примерами.
Украинские новости https://polonina.com.ua онлайн: всё важное о стране, регионах и мире — от экономики и инфраструктуры до культуры и спорта. Лента 24/7, материалы редакции, комментарии экспертов, фото и видео. Читайте, сохраняйте и делитесь — быстро и удобно.
Всё о строительстве https://hydromech.kiev.ua и ремонте в одном месте: материалы, технологии, дизайн, инженерия и безопасность. Экспертные статьи, инструкции, калькуляторы и кейсы. Помогаем планировать работы и экономить бюджет без потери качества.
PlavexNavigator – Pages load quickly, layout clean, and browsing is simple.
tekvo platform – Smooth structure, concise content, and pages are easy to follow
shopping platform – Mobile layout was intuitive, and categories made navigation simple.
sona bet bd
выпрямитель dyson airstrait ht01 оригинал выпрямитель dyson airstrait ht01 оригинал .
продвижение сайта клиники наркологии seo-kejsy7.ru .
дистанционное обучение 10-11 класс shkola-onlajn13.ru .
Xelarionix Online – Clear design, product details well organized and checkout process straightforward.
link hub – Came across it, store feels trustworthy and simple to navigate.
Trixo Hub Online – Pages load fast, interface clean and checkout steps easy to follow.
nolra digital – Pages load quickly, layout organized and product browsing is simple.
Expert Leadership Center – Offers perspectives that inspire smarter and more informed decisions.
Xelra Market – Fast loading pages, interface minimal and navigation intuitive.
Zaviro Store – Pages responsive, browsing easy, and checkout process is quick and simple.
Портал для строителей https://inter-biz.com.ua и заказчиков: советы по ремонту, обзоры материалов, расчёты, сметы и технологии. Реальные кейсы, чек-листы и рекомендации специалистов для надежного результата на каждом этапе работ.
Строительный портал https://prezent-house.com.ua строительство домов и зданий, ремонт квартир, инженерные системы и отделка. Пошаговые инструкции, обзоры материалов, расчёты и советы экспертов для частных и коммерческих проектов.
Женский журнал https://asprofrutsc.org онлайн: тренды бьюти и моды, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты, материнство, карьера и финансы. Экспертные материалы, понятные инструкции и идеи, которые можно применить сразу. Обновления ежедневно, удобная навигация.
online access – Quick access to information, pages load fast, very user-friendly
modern e-commerce hub – Sleek design shows the current trends in online shopping preferences.
actionpowersmovement source – Organized content, minimal clutter, and navigation is easy to follow
shopping platform – I was happy with how politely they responded.
Nevironexus Express Hub – Site opens quickly, layout neat and overall browsing experience is pleasant.
axory hub – Organized pages with clear content and smooth user experience
olvra corner – Fast and organized experience with content that feels accurate
sona bet
FlowEase – Opened without errors, and the pages were informative.
Rixaro Online Store – Site loads quickly, product info accurate and checkout steps easy to follow.
ClickMorixo – Clean interface, well-organized layout, and finding products is effortless.
online zorivoshop – Everything loaded fast, browsing felt seamless and straightforward.
Портал для женщин https://angela.org.ua о современном лайфстайле: бьюти-рутины, мода, здоровье, правильное питание, отношения, работа и отдых. Полезные подборки, честные обзоры, истории и советы экспертов — заходите за вдохновением 24/7.
Портал для женщин https://beautyrecipes.kyiv.ua про гармонию и результат: здоровье, красота, стиль, саморазвитие, семья и отношения. Обзоры косметики и процедур, планы питания, тренировки, советы по дому и вдохновляющие истории. Всё в одном месте, 24/7.
International Networking Hub – Designed in a way that supports smooth global engagement.
Visit NolaroView – Click redirected smoothly, browsing feels fast and information is well organized.
Всё, что важно https://inclub.lg.ua женщине: здоровье и гормоны, питание и фитнес, стиль и гардероб, отношения и самооценка, уют и рецепты. Экспертные статьи, тесты и подборки. Сохраняйте любимое и делитесь — удобно на телефоне.
Kryvox Online Shop – Layout simple, content clear and purchasing process effortless.
NevironPortal – Design simple but professional, pages loaded quickly, and information easy to find.
xenrix.click – Clean layout, pages load quickly and information is clear
official store – Good first impression, decent products, and smooth ordering process.
выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве выпрямитель дайсон купить в москве .
современные seo кейсы seo-kejsy7.ru .
visit ideasbecomeforward – Well-structured content, intuitive navigation, and overall user-friendly experience
TrustedDealsOnline – Easy-to-use site, deals are clearly listed and purchasing feels safe.
домашняя школа интернет урок вход shkola-onlajn13.ru .
visit olvix – Simple interface, easy-to-read content, and a pleasant browsing experience
Zylavo Central – Navigation simple, content well structured and browsing straightforward.
nexlo store – User-friendly layout, ordering process simple and everything ran without issues.
product marketplace – Listings are clear and easy to navigate, and filtering worked perfectly today.
Daily opportunity identification via crypto trading signals today maintains activity. Consistent signal flow without overwhelming volume keeps traders engaged with manageable position counts and attention requirements.
Visit Pelix – Site responsive, product info clear and purchasing worked perfectly.
Service comparison helps users identify best place to buy instagram likes for needs. Provider evaluation considering quality, pricing, delivery speed, and safety features reveals optimal service selection for individual requirements.
Geographic targeting through best local hookup sites prioritizes proximity. Location-based matching focuses on nearby users facilitating practical meetup arrangements without extensive travel requirements.
Логопедический центр в Красногорске помогает детям с особенностями развития от полутора до семи лет обрести речь и социальные навыки. Специалисты https://aba-krasnogorsk.ru/ работают с задержкой речевого развития, аутизмом, алалией и другими состояниями, применяя методики ABA-терапии и Денверскую модель раннего вмешательства. Педагоги подбирают индивидуальные программы для каждого ребёнка, учитывая темперамент и интересы, а родители получают рекомендации для домашних занятий. Учреждение формирует бытовые умения, исправляет избирательность в еде и учит преодолевать эмоциональные срывы мирно.
Korla Store – Navigation easy, pages load fast and the checkout process was clear.
nolix network – Smooth experience with well-organized information and clean layout
Интернет-магазин SerialExpress предлагает более 15000 сериалов на DVD с доставкой почтой России и СДЭК по всей стране. Ищете интересные сериалы купить? На serialexpress.ru представлены российские и зарубежные сериалы, теленовеллы, турецкие дорамы, мультсериалы и документальные фильмы в максимально высоком качестве видео и звука. Ассортимент регулярно пополняется свежими релизами, предоставляется услуга индивидуальной записи кинопродукции, а постоянные покупатели с аккаунтом получают прогрессивные бонусы. Оперативная комплектация покупок и разнообразный каталог превращают платформу в комфортное решение для поклонников многосерийных произведений.
Vexaro Web – Navigation smooth, content organized and checkout straightforward without issues.
item store – Stumbled onto it and ended up saving the page.
PrixoNavigator – Clean layout, fast pages, and checkout process effortless.
Korva Portal – Came across this and enjoyed how easy the layout is to follow
Torix Portal – Interface clean, content structured well, and checkout quick and easy.
actioncreatesforwardpath access – Content is logically structured, pages load fast, and layout is simple
Портал бесплатного размещения ТопДоска предоставляет скоростной отбор предложений и возможностей по стране с помощью удобной навигации. На https://topdoska.ru/ размещены объявления в 2581 рубриках, охватывающих недвижимость, транспорт, работу, электронику, астрологию и бизнес-предложения. Платформа работает в 3843 регионах страны, позволяя частным лицам и организациям публиковать предложения без оплаты. Опция формирования индивидуального магазина и премиум-инструменты продвижения трансформируют систему в продуктивное средство роста продаж и вовлечения покупателей.
DeFi protocol metrics enhance best crypto signals for ecosystem tokens. TVL changes, protocol revenue, and user growth statistics inform trading decisions for DeFi governance and utility tokens.
klyvo homepage – Straightforward design with readable, helpful information
EasyBond – Responsive site, pages load properly, and content seems reliable.
I analyzed my competitor’s growth and noticed patterns. The successful ones all had rapid early growth, which I later learned included strategic follower acquisition. To compete effectively, I needed to buy twitter followers and level the playing field in my niche.
click portal – Fast checkout experience, confirmation arrived quickly afterwards.
Visit Zexaro Forge – Pages responsive, layout clear and browsing felt effortless.
Authenticity preservation maintains long-term credibility. Services delivering engagement from active accounts perform better. When you buy real tiktok followers and likes, you’re ensuring your growth looks legitimate to both platform algorithms and human viewers evaluating your content.
купить дайсон выпрямитель донецк vypryamitel-dsn-kupit-4.ru .
Туристический портал https://atrium.if.ua о путешествиях: направления, отели, экскурсии и маршруты. Гайды по городам и странам, советы туристам, визы, билеты и сезонность. Планируйте поездки удобно и вдохновляйтесь идеями круглый год.
seo кейсы seo кейсы .
sona bet
product marketplace – Everything is neatly arranged, product info is easy to understand, and photos match the items.
Zarix Central – Site loads quickly, product info clear and browsing simple today.
онлайн-школа для детей shkola-onlajn13.ru .
official site – Clear design, fast-loading pages, information is simple to understand
Комфортные поездки по Краснодарскому краю и Крыму начинаются с выбора надежного трансфера. Служба такси в Анапе предлагает пассажирам удобный онлайн-расчет стоимости поездки и круглосуточную работу диспетчерской службы. География маршрутов впечатляет: от аэропорта Анапы до Сочи, от Геленджика до курортов Крыма — Ялты, Севастополя, Судака. Профессиональные водители знают все особенности дорог, а современный автопарк обеспечивает безопасность передвижения. На сайте https://anapa-taxi-transfer.ru/ можно выбрать нужный маршрут из обширного списка направлений и получить точную стоимость до начала поездки. Фиксированные цены на трансфер, отсутствие скрытых доплат и возможность заказа экскурсий делают эту службу оптимальным выбором для туристов и местных жителей, ценящих пунктуальность и комфорт.
WorldBusinessConnections – Informative and actionable, supports understanding cross-border relationships.
focusdrivesmovement network – Clear layout, fast pages, and content is logically presented
RixvaHub – Clean interface, fast site speed, and shopping experience feels simple and efficient.
UlvaroLink – Very clean interface, responsive site, and products clearly displayed.
CorporateRelationsNavigator – Structured and useful, forming professional connections feels smooth.
Выбор памятника — важное решение, требующее профессионального подхода и внимания к деталям. Компания «Возрождение» предлагает широкий ассортимент гранитных изделий высокого качества с гарантией долговечности. Мастера используют современное оборудование для точной обработки камня и создания художественных композиций. На сайте https://vozrogdenie1.ru/ представлены вертикальные, горизонтальные и комбинированные памятники различных ценовых категорий. Специалисты проводят бесплатные консультации и помогают подобрать оптимальный вариант оформления мемориала. Доставка и установка выполняются опытными бригадами с соблюдением всех технологических норм.
QuickXaneroClick – Pages responsive, interface neat, and content easy to explore.
visit qavon – Smooth experience, pages look modern and content is straightforward
Maverounity official site – Everything looks well put together and inspires confidence.
portal zaviroplex – Link functioned correctly, visuals loaded properly and text made sense.
Zavirobase Online – Smooth interface, pages load without delay and shopping feels seamless.
Visit Kryvox Bonding – The website feels well-organized, easy to navigate, and information appears trustworthy.
Learn more at Morixo Trustee – Professional appearance, concise information, and navigation flows smoothly.
Quvexa Holdings Info – Logical structure, pages load quickly, and content is simple to read.
Nolaro Trustee official site – Easy-to-read content, strong design, and the user experience is clear.
online retailer – I felt confident paying and received confirmation instantly.
Qelaro Bonding portal – Professional appearance, concise information, and pages load quickly.
Kryxo Store – Clean layout, pages load fast and checkout steps simple to follow.
Выпадающие автопороги от производителя РФ ликвидируют задачи сохранения тепла и защиты от шума без образования порогов в проёме. Ищете выдвигающийся порог? На smartporog.ru представлены модели LDM-01, LDM-02, LDM-03, LDM-04, LDM-05 и накладной LDM-07 по ценам от 611 рублей для межкомнатных, алюминиевых, пластиковых и противопожарных дверей. Интеллектуальные пороги блокируют сквозное движение воздуха, температурные потери, пылевые частицы и нежелательные запахи, демонстрируют огнеупорные и дымоизолирующие качества, критичны для клиник, учебных организаций, ритейла и авиатерминалов где применяются грузовые тележки. Выпуск внутри страны поддерживает фиксированный ценник в российских деньгах вне зависимости от валютных флуктуаций.
visit nixra – Clean layout and intuitive navigation, really enjoyed exploring
focusbuildsenergy hub – Simple layout, navigation is intuitive, and content is easy to read
EasyYavon – Site responds fast, layout looks neat, and content is simple to follow.
FutureOpportunityGuide – Easy-to-use, identifying opportunities for the long term is simple and efficient.
Zavix Main – Pages loaded quickly, layout is clean, and product info was easy to read.
Quvexa Trust Site – Easy-to-use layout, content is organized, and the site feels professional.
seo кейсы seo кейсы .
click site – Smooth navigation, site responded quickly and everything was in order.
Образовательная студия Бурдинцевой в Москве проводит занятия с работой на настоящих посетителях начиная с четвёртого урока. Ищете курсы парикмахеров? На j-center.ru представлены программы для начинающих и практикующих мастеров: универсальные курсы от 9000 рублей, колористика за 36000 рублей, мужские стрижки и повышение квалификации. Учащиеся приобретают ценнейшие навыки в формате действующей парикмахерской, осваивают женские и мужские причёски, колорирование, прикорневой объём и актуальные методики. После завершения обучения вручается сертификат государственного образца, а талантливым выпускникам обеспечивается работа в столичных и подмосковных салонах красоты.
Требуется работа в Израиле? Откройте сайт 4israel.co.il/ru/jobs/ и вы увидите огромное число предложений. Просто выбирайте округ Израиля и город, а сайт покажет вам все выгодные предложения о работе. Трудоустройство в Израиле это множество бесплатных предложений – вы точно найдете для себя должность или размещайте свои объявления и получайте ответы соискателей. Наш ресурс наиболее комфортный для подбора работы и персонала. Детальнее на портале.
Features – Key information is easy to find with pages that load without delay.
Connexion a un compte 1xbet telecharger 1xbet apk
Company homepage – Well-organized design, intuitive browsing, and details are easy to read.
vexla web – Fast experience with organized pages and content that’s useful
VexaroUnity Network – Innovative idea, the site explains its principles clearly and realistically.
Ищете ежедневные задания в игре sniper 3d assassin? Портал sniper3d.ru превратился в надежного гида для фанатов культового снайперского экшена Sniper 3D Assassin. Сайт содержит всеобъемлющую информационную базу: развернутые инструкции по 825 миссиям в 21 локации, данные обо всем арсенале и обмундировании, методики игры на PvP-арене и в мировых операциях. Платформа обеспечивает видеогайды, свежие сообщения о патчах, консультации специалистов и функцию загрузки приложения. Продуманный интерфейс без навязчивых объявлений создает комфортную среду для новых пользователей и матерых стрелков.
Home – Clean interface with straightforward navigation and content that’s easy to read.
Official holdings site – The menu flow feels natural, making it easy to grasp the offerings right away.
Features – Key points are highlighted and structured, making comprehension effortless.
Support – Helpful information, clear layout, and pages load quickly for a smooth experience.
rixon info – Organized layout, smooth scrolling, and content is accessible quickly
xeviro bonding overview – Everything loads without delay, which feels reassuring.
main hub – Easy navigation, concise content, professional appearance throughout
SecureShopOnline – Clear and practical, shopping for products feels effortless.
Portfolio – Visual content is organized neatly, making it easy for users to explore.
Online bond portal – Well-ordered layout that supports easy reading.
idea growth center – Learning here feels engaging and useful rather than abstract.
sex
Kryvox hub – Clean pages, navigation feels smooth, and content is simple to access.
escort
Tutorials – Step-by-step guides are organized clearly for simple learning.
Portfolio – Visuals are displayed cleanly, ensuring visitors can explore content easily.
The best independent casinos https://montparnasse.co.uk with fair terms, fast payouts, and transparent licensing. A review of trusted platforms without major holdings, offering unique bonuses, popular slots, and convenient deposit methods.
Home – Clean layout, simple navigation, and information is easy to access for visitors.
написание студенческих работ на заказ написание студенческих работ на заказ .
ставки на спорт мелбет ставки на спорт мелбет .
Start with the trust site – Clear explanations and steady language build confidence.
official xeviro capital page – Clear sections make finding information quick and convenient.
Kasyna online https://verde-kasyno-online.pl graj z bonusami w 2026 roku. Aktualne oferty, szybkie logowanie i latwa rejestracja, popularne sloty i gry stolowe. Przeglad warunkow, metod wplat i wyplat dla komfortowej gry online.
official kavlo – Easy to explore, the site feels current and well put together
check nixra – Fast-loading pages with clear organization, very user-friendly
Tutorials – Step-by-step instructions are well structured and easy to follow.
kavioncore.bond – Nice experience, everything loads quickly and information is concise and understandable.
SafeShopHub – Very reliable platform, online shopping feels secure and hassle-free.
clarity insights portal – Straightforward layout ensures users can understand concepts efficiently.
Downloads – Files and resources are organized efficiently, providing quick access.
velixo spot – Logical structure, concise headings, and information is easy to digest overall
Financial platform – Clear structure, intuitive menus, and information is straightforward.
Updates – Latest information is laid out neatly, helping users stay informed easily.
Updates – Smooth interface, pages load quickly, and content is easy to navigate.
this holdings website – Comes across as reliable with well-structured communication.
useful link – Well-structured sections, quick-loading pages, very readable content
Partners – Collaboration details are well-organized and easy to navigate.
Check capital details – Organization is logical, making it simple to find relevant topics quickly.
Kavionline official page – Simple site navigation, accessible design, and well-presented content.
Проблемы с зубами? https://www.stomatologiya-montenegro.com: диагностика, лечение кариеса, отбеливание, импланты и ортопедия. Индивидуальный подход, безопасные материалы, точные технологии и забота о здоровье зубов и дёсен.
finance investment portal – Seems trustworthy and suitable for sustained investment plans.
Support – Guides and resources are arranged logically, providing fast access to key information.
trivoxline.bond – The site feels reliable, with a clean design and fast-loading content.
bavix corner – Calm browsing experience with well-spaced content
Maveroline resources – Simple interface, responsive layout, and information is easy to follow.
ProfessionalNetworkHub – Insightful platform, building trustworthy business relationships is straightforward.
Gallery – Quick-loading pages, simple design, and content is easy to explore visually.
future steps hub – Practical tips and easy navigation simplify long-term planning.
investment guidance site – Navigation flows smoothly, and content is clear at a glance.
yaverobonding.bond – Nice experience overall, pages are organized and fairly user friendly.
talix info – Well-laid-out pages, readable headings, and overall pleasant browsing experience
Support – Helpful guides and resources are easy to navigate.
trusted resource – Navigation is effortless and content is concise and useful
Trust services online – Modern design, informative sections, and smooth interaction.
bond services page – Smooth scrolling, clear headings, and simple layout improve usability.
Access trust site – The layout helps beginners grasp information without confusion.
News – Information is concise, pages load quickly, and content is easy to follow.
PayID casinos https://mindwellcanada.com play online quickly and securely. Instant deposits and withdrawals, convenient payments, licensed sites, popular slots, and live games. A selection of reliable casinos with up-to-date terms.
secure trustco portal – Navigation is simple, and the content feels well-arranged.
online investment site – Content is presented simply, which helps with quick browsing.
Events – Organized design, intuitive interface, and event details are clear and accessible.
Official bond hub – Neat layout, reliable structure, and the site feels professionally maintained.
EnterpriseStrategyHub – Informative platform, enterprise frameworks are clear and actionable.
Ranking wyplacalnych https://kasyno-darmowe-spiny.pl kasyn online z szybkimi wyplatami. Analiza wiarygodnosci finansowej, licencji, limitow i czasu wyplat. Lista kasyn, ktorym gracze ufaja w latach 2025–2026.
Portfolio – Visuals are organized cleanly and load quickly for easy browsing.
yavero capital platform – Appears valuable and may be worth revisiting.
browse xenrix – Fast response times, clear design, very user-friendly experience
Explore Korivo – Navigation flows smoothly, structure makes sense, and content is clear.
trusted investment portal – Logical flow, neat design, and content is easy to locate.
Portfolio – Fast-loading visuals with clean layout make exploring content simple.
trusted finance site – Browsing is smooth and all information is easy to follow.
Careers – Easy interface, organized pages, and details are simple to find.
check loryx – Organized structure, readable text, and content that draws you in
finance info site – Browsing through the details feels smooth and effortless.
Corporate hub – Simple design, responsive browsing, and key details are easy to locate.
TrustRelationsHub – Professional and helpful, global networking is simple and effective.
Community – Interactive sections are neatly structured to encourage user participation.
investment guidance site – Well-structured pages and fast responses make it easy to browse.
yavero holdings overview – Clear content presentation makes understanding offerings effortless.
Korva Portal – Came across this and enjoyed how easy the layout is to follow
Korivo bond page – Easy exploration, solid presentation, and useful details are available fast.
Careers – Job listings are structured logically and pages load efficiently for visitors.
<investment info page – Navigation feels natural, text is concise, and browsing is seamless.
Cost-effective source buy facebook page verification provides access to choose logins for traffic work. When you plan to buy a Facebook account for advertising, most often the key isn’t “just access”, but checkout passability: confident spend, “green” status markers in Ads Manager, and warmed-up fan pages. We’ve put together a clear navigation so you can understand without extra questions which account type to pick before ordering.Quick start: start with sections Auto-registered accounts, and for serious volume — jump directly to purpose-built listings: Reinstated Kings. Important: buying is only the entry point. What matters next is your launch setup: how the access is organized, how you share pixels and access carefully, how you react to policy feedback, and how you duplicate campaigns. Key advantage of this platform — comes down to a massive media-buyer library, in which we’ve curated working guides for passing reinstatement checks (ZRD). On the site you’ll find assets for FB for any goal: from mixes and up to trusted BMs with passed restrictions. When buying with us, you get not only a valid profile, but also responsive a consultation, a clear product description, a safety net for validity, and very competitive prices among sellers. Disclaimer: use digital assets legally and always in accordance with Facebook rules.
professional bond site – Straightforward layout makes finding information quick and easy.
Tutorials – Smooth menus, simple layout, and content is concise and easy to read.
Visit the core platform – Navigation is smooth, and the content is straightforward to understand.
Source page – Everything seems clearly explained, making the project easy to understand.
Tech information site – Clean layout, responsive design, and details are clearly presented.
Ищете тяговые батареи купить? Зайдите на портал e-battery.ru где можно приобрести по привлекательным расценкам тяговые батареи для электропогрузчиков, электрических тележек и штабелеров. У нас широкий ассортимент продукции для любой техники, а также доставка по всей России. Поиск подходящего тягового АКБ выполняется с помощью фильтра подбора, в котором вводятся основные показатели батареи: напряжение в вольтах и электрическая емкость в ампер-часах.
financial trust platform – The layout works well and browsing across pages is seamless.
LearnSmartPro – Clear guidance, strategies are easy to understand and apply.
Gallery – Images are displayed in a clean layout for smooth viewing.
Trust services online – Clear layout, logically arranged content, and researching key points is fast.
explore here – Well-laid-out pages, fast browsing, very easy to understand content
bavlo spot – Functional layout, intuitive browsing, and overall positive experience
Events – Event details are well-arranged and easy to browse, with smooth page transitions.
online investment site – Well-arranged content, fast page loading, and smooth user experience.
Need an AI generator? more info The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
trusted bond site – Site layout is intuitive, allowing easy navigation through content.
Blog – Well-structured design, fast-loading content, and navigation feels effortless.
Site web fonctionnel de 1xbet 1xbet apk
Mivaroline official page – Clean navigation, smooth interface, and helpful content is easy to follow.
Primary platform link – Navigation is smooth, and the content is arranged for easy reading.
investment resource – Information shows up quickly and the layout feels lightweight.
Ищете alcohol delivery dubai? Онлайн-магазин store-dubai-drinks.com предлагает быструю и легальную доставку премиального алкоголя по всему Дубаю с полным соблюдением местного законодательства. В коллекции собраны премиум-напитки: виски линеек Chivas и Johnnie Walker, коньячные изделия Hennessy, текила бренда Patron, шампанские вина и дистилляты топовых международных марок. Сервис гарантирует конфиденциальность заказов, оперативную доставку и профессиональную поддержку клиентов, что делает покупку алкоголя для туристов и резидентов максимально комфортной и безопасной.
GlobalPartnerInsights – Clear and actionable, learning about international business relationships is easy.
useful page – Clean design, reliable links, easy to navigate from start to finish
Primary trust site – A simple and clear presentation that helps build confidence.
ulvirotrustco.bond – Smooth browsing experience, platform feels professional and well-organized.
bond services page – Layout is professional, and the overall impression inspires trust.
xalirobond.bond – Easy to browse, layout is clean and information is concise and clear.
Official xeviro hub – The content is clear, pages are responsive, and the site feels trustworthy overall.
official site – A straightforward design keeps attention on the main offerings.
explore plavix – Fast-loading site with easy-to-follow structure, really enjoyable
ulvionbond.bond – Site feels credible with a clean layout and professional design.
financial guidance – Everything is organized, and navigation feels natural.
1win cashback bonus 1win cashback bonus
Base project link – Clean visuals and a logical layout make navigation simple.
Explore project – Concise information combined with intuitive navigation enhances the user experience.
professional trust page – The site looks authentic and carefully structured.
xelvix.click – Clean layout, easy to read and navigate through pages
financial hub – Browsing was effortless with clearly presented information.
bond info hub – Navigation feels natural, and details are easy to locate.
UlvorDirect – Pages open instantly, design clean, and navigation intuitive.
secure investment hub – Content is organized logically, pages load quickly, and browsing feels natural.
爱一帆下载海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
我們的台灣運彩官方授權專家團隊第一時間更新官方各大聯盟的比賽分析,包括NBA、MLB、中華職棒等。
Приветствую! Очень актуальная тема — гул в салоне. Дело в том, что ищешь готовое решение — могу рекомендовать ребятам тут: шумоизоляция автомобилей. На практике главная причина грохота по крыше — это резонанс металла в нишах. Как это работает? Например, при повороте характер шума меняется — значит резонируют арки. Что делать для самостоятельной работы: снятие локера, подготовка, укладка вибропоглотителя с обязательной прикаткой. Резюмируем: удаётся достигать классных результатов — ощутимая тишина.
Приветствую! Сегодня затронем тему — проблемы с кровлей над стоянкой. Суть в том, что кровля над паркингом — особый случай. Нужна надёжная гидроизоляция — могу рекомендовать: монтаж ПВХ кровли. Как это работает: делают примыкания — вода не проходит. Так вот ПВХ мембрана — не боится масел и бензина. Основные этапы: подготовка бетона. Вместо заключения: удаётся достигать классных результатов.
Resources – Files and links are arranged cleanly for fast browsing and easy access.
investment services site – Easy-to-read content makes the platform feel reliable.
seo network seo network .
seo partner program seo partner program .
Looking for a casino? 8mbets bd Slots, table games, and live casino all in one place. Quick login, convenient registration, modern providers, stable payouts, and comfortable player conditions.
Playing at the casino? 8mbets casino Play online for real money. We offer a wide selection of slots, live dealers, fast payments, easy login, and exciting offers for new and returning players.
Do you love gambling? jwin 7 Online is safe and convenient. We offer a wide selection of games, modern slots, a live casino, fast deposits and withdrawals, clear terms, and a stable website.
finance trustco page – Quick responsiveness and well-laid-out sections make it easy to use.
Official core homepage – A no-frills layout that highlights the services effectively.
奥美迦奥特曼高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
trusted investment portal – Professional feel, simple design, and reading through content is easy.
Hello .!
I came across a 152 interesting platform that I think you should explore.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://talktobusiness.com/financial-rules-for-every-day-that-will-help-you-increase-your-capital/
And don’t overlook, guys, that one always are able to inside this article locate responses to your the absolute complicated queries. We tried — lay out the complete content in an very accessible way.
Resources – Files and links are arranged logically, making it easy to locate needed materials.
Explore project – Straightforward design helps users locate information quickly and efficiently.
QuvexSpot – Fast-loading pages, sections well-structured, and content seems accurate.
Продажа IQOS ILUMA https://ekb-terea.org и стиков TEREA в СПб. Только оригинальные устройства и стики, широкий ассортимент, оперативная доставка, самовывоз и поддержка клиентов на всех этапах покупки.
zylavoline insight – Quick site speed enhances the clarity of the main message.
Купить IQOS ILUMA https://spb-terea.store и стики TEREA в Санкт-Петербурге с гарантией оригинальности. В наличии все модели ILUMA, широкий выбор вкусов TEREA, быстрая доставка по СПб, удобная оплата и консультации специалистов.
online investment hub – Structured layout makes information simple to follow.
online investment page – Well-structured site helps users find info without confusion.
trivoxbond.bond – Solid platform, the information is clear and simple to navigate.
IQOS ILUMA https://terea-iluma24.org и стики TEREA — покупка в Москве без риска. Гарантия подлинности, большой выбор, выгодные условия, доставка по городу и помощь в подборе устройства и стиков.
financial hub – Layout is neat, sections are clear, and reading information is effortless.
Services – Well-organized sections present details in a way that is both clear and reliable.
оптимизация сайта франция цена prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru .
Line information page – Stumbled on this page and the information is presented neatly.
CoreBridge Access – Presentation communicates professionalism while remaining user-friendly.
ideas forward – Words make conceptual thinking feel purposeful and dynamic.
enduringcapitalfoundation.bond – Well organized, layout communicates stability and a sense of security.
оптимизация сайта франция цена оптимизация сайта франция цена .
zorivoline network – Gives off early potential that merits occasional follow-up.
Main project page – The site feels professional, with organized sections and quick access to details.
learnworld.bond – Friendly and modern, site promotes learning and makes exploration intuitive.
bondedhistory.bond – Straightforward layout, messaging highlights lasting principles clearly.
QuickClickMorixo – Interface organized, responsive pages, and product info simple to read.
bondworks.bond – Friendly design, content highlights trust and makes navigation simple.
1win qeydiyyat necə olur https://1win5762.help
stonecrestcapital.bond – Well organized, content is easy to follow and inspires confidence in users.
1win az casino 1win az casino
understated home shop – Clean design choices make the overall experience feel calm and polished.
WillowWares – Products are displayed clearly and checkout is quick.
памятник на могилу
financial hub – Easy to browse, sections are well structured, and information is trustworthy.
online finance page – Navigation is easy, and the structure feels trustworthy.
Features – Key details are highlighted and organized logically for effortless understanding.
Vector Navigator – Layout and visuals feel professional, making content accessible.
Bonded Unity Pathway – Clean and intuitive, unity theme is clear and easy to follow.
zorivotrustco project – Comes off as reliable with thoughtful layout choices.
trustcircle.bond – Cohesive interface, navigation is simple and content reinforces security effectively.
puretrustbond.bond – Clear messaging, site emphasizes trust and transparency in an approachable way.
ideaengine.bond – Inspiring presentation, content encourages imaginative solutions and forward thinking.
investment guidance hub – Clear headings, simple design, and friendly presentation.
strongholdco.bond – Polished layout, site gives a reliable impression and browsing is smooth.
Primary platform link – Clean and professional, with concise information and smooth navigation.
профессиональное продвижение сайтов профессиональное продвижение сайтов .
Main trust homepage – The layout is tidy, and switching between sections is seamless.
PortalPlivox – Well-structured layout, pages open quickly, and purchase process simple.
SunnyMeadowStore – Bright layout helps users find items without hassle.
growth link – Wording highlights progress and gives a sense of purposeful direction.
раскрутка сайта франция цена раскрутка сайта франция цена .
Portfolio – Visuals are displayed cleanly, providing a clear overview and smooth browsing experience.
stress free outlet – A friendly layout removes friction, letting you shop and pay with ease.
Midpoint Access – Easy navigation with clear sections helps users find information fast.
смотря фильмы онлайн смотреть кино без подписки и смс
Стоматологическая сеть Севастополя оказывает широкий перечень услуг по уходу за полостью рта для всех. Квалифицированные специалисты работают на новейшей технике с проверенными европейскими материалами. Учреждение предоставляет услуги терапии, ортопедии, имплантологии и эстетики улыбки с использованием прогрессивных методов. Запись на прием доступна на сайте https://24antosplus.ru/ в любое удобное время суток. Пациентам гарантируется индивидуальный подход и комфортные условия лечения без боли и стресса.
Anchor Capital Flow – Professional layout, content communicates expertise and reliability naturally.
сервис email рассылок https://email-rassylka.ru
задвижки 30с41нж ду 100 30с41нж задвижка
growthstream.bond – Engaging interface, concepts are clear and navigation is effortless throughout.
zylavobond interface – Site layout feels logical and readable, with no clutter.
pathforward.bond – Clean design, content highlights teamwork and clear direction.
indigoharborboutique.shop – Clean and inviting, the shopping experience is straightforward and visually appealing.
driveforward.bond – Dynamic design, pages motivate consistent action and support goal achievement.
укладка плитки на кладбище
BlueHarborStore – Items are easy to locate and the purchasing process is hassle-free.
Ищете alcohol delivery dubai? Платформа drinks-delivery.com — лицензированный сервис доставки премиального алкоголя в Дубае с широким ассортиментом пива, вин, виски, коньяков, текилы и крепких напитков мировых брендов. Организация ведет деятельность в рамках действующих регуляций Дубая, подтверждая законность всех поставок, анонимность клиентов и надежность расчетов. Оперативная доставка, интуитивная структура каталога и квалифицированная консультационная помощь превращают приобретение спиртного в удобный процесс для жителей и туристов.
Official Yavero Trust Co – User-friendly design, reliable content, and logical layout throughout.
24小時即時更新nba即時比分、賽程表,以及NBA球星數據統計和表現分析。
ZaviroCenter – Clean design, pages load quickly, and finding information is hassle-free.
Unity Trust Insight – Clean structure, site promotes trustworthy interaction and clarity.
Где служат по контракту в России – контракт на СВО 2026 https://vc.ru/1411857
https://pamyatniki-granitnye.by/
Platform overview – Easy to scan, and the overall structure feels logical and clean.
глубокий комлексный аудит сайта prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve115.ru .
visit zylavocore – The interface feels structured, yet welcoming and easy to navigate.
VixaroEase – Smooth navigation, pages open quickly, and categories easy to browse.
zylavoline guide – Speedy loading paired with direct messaging ensures a smooth experience.
Ideas to Action Hub – Motivating content, helps users turn thoughts into concrete actions easily.
QuickClickTrivox – Navigation smooth, responsive layout, and overall browsing experience effortless.
Momentum Hub – Focused content conveys energy and forward progression naturally.
thoughtful moving advice – The wording inspires reflection instead of rushed action.
View project details – Professional presentation with logical content placement makes browsing easy.
Bonded Gateway Hub – Content presents a professional, reliable, and future-focused experience.
motivated movement hub – Layout supports easy understanding and purposeful direction.
affordable finds click – Easy-to-use platform, discovering products is simple and enjoyable.
opalcrestoutletonline.shop – Smooth browsing, items are well presented and shopping feels natural.
build your momentum portal – Offers structured advice to grow consistently online.
progresscatalystlegacy.bond – Balanced design, site promotes practical progress and purposeful activity.
take action with clarity – Clear guidance encourages immediate application of ideas.
start growing here – Feels inviting and clearly focused on forward movement.
XanixDirect – Interface professional, pages responsive, and checkout process uncomplicated.
approach ideas click – Clear and simple, content promotes adopting better techniques.
midnight cove outlet – Strong visual tone, browsing feels easy and the buying process is smooth.
Пояснительная записка к дипломной работе (проекту) – пример оформления ПЗ в дипломе, ГОСТ 2026 https://vc.ru/1457725
https://vc.ru/1581602, Накрутка реакций в Телеграмме бесплатно – 18 лучших сайтов
strongunity.bond – Clean design, content communicates reliability and clear direction effectively.
merit bonds hub – Well-structured site, great for reviewing investment options easily.
smartbuy curve – Clean platform, makes finding deals smooth and pleasant.
affordable essentials portal – User-friendly layout helps you find products fast.
idea explorer – Engaging content, really sparks creativity for new projects today.
ZorlaHome – Navigation intuitive, pages load quickly, and shopping process is simple.
midnight field brand – Clear and tidy structure, browsing is easy and the site feels solid.
momentum guide – Clear structure and tone suggest consistent progress and planning.
lynx financial hub – Interface feels responsive and browsing is simple.
interactive click hub – Fun interface, motivates users to explore all available options.
Play puzzles https://apps.apple.com/kz/app/puzzlefree-ai-jigsaw-puzzles/id6751572041 online for free – engaging puzzles for kids and adults. A wide selection of images, varying difficulty levels, a user-friendly interface, and the ability to play anytime without downloading.
modern deals hub – Offers a fresh and forward-focused online store experience.
сиськи шлюх шлюхи брянск
Opportunity-focused resource – Smooth experience with a clear and modern interface.
Упаковочное и фасовочное оборудование https://vostok-pack.ru купить с доставкой по всей России в течении 30 дней. Лучшие цены на рынке. Гарантия на оборудование. Консультационные услуги. Покупайте упаковочные машины для производства со скидкой на сайте!
Growth insight network – So far it feels clear and approachable.
corporate alliances hub – Solid platform, provides professional guidance for making smart corporate choices.
online momentum tracker – Practical and intuitive, supports focused growth strategies.
Являешь патриотом? контракт сво казань выплаты как оформить, какие требования предъявляются, какие выплаты и льготы предусмотрены. Актуальная информация о контрактной службе и порядке заключения.
secure bonds page – Transparent platform reassures and simplifies bond research.
ClickEaseXelivo – Pages responsive, layout clean, and finding information was hassle-free.
оптимизация и продвижение сайтов москва оптимизация и продвижение сайтов москва .
статьи о маркетинге statyi-o-marketinge2.ru .
focus advantage – Relatable language emphasizes focus as a source of energy and direction.
Explore Mavero Holdings – Clean structure, trustworthy design, and content is straightforward to follow.
Интернет в машину через модем https://router-dlya-avtomobilya.ru
Что вышло сейчас: семейная психотерапия: путь к гармонии и исцелению
forward steps hub – Makes incremental progress feel simple and doable.
Как устроиться по контракту на СВО в России в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1567660
E-commerce shopping hub – Smooth interface, quick loading, and easy exploration of products.
Women’s World Cup livescore, growing women’s football with full coverage
buy click center – Stress-free checkout, makes shopping online convenient and fast.
מאחורי גבי, אחת הדלתות של קונג נפתחה מעט, וגרמה לפנים של ג ‘ ולינו. “איבדתי אפילו דירות דיסקרטיות” אני כאן. דיברתי עם הנהג. עכשיו אני אלך לעיקר. אתה איתי? עצרתי ליד. כן כנראה. אני לעזאזל! לעזאזל!!! היא נאנקה במידות נחנקת בגניחות הלחישה. הבית היה הולך מתחת לגרג, ואני הייתי שם כרית על הראש שלי כדי לא לשמוע את החברה שלי גונחת. בבוקר הם שוב העמידו פנים שלא היה sexforyou
future thinking hub – Exciting insights, motivates users to explore ideas beyond the present.
bond learning portal – Well-maintained design, guides beginners effectively.
the best adult generator pornjourney create erotic videos, images, and virtual characters. flexible settings, high quality, instant results, and easy operation right in your browser. the best features for porn generation.
Corporate networking solution – The site gives a polished and organized impression.
сервисы бесплатной рассылки email рассылки онлайн сервис
Mavero Trustline digital site – Professional structure, clear messaging, and visitors can understand the content quickly.
1win telegram 1win telegram
https://vc.ru/1738901 ТОП-25 сервисов для накрутки реакций в Телеграм в 2026 году
Качественный автосервис в Анапе — это не просто ремонт, а комплексная забота о вашем автомобиле. Автосервис «LEMON CAR» на улице Чехова предлагает полный спектр услуг: от компьютерной диагностики до кузовного ремонта и 3D развал-схождения. Профессиональные мастера используют современное оборудование и не боятся предоставлять гарантию на выполненные работы. Особенность сервиса — прозрачность ценообразования: после тщательной диагностики клиент получает полную информацию о неисправностях и стоимости ремонта без неожиданных доплат. Подробнее об услугах и акциях можно узнать на https://lemon-car.ru/, где также доступна онлайн-запись. Слесарный ремонт, автоэлектрика, ремонт двигателя и КПП — весь комплекс работ выполняется с соблюдением технологий и сроков, что подтверждают многочисленные положительные отзывы клиентов сервиса.
Покупка или продажа недвижимости в Ставропольском крае требует глубоких знаний местного рынка и юридической грамотности. Агентство Arust предлагает полный цикл услуг: от подбора выгодных вариантов до безопасного завершения сделки с гарантией результата. Опытные риелторы и юристы компании проверяют каждый объект на обременения, приводят документацию в полное соответствие требованиям законодательства и контролируют все этапы оформления. На сайте https://ar26.ru/ вы найдете актуальную информацию о доступных предложениях и сможете оставить заявку на консультацию со специалистами агентства.
explore more hub – Always discovering fresh and engaging content with every visit.
Secure shopping site – Navigation is clear, and the store conveys trust.
заказать анализ сайта заказать анализ сайта .
оптимизация сайта блог statyi-o-marketinge2.ru .
skill boost click – Clear guidance, teaches concepts that can be used instantly.
innovation portal – Bright and appealing, full of imaginative ideas.
big-bag-rus.ru — производитель биг-бэгов и контейнеров МКР (мешки МКР) из полипропилена: мягкая тара для перевозки и хранения сыпучих грузов. Подбор конструкции, размеры и грузоподъёмность под задачу, оптовые цены, доставка по России. Купить биг-бэги напрямую: биг-бэги
skill growth portal – Practical resources, motivates ongoing development and knowledge building.
Visit Mivaro Trust Group – Navigation is smooth, content is detailed, and the site feels genuinely useful.
Innovative strategy site – Content is engaging, and the design keeps the user interested.
top picks shopping site – The layout helps you focus on practical buying choices.
tech-savvy store – Fresh design, site makes exploring products quick and enjoyable.
לראות את מכלול הרגשות שהשתקפו באותו רגע על פניה היפות של פילגשו המושחתת. אבל בחצי החשכה שלפני עלות השחר, חצי הכדור של התחת האלסטי המענג שלה היה לבן בבירור, ועלה בקצב וירד לקצב אותו בזהירות, כאלה לא משכו אותי, למרות שהייתי מרוצה מכך שאני עדיין מעורר עניין. לאחר שהסגירו את העסק במהירות וקיבלו פנסיה, הליוויטרנסווסטיטים שכרו את דירתם לחבר וקיבלו תשלום מראש befamous
shopping deals hub – Simple navigation, makes browsing for deals enjoyable.
ובלונדינית קטנה אחת בבגד ים כחול פתוח ישבו ליד השולחן. על השולחן היה מתאבן פרימיטיבי של פירות וגבינה, בקבוק יין ובקבוק קלח של קוניאק. אלינה כמעט לא שתתה, רק קצת הרסה את היין, אבל שהיא כבר מונחת על מדף באמבטיה. אם איבדתי אותה במועדון, אני פשוט הולכת לשירותים של גברים, תשע פעמים מתוך עשר היא כבר קופצת על הזין של מישהו. אני יכול לזיין אותך בתחת? בטח! וואו, כמה la-paloma
Лучшие 12 способов для накрутки подписчиков на Твич в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1470146
https://vc.ru/1786080 До какого возраста можно поступить в вуз, со кольки лет можно поступить в колледжуниверситет
Mivaro Trust Group online site – Navigation is simple, content is informative, and overall the user experience is smooth.
заказать продвижение сайта в москве заказать продвижение сайта в москве .
corporate alliance hub – Smooth interface, finding collaboration methods is simple and fast.
С 2011 года ООО ТК «Регион Новые Технологии» осуществляет поставки промышленного оборудования по территории России: насосное оборудование более 19 модификаций, электродвигатели, вентиляторы, частотные преобразователи и автоматику от проверенных производителей. Подробная информация доступна на сайте https://ufk-techno.ru/ Компания обеспечивает полный цикл сервиса — от подбора оборудования до гарантийного обслуживания, предлагает запчасти, ремонт, индивидуальную комплектацию и доставку по РФ и СНГ по конкурентным ценам.
seo и реклама блог statyi-o-marketinge2.ru .
escort
This platform emphasizes simplicity and organization to deliver a pleasant browsing experience. Menus are straightforward, pages respond quickly, and layouts remain clean. With bedpage, users can browse listings efficiently and comfortably. The Escorts in Miami listings are well structured, allowing easy comparison of profiles and information. Everything appears updated and consistent. Overall, the site provides a dependable and user friendly experience.
Global business hub – The site feels international, and the business focus is easy to understand.
online shopping spot – Simple navigation, allows for quick searches and purchases easily.
educational click site – Clean structure makes understanding features easy.
path to success site – Practical and uplifting, helps organize plans for the future.
Как рэб защищает от беспилотников – контракт на СВО Россия 2026
Подробнее о формате https://vc.ru/1565968
Morixo Capital web portal – Professional appearance, clear hierarchy, and content is easy to understand.
https://vc.ru/1657216, Какие типы взрывчатки используются на СВО: основные виды и отличия
1win nigeria https://www.1win5745.help
Севастопольская сеть стоматологий обеспечивает комплексный уход за зубами для пациентов любого возраста. Квалифицированные специалисты работают на новейшей технике с проверенными европейскими материалами. Клиника специализируется на лечении, протезировании, имплантации и эстетической стоматологии с применением инновационных методик. Запись на прием доступна на сайте https://24antosplus.ru/ в любое удобное время суток. Пациентам гарантируется индивидуальный подход и комфортные условия лечения без боли и стресса.
networking insights click – Clear guidance, platform offers actionable advice for professional growth.
W 2026 roku w Polsce dziala kilka kasyn https://kasyno-paypal.pl online obslugujacych platnosci PayPal, ktory jest wygodnym i bezpiecznym sposobem wplat oraz wyplat bez koniecznosci podawania danych bankowych. Popularne platformy z PayPal to miedzynarodowi operatorzy z licencjami i bonusami, oferujacy szybkie transakcje oraz atrakcyjne promocje powitalne
Paysafecard https://paysafecard-casinos.cz je oblibena platebni metoda pro vklady a platby v online kasinech v Ceske republice. Hraci ji ocenuji predevsim pro vysokou uroven zabezpeceni, okamzite transakce a snadne pouziti. Podle naseho nazoru je Paysafecard idealni volbou pro hrace, kteri chteji chranit sve finance a davaji prednost bezpecnym platebnim resenim
Consumer-focused marketplace – Navigation works well and the shopping flow is enjoyable.
seo partner poiskovoe-seo-v-moskve.ru .
статьи про продвижение сайтов статьи про продвижение сайтов .
positive progress portal – Feels uplifting and practical for daily forward movement.
W 2026 roku w Polsce https://kasyno-revolut.pl pojawiaja sie kasyna online obslugujace Revolut jako nowoczesna metode platnosci do wplat i wyplat. Gracze wybieraja Revolut ze wzgledu na szybkie przelewy, wysoki poziom bezpieczenstwa oraz wygode uzytkowania. To idealne rozwiazanie dla osob ceniacych kontrole finansow
Morixo Holdings digital site – Layout is clean, pages load well, and credibility feels established.
Жіночий портал https://soloha.in.ua про красу, здоров’я, стосунки та саморозвиток. Корисні поради, що надихають історії, мода, стиль життя, психологія та кар’єра – все для гармонії, впевненості та комфорту щодня.
bonus casino 1win bonus casino 1win
Hello guys!
I came across a 153 helpful website that I think you should visit.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find helpful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://www.informationng.com/2022/10/how-to-learn-to-say-no-five-simple-steps.html
Additionally do not neglect, guys, — a person always are able to within the article locate solutions to the most the very tangled inquiries. We tried to lay out all of the content via the extremely easy-to-grasp manner.
Портал для жінок https://u-kumy.com про стиль, здоров’я та саморозвиток. Експертні поради, чесні огляди, лайфхаки для дому та роботи, ідеї для відпочинку та гармонійного життя.
shoproute marketplace hub – Smooth experience, selecting items is simple and clear.
Collaborative strategy site – Relevant ideas are easy to find, and the partnership focus is strong.
Online study hub – Site design supports easy navigation and effective learning.
Galatasaray Football Club https://galatasaray.com.az latest news, fixtures, results, squad and player statistics. Club history, achievements, transfers and relevant information for fans.
UFC Baku fan site ufc-baku.com.az/ for fans of mixed martial arts. Tournament news, fighters, fight results, event announcements, analysis and everything related to the development of UFC in Baku and Azerbaijan.
Barcelona fan site https://barcelona.com.az/ with the latest news, match results, squads and statistics. Club history, trophies, transfers and resources for loyal fans of Catalan football.
Прогноз курса доллара от internet-finans.ru. Ежедневная аналитика, актуальные котировки и экспертные мнения. Следите за изменениями валют, чтобы планировать обмен валют и инвестиции эффективно.
global organization global ideas that implements healthcare initiatives in the Asia-Pacific region. Working collaboratively with communities, practical improvements, innovative approaches, and sustainable development are key.
clicktolearnandgrow.click – Found this today, content seems helpful and worth checking again.
Rafa Silva https://rafa-silva.com.az is an attacking midfielder known for his dribbling, mobility, and ability to create chances. Learn more about his biography, club career, achievements, playing style, and key stats.
Practical online sales hub – Navigation is clear, and managing products is uncomplicated.
Сайт города Одесса https://faine-misto.od.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, культура, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей Одессы в удобном формате.
Новости Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua сегодня: события города, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни Житомира онлайн.
Сайт города Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, экономика, культура и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей города.
Организация свадьбы в Санкт-Петербурге требует профессионального подхода и внимания к деталям. Арт-студия «Праздничный город» специализируется на проведении торжественных мероприятий под ключ: от выездной регистрации до оформления банкетного зала живыми цветами. Команда опытных организаторов, декораторов, фотографов и видеооператоров создает неповторимую атмосферу вашего праздника. Студия предлагает разработку свадебного стиля, организацию кортежа, заказ торта и подбор артистов для музыкального сопровождения. Кроме свадеб, компания организует выпускные вечера и корпоративные мероприятия. Познакомиться с портфолио и свадебными проектами можно на https://svadba-812.ru/, где представлены все услуги и цены. Профессионализм команды «Праздничного города» превращает важный день в безупречное торжество, которое запомнится надолго.
Ищете сериал русский смотреть онлайн бесплатно? Специализированная платформа russkie-serial.net концентрируется на российском кинематографе, предлагая зрителям бесплатный просмотр отечественных сериалов в HD-качестве без регистрации. Коллекция содержит актуальные новинки текущего сезона, легендарные телепроекты минувших периодов, детективные истории, масштабные исторические полотна, юмористические сериалы и романтические постановки от крупнейших отечественных вещателей. Портал предоставляет оперативное воспроизведение файлов, совместим со всеми платформами, постоянно расширяется актуальными выпусками и oferует интуитивный фильтр по артистам, кинорежиссёрам и направлениям для ценителей профессионального русскоязычного медиаматериала.
Агентство наружной рекламы Буквица https://bukvica.ru/ оказывает полный комплекс услуг в сфере наружной рекламы и оформления внутренних пространств. Мы разрабатываем дизайн, производим и монтируем вывески, объемные буквы, световые конструкции, навигацию, крышные установки, вывески из неона и брендирование. Берём на себя согласование вывесок в государственных органах и реализуем проекты под ключ, точно в срок.
forward clarity – Branding communicates trust and inspires moving forward.
Strategic business network – Content is coherent, and navigation feels seamless.
Портал города Хмельницкий https://faine-misto.km.ua с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения местных властей, происшествия, экономика, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Львова https://faine-misto.lviv.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная повестка. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни города онлайн.
Днепр онлайн https://faine-misto.dp.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
Enterprise partnership portal – The layout is intuitive and the idea is easy to grasp.
Автомобильный портал https://avtogid.in.ua с актуальной информацией об автомобилях. Новинки рынка, обзоры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и практические рекомендации для ежедневного использования авто.
Новости Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua события города, происшествия, экономика и общество. Актуальные обзоры, аналитика и оперативные материалы о том, что происходит в столице Украины сегодня.
Управление финансами малого и среднего бизнеса часто превращается в хаос: отчёты не отражают реальность, кассовые разрывы возникают внезапно, а прибыль остаётся загадкой. Финансовый директор Грубов Вадим Алексеевич с опытом 25+ лет на https://findir.info/ выстраивает целостную систему: от настройки 1С и управленческого учёта до бюджетирования и налоговой оптимизации. Это не разовые консультации, а полноценное сопровождение собственника — с диагностикой, внедрением регламентов и понятной отчётностью, которая помогает принимать взвешенные решения и расти без финансовых рисков.
познавательный блог https://zefirka.net.ua с интересными статьями о приметах, значении имен, толковании снов, традициях, праздниках, советах на каждый день.
Обустройство дома качественной мебелью больше не требует многочасовых походов по магазинам и мебельным салонам столицы. Интернет-магазин “Мебельный базар” собрал под одной крышей продукцию ведущих российских, итальянских, китайских и белорусских производителей — от классических спален и современных гостиных до эксклюзивных обеденных групп и дизайнерской мягкой мебели. На сайте https://bazar-mebel.ru/ представлен широкий ассортимент с подробными описаниями, фотографиями и актуальными ценами, а удобная система доставки и профессиональной сборки по Москве делает покупку максимально комфортной для каждого клиента.
Документы для контракта на СВО в России в 2026 году – что нужно знать https://vc.ru/1516523
Growth direction portal – Pages move fast and the layout feels logical.
12 лучших способов для накрутки просмотров в Твич в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1547356
escort
Using bedpage feels intuitive thanks to its clean layout and clear structure. Listings are presented neatly, allowing important details to stand out without clutter. When checking Escorts in Las Vegas, profiles are easy to read and compare. Navigation remains consistent across categories, improving comfort while browsing. Pages load smoothly without interruptions. Overall, the experience feels efficient and balanced, making the platform a practical choice for users who prefer organized content and straightforward online navigation.
Портал для пенсионеров https://pensioneram.in.ua Украины с полезными советами и актуальной информацией. Социальные выплаты, пенсии, льготы, здоровье, экономика и разъяснения сложных вопросов простым языком.
Блог для мужчин https://u-kuma.com с полезными статьями и советами. Финансы, работа, здоровье, отношения и личная эффективность. Контент для тех, кто хочет разбираться в важных вещах и принимать взвешенные решения.
Объясняем сложные https://notatky.net.ua темы просто и понятно. Коротко, наглядно и по делу. Материалы для тех, кто хочет быстро разобраться в вопросах без профессионального жаргона и сложных определений.
Business direction finder – The layout is clean and the message is easy to understand.
мостбет ставки на спорт http://mostbet2026.help/
Полтава онлайн https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
Портал города https://u-misti.odesa.ua Одесса с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения властей, происшествия, экономика, спорт, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Житомира https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Оперативные обновления, обзоры и важная информация о жизни Житомира онлайн.
Накрутка просмотров Телеграм: 25 лучших сервисов (Обновил)
Узнать подробнее: https://vc.ru/1344177
https://vc.ru/1627250, Контракт в Волгограде на СВО – особенности и перспективы 2026 года
Новости Хмельницкого https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua сегодня на одном портале. Главные события города, решения властей, происшествия, социальная повестка и городская хроника. Быстро, понятно и по делу.
Львов онлайн https://u-misti.lviv.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Важные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни одного из крупнейших городов Украины.
Новости Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua сегодня — актуальные события столицы, происшествия, политика, экономика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и ключевые темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Платформа объявлений Напики соединяет реализаторов и приобретателей из российских регионов посредством комфортного веб-инструмента. На https://napiki.ru/ представлено более 3800 объявлений в 1553 рубриках: недвижимость, транспорт, работа, товары для дома, бытовая электроника и услуги. Платформа позволяет частным лицам и компаниям размещать предложения бесплатно, а специальные услуги продвижения ускоряют продажу. Участники выявляют интересные условия в локальной зоне и прилегающих субъектах, а формирование индивидуального магазина усиливает лояльность покупателей к компании.
Куда идти служить по контракту в 2026 году – насыщенные возможности СВО в России https://vc.ru/1482011
https://vc.ru/1806313 Монография – что это, как написать, структура + пример
Fresh ideas website – Moving through the site feels smooth and intuitive.
Актуальные новости https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua Черновцов на сегодня. Экономика, происшествия, культура, инфраструктура и социальные вопросы. Надёжные источники, регулярные обновления и важная информация для жителей города.
Винница онлайн https://u-misti.vinnica.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Главные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни города в удобном формате.
seo бесплатно seo бесплатно .
seo базовый курc kursy-seo-4.ru .
Сервис https://storedrinks.com/ обеспечивает доставку премиального алкоголя в Дубае менее чем за 60 минут с широким выбором пива, вина, крепких напитков и эксклюзивных позиций от мировых производителей. Сервис функционирует с официальным разрешением, обеспечивает приватность клиентов и строгое следование законодательству Эмиратов в каждой транзакции. Заказчики оперативно доступ к обновленному меню в WhatsApp, совершают транзакцию в несколько касаний и получают безупречный сервис с квалифицированной поддержкой на каждом шаге.
Как бесплатно накрутить Likee – 25 лучших сервисов в 2026 году https://vc.ru/1347009
application melbet melbet telecharger
Новости Днепра https://u-misti.dp.ua сегодня — актуальные события города, происшествия, экономика, политика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и главные темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Городской портал https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua Черкасс — свежие новости, события, происшествия, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, городская хроника и полезная информация для жителей и гостей города.
riobet casino онлайн https://riobetcasino-money.ru
Поставляем грунт https://organicgrunt.ru торф и чернозем с доставкой по Москве и Московской области. Подходит для посадок, благоустройства и озеленения. Качественные смеси, оперативная логистика и удобные условия для частных и коммерческих клиентов.
Career clarity platform – Nothing feels confusing thanks to the neat design.
букмекерская контора мостбет http://www.mostbet2026.help
Ищете упд услуги грузополучатель? Специализированный портал gdlog.ru представляет собой комплексную информационную площадку для участников железнодорожной логистики, объединяющую перевозчиков, экспедиторов и владельцев подъездных путей. Платформа содержит свежий каталог из 290 организаций, оказывающих работы по обработке железнодорожных составов, аренде вагонов, транспортировке контейнеров и терминальному хранению в пунктах назначения по территории РФ. Посетители обладают мгновенным инструментом выбора партнёров по областям, пунктам погрузки, направлениям деятельности и взаимодействуют без посредников с операторами логистических услуг для планирования перевозочного процесса.
курсы seo курсы seo .
Банный комплекс в Тульской области — идеальное место для качественного отдыха вдали от городской суеты. «Провинция» в поселке Ильинка предлагает гостям традиционную русскую баню, турецкий хамам и просторный бассейн площадью 100 квадратных метров с джакузи. Комплекс подходит для проведения дней рождения, корпоративов, деловых встреч и даже фотосессий. Две спальные комнаты, большой зал с кухней, бильярд и караоке создают все условия для длительного отдыха компанией. На территории обустроена большая беседка с барбекю для приятных вечеров на свежем воздухе. Забронировать посещение можно на https://banitula.ru/, где представлена подробная информация о ценах и услугах. Комплекс расположен по адресу: Центральная улица, 19А, корпус 5, что обеспечивает удобный подъезд и тихое расположение для полноценного расслабления.
учиться seo kursy-seo-5.ru .
connexion en ligne 1win 1win telecharger
Купить подписчиков в Телеграм канал – Актуальный рейтинг из 20 эффективных сервисов в 2026 году https://vc.ru/2241491
joycasino зеркало рабочее промокод joycasino
https://vc.ru/1497201, 25 Надежных Сервисов для Бесплатной Накрутки Подписчиков в Telegram 2026
скачать mostbet casino https://mostbet2026.help/
https://vc.ru/1375734 – 25 сервисов для накрутки просмотров в ТГ живых и ботов в 2026 году
Op zoek naar een casino? WinnItt biedt online gokkasten en live games. Het biedt snel inloggen, eenvoudige navigatie, moderne speloplossingen en stabiele prestaties op zowel computers als mobiele apparaten.
midnightquarry.shop – Bold branding stands out, pages load quickly and the shopping flow feels intuitive.
Idea inspiration page – Designed to spark curiosity and creative thinking.
https://vc.ru/2069389 – Накрутка подписчиков ВК 2026 – 19 проверенных сайтов для качественного продвижения
Накрутка голосов в опросе ВК – ТОП-27 способов в 2026 году. Наш рейтинг https://vc.ru/1547441
цены на квартиры светский лес сочи жк официальный сайт
курсы по seo курсы по seo .
обучение продвижению сайтов обучение продвижению сайтов .
Накрутка Telegram бесплатно – Рейтинг 23 проверенных сервисов для успешного продвижения (Почему большинство проваливается)
Ознакомьтесь с описанием и условиями https://vc.ru/1970926
https://vc.ru/2048001 – Как быстро набрать подписчиков в Telegram-канал – 23 надежных сервиса на 2026 год
seo курсы seo курсы .
курсы по seo курсы по seo .
Производим пластиковые https://zavod-dimax.ru окна и выполняем профессиональную установку. Качественные материалы, точные размеры, быстрый монтаж и гарантийное обслуживание для комфорта и уюта в помещении.
Изделия из пластмасс https://ftk-plastik.ru собственного производства. Продажа оптом и в розницу, широкий ассортимент, надёжные материалы и стабильные сроки. Выполняем заказы любой сложности по техническому заданию клиента.
Жалюзи от производителя https://balkon-pavilion.ru изготовление, продажа и профессиональная установка. Большой выбор дизайнов, точные размеры, надёжная фурнитура и комфортный сервис для квартир и офисов.
Производство оборудования https://repaircom.ru с предварительной разработкой и адаптацией под требования клиента. Качественные материалы, точные расчёты, соблюдение сроков и техническая поддержка.
https://vc.ru/2168256, Массфолловинг – Мой рейтинг 23 надёжных платформ в 2026 году
Szukasz kasyna? kasyno pl w Polsce: wybor najlepszych stron do gry. Licencjonowane platformy, popularne sloty i kasyna na zywo, wygodne metody platnosci, uczciwe warunki i aktualne oferty.
Ищешь блины для штанки? блины на штангу на заказ для эффективных силовых тренировок. Чугунные и резиновые диски, разные веса, долговечность и удобство использования. Решение для новичков и опытных спортсменов.
Grasz w kasynie? internetowe kasyno w Polsce to najlepsze miejsca do gry w latach 2025–2026. Zaufane strony, sloty i gry na zywo, przejrzyste warunki, wygodne wplaty i wyplaty.
Накрутка ВК плей лайв – ТОП 25 лучших сервисов и способов для бесплатной накрутки https://vc.ru/1495621
Производим торговую мебель https://woodmarket-for-business.ru для розничного бизнеса и сетевых магазинов. Функциональные конструкции, современный дизайн, точные размеры и полный цикл работ — от проекта до готового решения.
Оборудование для отопления https://thermostock.ru и водоснабжения: котлы, циркуляционные насосы, радиаторы, мембранные баки и комплектующие от ведущих производителей. Что вы получаете: сертифицированные товары, прозрачные цены, оперативную обработку заказа. Создайте комфортный микроклимат в доме — выбирайте профессионалов!
https://vc.ru/1512847, 25 надежных сервисов для раскрутки Тик Ток в 2026 году
Нужен памятник? заказать памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Нужно авто? заказ автомобилей из японии поиск, проверка, оформление и доставка авто из разных стран. Прозрачные условия, помощь на всех этапах и сопровождение сделки до получения автомобиля.
Объединить кредиты в один удобно при нескольких займах. Вместо разных дат платежа остается одна. Это снижает вероятность ошибок. Подбор кредита в Казахстане упрощает поиск условий. Онлайн оформление экономит время – перейти
студия реальный дизайн дизайн интерьеров ресторанов
Mini electric vehicles are small, compact EVs designed mainly for city driving and short commutes. They are affordable, easy to park, and consume very little energy – nissan electric suv
Нужен памятник? купить памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Промышленные предприятия России получили надежного партнера в сфере поставок насосного оборудования и электродвигателей благодаря компании ООО ТК «Регион Новые Технологии», работающей на рынке с 2011 года. Специализация на широком спектре насосов — от консольных и погружных до химических и шламовых — позволяет закрывать потребности самых разных отраслей промышленности. На сайте https://ufk-techno.ru/ представлен полный каталог продукции отечественного и зарубежного производства, включая электродвигатели, вентиляторы и частотные преобразователи, а также услуги по ремонту и техническому обслуживанию оборудования с доставкой по всей территории Российской Федерации.
Новое в категории: https://dzen.ru/a/aVPVZcPkRSDCJFVN
https://www.servisemaster.ru/ – Ремонт стиральных машин, Ремонт стиральных машин в Москве, Ремонт стиральных машин недорого, Ремонт стиральных машин на дому, Ремонт стиральных машин на дому в Москве, Ремонт стиральных машинок.
Компания ИдеалСтрой https://idealstr.ru/ выполняет полный комплекс работ по строительству домов под ключ в Подольске. Посетите наш сайт, ознакомьтесь с проектами, ценами и всеми нашими услугами. На сайте вы сможете рассчитать стоимость дома или коттеджа под ключ, а наше портфолио позволяет гарантировать лучшее качество работ и профессиональный подход к делу.
Накрутка Тик Ток подписчики – ТОП 25 лучших сервисов и способов для бесплатной накрутки https://vc.ru/1518981
Объединить кредиты в один удобно при большом количестве обязательств. Вместо нескольких платежей остается один. Это снижает риск просрочек. Подбор кредита в Казахстане помогает найти подходящий вариант. Онлайн оформление делает процесс проще https://spisok-kreditov.ru/02_kredit-nalichnymi.html/
Looking for gold news? Visit profi-forex.us – fully structured information and daily exclusive insights from 55 press centers located worldwide. You’ll find details on the dollar, euro, and various currencies, full stock exchange information, gold, gas, oil, and beyond, along with analytical pieces from industry professionals. Find out additional details on the platform.
Качественный автосервис в Анапе — это не просто ремонт, а комплексная забота о вашем автомобиле. Автосервис «LEMON CAR» на улице Чехова предлагает полный спектр услуг: от компьютерной диагностики до кузовного ремонта и 3D развал-схождения. Профессиональные мастера используют современное оборудование и не боятся предоставлять гарантию на выполненные работы. Особенность сервиса — прозрачность ценообразования: после тщательной диагностики клиент получает полную информацию о неисправностях и стоимости ремонта без неожиданных доплат. Подробнее об услугах и акциях можно узнать на https://lemon-car.ru/, где также доступна онлайн-запись. Слесарный ремонт, автоэлектрика, ремонт двигателя и КПП — весь комплекс работ выполняется с соблюдением технологий и сроков, что подтверждают многочисленные положительные отзывы клиентов сервиса.
Кредиты онлайн в Казахстане подходят для разных категорий заемщиков. Доступны различные суммы и сроки. Онлайн подбор кредита упрощает сравнение условий. Решение принимается быстро. Деньги можно получить удобным способом – рефинансирование кредита казахстан
Нужен проектор? projector24 большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Деньги в долг в Казахстане доступны через онлайн кредитование. Процесс оформления не занимает много времени. Решение приходит в короткие сроки. Можно выбрать кредит наличными. Это удобно при непредвиденных расходах https://spisok-kreditov.ru/08_refinansirovanie-kredita.html/
AWD electric cars use two or more motors to power all four wheels. This improves traction, acceleration, and stability in snow, rain, and off-road conditions https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-manufacturers/
AWD electric cars use two or more motors to power all four wheels. This improves traction, acceleration, and stability in snow, rain, and off-road conditions https://ev.motorwatt.com/ev-manufacturers/
Promin Partner connects drivers and couriers with legal work opportunities in Poland on leading platforms like Uber, Bolt, FreeNow, Glovo, Wolt. They assist with all required documentation, employment support, and ongoing guidance so you can start earning quickly with transparent terms and dependable service. Learn more: https://prominpartner.com/
Компания «Техносвязь» — профильное производство печатных плат в Екатеринбурге, работающее свыше двух десятилетий. Компания предлагает полный цикл услуг: от проектирования до серийного выпуска электронных устройств, включая автоматический и ручной монтаж, изготовление многослойных плат на различных материалах. Подробнее на https://www.techno-svyaz.ru/ Передовая техника, применение премиальных материалов глобальных брендов и опытная команда обеспечивают быстрое выполнение с безупречным качеством для партий любого масштаба.
Рефинансирование кредита в Казахстане помогает улучшить текущие условия. Можно снизить процентную ставку и ежемесячный платеж. Это актуально при изменении финансовой ситуации. Перекредитование позволяет объединить несколько обязательств. Управлять долгами становится проще – https://spisok-kreditov.ru/02_kredit-nalichnymi.html/
Онлайн-кинотеатр https://russkie-serial.net/специализируется исключительно на российских сериалах, предоставляя бесплатный доступ к тысячам отечественных проектов в высоком качестве. Пользователи найдут здесь премьеры 2025 года, популярные криминальные драмы, исторические саги, семейные мелодрамы и комедийные сериалы от всех ведущих российских каналов. Сервис функционирует без обязательной авторизации, обеспечивает просмотр на смартфонах и десктопах, каждый день пополняется новыми эпизодами и включает практичный поиск по исполнителям, периодам создания и категориям.
Нужен проектор? projector24.ru/ большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Do you need a master? Philadelphia handyman for apartments and houses. Repairs, installation, replacement, and maintenance. Experienced specialists, professional tools, and a personalized approach to every task.
Кредиты онлайн в Казахстане подходят для разных категорий заемщиков. Доступны различные суммы и сроки. Онлайн подбор кредита упрощает сравнение условий. Решение принимается быстро. Деньги можно получить удобным способом – потребительский кредит казахстан
Проблемы с авто? электрик ауди спб диагностика, ремонт электрооборудования, блоков управления, освещения и систем запуска. Опыт, современное оборудование и точное определение неисправностей.
Frederick County Conservation – Clear focus on nature and wildlife, content feels local and engaging.
Enterprise solutions site – Well thought out, the content comes across as clear and useful.
Answers Hub – Informative and engaging, resources provide actionable guidance for daily challenges.
Компания https://pitercomfort.ru/ специализируется на поставках оборудования для водоочистки, водоснабжения и отопления в Санкт-Петербурге. В ассортименте представлены фильтры для воды BWT, насосное оборудование, системы для бассейнов, реагенты для обслуживания инженерных систем и каркасные деревянные бассейны. Потребители имеют возможность использовать современные разработки австрийского бренда BWT для квартир, вилл и фабричных комплексов, включая обратноосмотические модули, УФ-стерилизацию и химводоподготовку.
trustedcorpnetwork – Efficient platform for connecting with commercial contacts, very straightforward.
clickforenterprisebonds – Solid advice provided, improved our approach to enterprise bonding significantly.
sociallinkhub – Great platform for meeting people with similar interests online.
Поклонники мобильного шутера Sniper 3D Assassin получили новый информационный ресурс, который станет настоящим помощником в освоении всех тонкостей игры. Портал Sniper3D.ru, запущенный в ноябре 2025 года, объединил под одной крышей детальные гайды по прохождению миссий в 21 регионе, подробные характеристики оружия всех уровней и практические советы по улучшению снаряжения. На https://sniper3d.ru/ игроки найдут актуальную информацию о спецоперациях, способах заработка золота и алмазов, а также секреты успешной игры на PvP-арене, что делает портал незаменимым инструментом как для новичков, так и для опытных снайперов.
networkhub – Reliable and efficient, quickly expanded my professional circle.
opportunityfinder – Insightful resources, simplified understanding complex market data.
Create Meaningful Things – Engaging and thoughtful, ideas spark innovation consistently.
taskhub – Insightful advice, helped me structure work efficiently.
workflowsolutions – Clear tips here, made daily task management much smoother.
OBDNet car tips – Helpful and easy to follow, makes understanding diagnostics simple.
digitalretailzone – Online shopping feels smooth and effortless, really enjoyed the layout.
shopandsavecenter – Shopping experience is smooth, making online purchases very fast and simple.
alliancesplanninghub – Advice here made structuring lasting partnerships more straightforward.
smooth buying hub – Checkout was straightforward and dependable, improving convenience.
execution mastery tips – Actionable guidance that made workflow and planning more productive.
Learning made friendly – Appealing concept, it looks welcoming rather than overwhelming.
квартиры без посредников жк светский лес сочи купить
химчистка белой обуви химчистка обуви из замши
clickforalliances – Very insightful partnership guidance, streamlined business expansion plans.
entrepreneurinsighttools – Provided clear, useful insights that I can act on today.
easybuyzone – Very flexible online shopping experience, made purchasing simple and efficient.
Happiness Tips Hub – Friendly and practical, posts inspire positive habits for everyday life.
smartpurchasezone – Useful recommendations, shopping online felt smooth and stress-free.
onlinebuyingcenter – Platform works well, made transactions fast and convenient.
strategic partnership tips – Useful advice that streamlined collaboration and long-term planning.
actionablethoughts – Clear and practical ideas, made workflow improvements easier.
Gardens AL News – Clear and calm, residents can follow local news effortlessly.
business alliance platform – The recommendations helped strengthen long-term professional ties.
enterprise alliance roadmap – Smart recommendations that guided growth-focused partnership planning.
onlineshopdaily – Easy ordering experience, received items promptly without issues.
dailyenergysaver – Simple steps that improve efficiency and lower energy bills.
bizeduportal – Materials are simple and informative, excellent for quick learning.
networkingprofessionals – Great experience, streamlined my professional connections effectively.
nextlevellearning – Learning modules are easy to understand, really helped me acquire strategic skills quickly.
growthstrategyzone – Strategy insights are actionable, helped me focus on key next steps efficiently.
Digital Know-How – Engaging and clear, content provides step-by-step explanations of digital concepts.
long-term business links – Helpful strategies that strengthened networking and project planning.
buyingtipsportal – Reliable advice, helped me select products without confusion.
Corporate partnership space – Good balance, the emphasis on trust and longevity stands out.
futurefocushub – Very actionable advice, helped organize priorities efficiently.
efficient shopping guide – Platform design is modern and helps locate products easily.
Laser treatment hub – Organized layout, service details are visible and booking is straightforward.
strategicpartnershiphub – Very informative, made understanding partnership structures simpler and quicker.
connectbusinessprofessionals – Easy-to-use platform, expanded my professional contacts quickly.
clickforinnovationideas – Very imaginative concepts, sparked some interesting project ideas.
collaborationcentral – Made team communication more organized and productive.
easycartportal – Online buying is effortless, transactions completed without any issues.
procollaborationtips – Collaboration tips are actionable, really strengthened teamwork efficiently.
business alliance roadmap – Practical insights that improved decision-making and partnership strategies.
startupstructureguide – Clear steps and trustworthy insights for developing solid business infrastructure.
Pathfinder Hub – Exciting and approachable, resources provide multiple options to explore.
shopnetworkcentral – Clear and intuitive system, shopping online was simple and fast.
corporate alliance roadmap – Actionable guidance that enhanced collaboration and reduced risk.
bondingzone – Useful insights, made forming meaningful business relationships faster.
teamcollabcentral – Helpful infrastructure advice, improved how we manage joint projects.
innovativebizideas – Insightful suggestions, gave clarity on exploring new business directions.
Padel Oviedo Portal – Concise and informative, updates are timely and player-friendly.
7k casino предоставляет доступ к актуальным онлайн играм. Каталог регулярно обновляется. Пользователь может выбирать подходящий формат. Сайт работает стабильно. Это поддерживает интерес: 7k casino официальный сайт
Corporate alliance network – Professional look, the concept aligns well with business growth goals.
skillgrowthcenter – Practical strategies, really supported improving my career prospects quickly.
futuristicshophub – Shopping online was simple, interface looks modern and neat.
innovation planning link – Useful inspiration that opened up new creative possibilities.
Модульные дома https://modulndom.ru под ключ: быстрый монтаж, продуманные планировки и высокое качество сборки. Подходят для круглогодичного проживания, отличаются энергоэффективностью, надежностью и возможностью расширения.
Share Your Knowledge – Supportive environment, posts encourage exchanging tips and learning from each other.
shopcentralglobal – Easy to browse and purchase, platform works very well.
commercialfinanceportal – Excellent resources, really useful for structuring investment strategies.
corporatealliancesportal – Very practical advice for growing business collaborations.
Mobihub allows quick learning and deployment of mobile proxies. The app explains core functions clearly. Users can experiment without risk. Setup time remains minimal. This makes the service beginner-friendly: best mobile proxy
Mobihub simplifies the launch of a mobile phone farm for income generation. Each device works as a separate proxy source. Centralized management is available through a dashboard. This reduces operational complexity. The system scales easily: mobile phone proxy
knowledge insights link – Helpful explanations that made mastering concepts simple and practical.
growthnavigator – Clear and practical, roadmap strategies were easy to follow.
Gardens AL Local Hub – Calm and organized, all neighborhood details are clear.
workhub – Streamlined communication, improved productivity across departments.
trusted business alliances – Helped reinforce professional relationships efficiently.
Медсправка 003 ву https://med-spravki-msk.ru
studyandadvance – Educational content is well structured, made learning fast and effective.
Специализированный коррекционно-речевой https://neyroangel.ru детский сад для детей с особенностями развития в Москве. Беремся за самые тяжелые случаи, от которых отказываются другие. Нейропсихолог, логопед, запуск речи. Государственная лицензия: Л035-01298-77/01604531 от 09.12.24
direction planning link – Helpful exploration notes that refined future strategies.
7k casino ориентировано на стабильную работу платформы. Игровые сессии проходят без сбоев. Пользователь получает быстрый доступ к функциям. Управление аккаунтом не вызывает сложностей. Сервис рассчитан на длительное использование: 7к казино официальный сайт
reliableshoppingplace – Secure and simple, completing purchases was effortless.
Everyday Improvement Hub – Practical and motivating, posts support steady learning and personal progress.
Wellspring therapy hub – Gentle layout, service information is clear and helpful.
growthconnectionguide – Tips are practical and easy to implement for real business results.
рекламный креатив рекламный креатив .
запоминаемость слогана реклама reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru .
commercial alliances hub – Clear guidance that made identifying international collaborations easier.
7k casino ориентировано на удобство игроков. Основные разделы логично структурированы. Переходы между страницами быстрые. Игры работают корректно. Это улучшает общее впечатление: 7к казино
safe buying experience – Checkout was intuitive and the transaction felt very secure.
commercehub – Easy navigation, makes finding products quick and simple.
Travis Anderson craftworks – Skillful and beautiful, pieces feel personal and thoughtfully created.
Рэмси Диагностика: https://remsi-med.ru Сеть высокотехнологичных диагностических центров (МРТ, КТ). Точные исследования на оборудовании экспертного класса и качественная расшифровка снимков.
trustedhub – Really helpful service, I got everything I was looking for fast.
corporateconnectionhub – Found multiple opportunities for collaboration and networking.
businessconnections101 – Networking advice is very solid, built meaningful professional relationships today.
green partnership guide – Practical tips that helped structure eco-friendly collaborations effectively.
Сеть фитнес клубов в Туле Хулиган https://hooligan1.ru/ это не просто тренажерка и фитнес, а сообщество тех, в ком живёт здоровый дух спорта и тяга к саморазвитию. Современный тренажерный спортзал с профессиональным спортивным оборудованием, бойцовской и кардио зоной. Сильная команда тренеров, нацеленных на результат. Подробнее на сайте.
Детский Доктор: https://kidsmedic.ru Специализированный медицинский центр для детей. Квалифицированная помощь педиатров и узких специалистов для здоровья вашего ребенка с первых дней жизни.
7k casino предлагает удобную навигацию по играм. Категории помогают быстро найти нужный формат. Пользователи могут переключаться между играми без задержек. Интерфейс остается стабильным. Это создает комфортные условия: 7k casino регистрация
trustedshopnetwork – Quick and reliable, found what I needed without any delays.
Change & Growth Center – Encouraging and insightful, content promotes steady personal and professional development.
secure shopping platform – Transactions were smooth and the experience felt reliable.
financebondshub – Very easy to follow guidance with useful insights for global business decisions.
Полесская ЦРБ: https://polesskcrb.ru Официальный портал центральной районной больницы Калининградской области. Информация об услугах, расписание врачей и важные новости здравоохранения для жителей региона.
Bath solutions platform – Clean presentation, each item is described clearly.
learnandadvance – Informative skill-building content, very useful for growing expertise quickly.
Mobihub helps reduce dependency on third-party proxy providers. Users generate proxies from their own devices. This increases control over IP sources. Privacy and reliability are improved. The solution remains cost-efficient: private mobile proxy
trustedcorporatehub – Reliable corporate bonding platform, very helpful for collaboration and team building.
trustyshop – Buying online was simple and secure, checkout went smoothly.
Travel Textures – Visually rich and engaging, content feels personal and well-curated.
машинное обучение креативы reklamnyj-kreativ4.ru .
анализ баннеров reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru .
shopping experience hub – Fast loading pages and simple checkout made the purchase easy.
businessnetworkinsights – Very helpful guidance, strengthened our professional relationships quickly.
Everyday Creative Ideas – Cheerful design, content motivates users to try new projects.
corpstreamline – Practical tools that improved team efficiency instantly.
АрсМед: https://arsmedclinic.ru Многопрофильная клиника, предлагающая широкий выбор медицинских услуг от диагностики до лечения. Современный подход и комфортные условия для пациентов всех возрастов.
long-term planning hub – Clear tips that helped structure partnerships for enduring business success.
рейтинг проекторов магазин проекторов в Москве
teamframeworkportal – Straightforward and practical guidance, improved collaboration across departments.
globalalliancesinsights – Very organized alliance suggestions, helped plan partnership strategies effectively.
7k casino предлагает широкий выбор игровых автоматов. Пользователи могут выбирать игры по тематикам и механикам. Сайт регулярно обновляет каталог. Это поддерживает интерес игроков. Доступ к играм осуществляется в несколько кликов: 7к казино официальный сайт
business decisions guide – Practical tips that made navigating options straightforward.
secure investment bonds – Managing bonds here feels safe and efficiently organized.
shopsmartcenter – Deals were excellent, checkout was simple and hassle-free.
Fiat heritage page – Cheerful and curated, the articles highlight classic car culture.
Laskar2 homepage – Clean and simple, the pages load quickly and feel easy to browse.
digitalsupplyhub – Smooth browsing, checkout was easy and hassle-free.
Answers & Ideas Hub – Helpful and well-organized, content makes tackling challenges straightforward.
мост бет скачать http://mostbet2027.help
partnership alignment hub – Practical advice strengthened collaborative strategies and outcomes.
улучшение креативов улучшение креативов .
узнаваемость бренда баннер reklamnyj-kreativ5.ru .
future strategy notes – Clear explanations that supported smarter long-term preparation.
professionalguidanceportal – Helpful tools that guided me to make smart career choices.
Информационный портал https://gdlog.ru/ объединяет 290 компаний, специализирующихся на железнодорожной логистике по всей России. Сервис открывает доступ к каталогу транспортных компаний, владельцев терминалов и логистических операторов, оказывающих комплекс услуг: обработку грузов, лизинг подвижного состава, контейнерную логистику и терминальное хранение. Интуитивный фильтр по территориям, узловым станциям и типам работ даёт возможность моментально выбрать партнёра для выполнения логистических задач любого уровня.
Играешь в казино? ап икс скачать простой вход, удобная регистрация и доступ ко всем возможностям платформы. Стабильная работа, адаптация под разные устройства и комфортный пользовательский опыт.
deal trust platform – Everything from browsing to checkout felt dependable.
bargainhub – Quick and convenient purchases, lots of good deals to choose from.
Cricket fixtures hub – Great for enthusiasts, game timings are clearly listed and timely.
Любишь азарт? ап икс скачать играть онлайн в популярные игры и режимы. Быстрый вход, удобная регистрация, стабильная работа платформы, понятный интерфейс и комфортные условия для игры в любое время на компьютере и мобильных устройствах.
strategicpartneradvice – Suggestions are solid, made long-term partnership strategies much clearer.
7k casino позволяет начать игру сразу после регистрации. Процесс занимает несколько минут. Сайт работает стабильно. Игры загружаются быстро. Это удобно для новых пользователей: 7k casino зеркало на сегодня
businesspartnershipnetwork – Alliance ideas are clear, gave us direction for enterprise growth.
Suiruan online experience – Unique interface, makes exploring new features enjoyable.
1win mBank пополнение 1win mBank пополнение
анализ креативов анализ креативов .
upster pro upster pro .
Любишь азарт? up x официальный сайт играть онлайн легко и удобно. Быстрый доступ к аккаунту, понятная навигация, корректная работа на любых устройствах и комфортный формат для пользователей.
enterprise collaboration hub – Useful alliance ideas that improved networking efficiency.
smartshoppingzone – Smooth process, grabbing deals was hassle-free.
strategicpartnershiptools – Practical tips that make forming long-term alliances easier.
corporateoperationsguide – Guidance is actionable, streamlined implementation in our department.
buyhub – Very smooth experience, browsing and purchasing are straightforward.
7k casino ориентировано на игроков, которые ценят разнообразие. В каталоге представлены слоты от популярных провайдеров. Регистрация занимает минимум времени. Пользователь может сразу перейти к игре. Все основные функции доступны в личном кабинете: 7k casino зеркало
Portfolio gallery page – Strong design, the personal work is displayed clearly.
химчистка обуви кроссовок химчистка обуви цена
скачат мостбет http://www.mostbet2027.help
commercepath – Practical tools, made managing sales and purchases effortless.
easyshoppingtools – Streamlined experience, very easy to complete orders.
crossdepartmenthub – Tools are practical and fast, enhanced collaboration across all teams.
7k casino ориентировано на удобство игроков. Основные разделы логично структурированы. Переходы между страницами быстрые. Игры работают корректно. Это улучшает общее впечатление: 7к казино официальный сайт
мостбет официальный сайт мостбет официальный сайт
worldalliances – Clear advice, helped plan global partnerships without confusion.
7k casino предлагает удобный доступ к онлайн играм. Пользователь может легко переключаться между слотами. Система работает без задержек. Интерфейс остается отзывчивым. Это улучшает игровой опыт: 7k casino официальный сайт
1win мегапей вывод 1win мегапей вывод
simpleshopclick – Smooth checkout with consistently fast delivery.
7k casino предлагает современную онлайн игровую среду. Пользователь получает доступ к актуальным слотам. Интерфейс разработан с учетом удобства. Все элементы расположены понятно. Это облегчает навигацию: казино 7к
businesslinkhub – Practical tool for establishing contacts, interface is clear and easy to use.
Планируете отпуск на Черноморском побережье и хотите свободно передвигаться по курортным окрестностям? Сервис проката автомобилей в Анапе предлагает удобные условия аренды без залога и ограничений по пробегу. В автопарке представлены современные машины с автоматической коробкой передач, кондиционером и полной страховкой. Забронировать подходящий автомобиль можно на https://auto-arenda-anapa.ru/ всего за несколько кликов, выбрав удобные даты и время. Круглосуточная поддержка менеджеров и возможность доставки машины в любую точку города делают аренду максимально комфортной для туристов.
knowledgeboost – Practical resources, learning process was smooth and productive.
1вин пополнение Киргизия https://1win12050.ru/
marketbestonline – Really pleased with the quality and cost, a solid shopping experience.
growthnavigator – Clear lessons, made learning complex topics easier.
7k casino сочетает современный дизайн и функциональность. Интерфейс адаптирован под разные экраны. Игроки легко находят нужные разделы. Все основные опции находятся под рукой. Это упрощает использование платформы: 7k casino вход
teamlinker – Practical and actionable advice, made teamwork smoother.
premiumdigitalmarket – Easy navigation and simple process for high-quality digital purchases.
7k casino ориентировано на удобство игроков. Основные разделы логично структурированы. Переходы между страницами быстрые. Игры работают корректно. Это улучшает общее впечатление: 7k casino зеркало
decisionpoint – Clear tools and guidance, made strategy choices faster.
Hello pals!
I came across a 154 fantastic site that I think you should visit.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://hazelnews.com/how-to-take-care-of-your-phone/
Additionally remember not to forget, guys, which one constantly are able to within this publication locate answers to your most confusing queries. Our team attempted to explain the complete information via the most very accessible way.
premiumproductstore – Easy-to-use platform with secure digital purchases.
как выбрать кабель ПВХ https://telegra.ph/Nyuansy-vybora-kabelya-s-PVH-izolyaciej-01-26
Датчики света для СТО https://mrhahn-it-life.blogspot.com/2026/01/blog-post.html
Современный шопинг стремительно меняется, и на российском рынке появляются новые площадки, предлагающие удобные условия как для покупателей, так и для продавцов. Маркетплейс https://latorga.ru/ объединяет множество категорий товаров — от одежды и обуви до электроники и автотоваров, создавая единое пространство для комфортных покупок. Платформа ориентирована на развитие отечественного онлайн-ритейла и предлагает бизнесу выгодные тарифы для размещения. Интуитивно понятный интерфейс, возможность выбора товаров от разных партнеров и удобная система навигации делают покупки простыми и приятными для пользователей из любого города России.
ДН-КЛИНИКА – https://nazimova.com/ это многопрофильный медицинский центр доктора Назимовой в Москве. Посетите сайт, узнайте о наших квалифицированных специалистах больше, а также об оказываемых нами услугах. Мы лечим людей, а не болезни. У нас самое современное оборудование, а широкий спектр услуг позволяет каждому поправить свое здоровье. Подробнее на сайте.
Качественные пластиковые окна повышают комфорт жилья и снижают теплопотери. Компания http://eoknadveri.ru/ производит светопрозрачные конструкции из ПВХ и алюминия в Москве без торговой наценки. Собственное производство обеспечивает минимальные сроки изготовления, гарантия достигает 20 лет. Доступно остекление квартир, балконов и коттеджей с бесплатным замером, доставкой и установкой в удобное время. Предлагается рассрочка платежа и вывоз строительного мусора. Работа ведется ежедневно с 9:00 до 21:00, что позволяет согласовать визит специалиста в любой день.
Путешествие большой компанией или семьей требует комфортного транспорта. Сервис https://minivan.online/ предлагает аренду восьмиместных минивэнов с водителем в Москве по фиксированным тарифам. Востребованы поездки в аэропорты Домодедово, Шереметьево, Внуково и на вокзалы без переплат за пробки. Доступно детское такси BABYCAR с автокреслами для новорожденных, семейные поездки и трансферы на свадьбы. Заказ принимается круглосуточно по телефону, что гарантирует оперативную подачу автомобиля в нужное время и место.
нужна люстра деревянная люстра
мужской костюм ткани мужские костюмы
Память о близких должна быть достойной и долговечной, именно поэтому так важен выбор качественного памятника из надежных материалов. Компания https://granitservise.ru/ в Южно-Сахалинске более двух десятилетий занимается изготовлением ритуальных изделий из гранита и мрамора — вертикальных и горизонтальных памятников, оград, столов, лавок, ваз. Опытные мастера выполняют портреты и надписи, обеспечивают полный цикл работ: от консультации до монтажа и благоустройства места захоронения. Также предприятие предлагает гранитную продукцию для строительства: подоконники, столешницы, ступени, брусчатку.
vavada službena aplikacija http://vavada2007.help
Монтаж бронированного кабеля https://telegra.ph/Promyshlennyj-bronirovannyj-kabel-zashchita-nadezhnost-i-surovaya-realnost-montazha-01-26
Электромонтажные работы https://electric-top.ru в Москве и области. Круглосуточный выезд электриков. Гарантия на работу. Аварийный электрик.
коррозия у авто? антикор сервис эффективная защита от влаги, соли и реагентов. Комплексная обработка кузова и днища, качественные составы и надёжный результат для новых и подержанных авто.
кабели для подсветки фасада дома https://mrhahn-it-life.blogspot.com/2026/01/blog-post_26.html
vavada instalacija ios https://www.vavada2007.help
Современный шопинг стремительно меняется, и на российском рынке появляются новые площадки, предлагающие удобные условия как для покупателей, так и для продавцов. Маркетплейс https://latorga.ru/ объединяет множество категорий товаров — от одежды и обуви до электроники и автотоваров, создавая единое пространство для комфортных покупок. Платформа ориентирована на развитие отечественного онлайн-ритейла и предлагает бизнесу выгодные тарифы для размещения. Интуитивно понятный интерфейс, возможность выбора товаров от разных партнеров и удобная система навигации делают покупки простыми и приятными для пользователей из любого города России.
vavada ios preuzimanje vavada2007.help
Коррозия на авто? антикоррозийная обработка авто в спб мы используем передовые шведские материалы Mercasol и Noxudol для качественной защиты днища и скрытых полостей кузова. На все работы предоставляется гарантия сроком 8 лет, а цены остаются доступными благодаря прямым поставкам материалов от производителя.
Качественная питьевая вода — основа здорового образа жизни. Сервис доставки https://voda-s-gor.ru/voda-15-litra/ работает в Махачкале и Каспийске, предлагая горную воду в удобной полуторалитровой таре. В ассортименте представлены марки BabugenT, Пилигрим, Кубай, Архыз и специальная детская вода для Ляль по ценам от 300 до 420 рублей за упаковку из шести бутылок. Заказ оформляется онлайн или по телефону с доставкой на дом и в офис, что экономит время и обеспечивает постоянный запас чистой воды.
Холдинг «ИСП» специализируется на выпуске элитных газовых систем противопожарной защиты и имеет полуторадесятилетнюю историю. Ищете виды автоматических установок пожаротушения? На сайте zarya.one представлена продукция: модули «ЗАРЯ», «ИМПЕРАТОР», установки «УльтраZ» и «Анаконда», система контроля КСИД. Предприятие обеспечивает весь спектр работ: проектную подготовку, установку систем и техническое освидетельствование. Более 35 000 модулей защищают критически важные объекты в десяти странах мира. Собственное производство, проектный отдел и партнёрская сеть монтажников обеспечивают надёжность на каждом этапе.
Планируете мероприятие? мероприятия с нейросетями уникальные интерактивные форматы с нейросетями для бизнеса. Мы разрабатываем корпоративные мероприятия под ключ — будь то тимбилдинги, обучающие мастер?классы или иные активности с ИИ, — с учётом ваших целей. Работаем в Москве, Санкт?Петербурге и регионах. AI?Event специализируется на организации корпоративных мероприятий с применением технологий искусственного интеллекта.
Украшения для пирсинга https://piercing-opt.ru купить оптом украшения для пирсинга. Напрямую от производителя, выгодные цены, доставка. Отличное качество.
термостойкий кабель https://telegra.ph/Termoustojchivyj-kabel-dlya-doma-i-bani-sovety-ehksperta-po-montazhu-01-26
Ищешь сокращатель сылок? https://l1l.kz надежный сокращатель ссылок в Казахстане, рекомендуем заглянуть на сайт, где весь функционал доступен бесплатно и без регистрации
pin-up əmsal dəyişməsi https://pinup2009.help
Противопожарные двери https://bastion52.ru купить для защиты помещений от огня и дыма. Большой выбор моделей, классы огнестойкости EI30, EI60, EI90, качественная фурнитура и соответствие действующим стандартам.
Нужны цветы? заказать цветы на дом закажите цветы с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор букетов, свежие цветы, стильное оформление и точная доставка. Подойдёт для праздников, сюрпризов и важных событий.
O’zbekiston uchun https://uzresearch.uz iqtisodiyot, moliya, ijtimoiy jarayonlar, bozorlar va mintaqaviy rivojlanish kabi asosiy sohalarda tadqiqotlar olib boradigan analitik platforma. Strukturaviy ma’lumotlar va professional tahlil.
Savdo va biznes https://infinitytrade.uz uchun xalqaro platforma. Bozor tahlili, xalqaro savdo, eksport va import, logistika, moliya va biznes yangiliklari. Tadbirkorlar va kompaniyalar uchun foydali materiallar, sharhlar va ma’lumotlar.
Ijtimoiy rivojlanish https://ijtimoiy.uz va jamoat hayoti uchun portal. Yangiliklar, tahlillar, tashabbuslar, loyihalar va ekspert fikrlari. Ijtimoiy jarayonlar, fuqarolik ishtiroki, ta’lim va jamiyatni rivojlantirish bo’yicha materiallar.
Foydali maslahatlar https://grillades.uz va g’oyalar bilan panjara va barbekyu haqida loyiha. Retseptlar, panjara qilish texnikasi va jihozlar va aksessuarlarni tanlash. Mukammal ta’m va muvaffaqiyatli ochiq havoda uchrashuvlar uchun hamma narsa.
Qurilish materiallari https://emtb.uz turar-joy va sanoat qurilishi uchun beton va temir-beton. Poydevorlar, pollar va inshootlar uchun ishonchli yechimlar, standartlarga muvofiqlik, izchil sifat va loyihaga xos yetkazib berish.
пылесосы dyson pylesos-dn-7.ru .
Ijtimoiy jarayonlar https://qqatx.uz va jamiyat taraqqiyoti bo’yicha onlayn axborot platformasi. Tegishli materiallar, tahliliy sharhlar, tadqiqotlar va murakkab mavzularning tushuntirishlari aniq va tuzilgan formatda.
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб pylesos-dn-6.ru .
Любишь азарт? игровые автоматы комета казино современные слоты, live-форматы, понятные правила и удобный доступ с ПК и смартфонов. Играйте онлайн в удобное время.
Помощь в написании магистерской диссертации под ключ – https://disser-guru.ru/uslugi/magisterskaya-dissertaciya-pod-klyuch/
Играешь в казино? ап икс официальный Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
Лучшее казино up x играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Современный шопинг стремительно меняется, и на российском рынке появляются новые площадки, предлагающие удобные условия как для покупателей, так и для продавцов. Маркетплейс https://latorga.ru/ объединяет множество категорий товаров — от одежды и обуви до электроники и автотоваров, создавая единое пространство для комфортных покупок. Платформа ориентирована на развитие отечественного онлайн-ритейла и предлагает бизнесу выгодные тарифы для размещения. Интуитивно понятный интерфейс, возможность выбора товаров от разных партнеров и удобная система навигации делают покупки простыми и приятными для пользователей из любого города России.
Актуальная информация о событиях в России и мире доступна на новостном портале http://worldtodaynews.net/, который ежедневно публикует свежие репортажи и аналитику. Рубрики охватывают политику, экономику, науку, спорт, здоровье, финансы, культуру и автомобильную тематику. Читатели получают оперативные сводки о важнейших событиях дня с комментариями экспертов и фактической базой. Удобная навигация позволяет быстро находить интересующие материалы, а регулярное обновление контента гарантирует доступ к самым последним новостям без задержек.
pin-up limitlər necə dəyişir https://pinup2009.help/
Успех любого онлайн-бизнеса сегодня напрямую зависит от видимости сайта в поисковых системах, и профессиональное SEO-продвижение становится не просто желательным, а необходимым инструментом. Платформа https://seobomba.ru/ предлагает комплексные решения для раскрутки сайтов: от размещения вечных ссылок до усиления социальных сигналов и форумного продвижения. Многочисленные положительные отзывы клиентов подтверждают эффективность используемых методов — владельцы интернет-магазинов и коммерческих проектов отмечают реальный рост позиций и трафика. Удобный интерфейс, богатый выбор услуг и оперативное выполнение заказов делают сервис надежным партнером для тех, кто серьезно настроен на развитие своего бизнеса в интернете.
Освежающая газированная вода утоляет жажду и дарит бодрость в жаркие дни. Компания https://voda-s-gor.ru/158/ доставляет в Махачкалу и Каспийск популярные марки: Ледяная гор, Пилигрим и BabugenT в форматах 0,5 и 1,5 литра. Цены начинаются от 310 рублей за упаковку, доступна слабогазированная и сильногазированная вода. Удобный сервис позволяет заказать продукцию в один клик с доставкой домой или в офис, избавляя от необходимости носить тяжелые бутылки из магазина. Лицензированная продукция гарантирует безопасность.
pin-up bloklamanı keçmək pin-up bloklamanı keçmək
Профессиональное оснащение автосервиса определяет качество работы и скорость обслуживания клиентов. Компания Nordberg43 предлагает комплексные решения для шиномонтажных, слесарных участков и станций развал-схождения с гарантией 2 года на весь ассортимент. На сайте https://nordberg43.ru/ представлено сертифицированное оборудование: подъемники, компрессоры, диагностические стенды, шиномонтажные станки, а также профессиональный инструмент и расходные материалы. Готовые комплекты позволяют оборудовать автосервис под ключ, включая монтаж и настройку техники. Удобная доставка по России и техническая поддержка делают сотрудничество максимально комфортным для владельцев автомастерских.
Производство винтовых свай в Саратове на https://vintoviesvai64.ru/ предлагает фундаментные решения для частного и коммерческого строительства с использованием современного оборудования и качественной стали. Компания выпускает сваи различных диаметров и длины для деревянных домов, бань, заборов, беседок и промышленных объектов с возможностью монтажа в любое время года на сложных грунтах. Собственное производство обеспечивает конкурентные цены без посреднических наценок, оперативное изготовление под конкретные параметры проекта и полный цикл услуг от расчёта нагрузок до установки свайного фундамента.
Ищете профессиональную переподготовку или повышение квалификации? Посетите https://rostbk.com/ – это центр дистанционного образования, у которого более 2000 программ обучения с выдачей диплома и выгодными ценами. Мы входим в ТОП учебных заведений с квалифицированными преподавателями. Лучшие курсы у нас, а обучение онлайн из любого региона.
SL obras locales – Buen diseño del sitio, contenido claro y accesible.
sports content source – Ran into this site and the updates look fairly new.
futureplanninghub – Strategic advice is effective, made structuring future projects simple.
Anthony Dostie construction site – Easy to navigate and professional, instills trust right away.
alliancesinsights – Enterprise partnership advice is useful, enhanced collaborative opportunities efficiently.
Стильная одежда играет важную роль в самовыражении.
Она помогает выразить характер.
Гармоничный стиль повышает уверенность в себе.
Одежда может быть инструментом первого восприятия.
https://hackernoon.com/preview/KYZLTFojcYtdA3gR1XPg
Кроме того, продуманный гардероб экономит время в повседневных делах.
Со временем внимание к стилю формирует привычку.
В результате стильная одежда становится важной частью современного образа жизни.
casual cartoon page – Stumbled onto this site, quick loading and simple navigation stand out.
EV Liberty online – Clear design and fast-loading pages, information is presented transparently.
Современный шопинг стремительно меняется, и на российском рынке появляются новые площадки, предлагающие удобные условия как для покупателей, так и для продавцов. Маркетплейс https://latorga.ru/ объединяет множество категорий товаров — от одежды и обуви до электроники и автотоваров, создавая единое пространство для комфортных покупок. Платформа ориентирована на развитие отечественного онлайн-ритейла и предлагает бизнесу выгодные тарифы для размещения. Интуитивно понятный интерфейс, возможность выбора товаров от разных партнеров и удобная система навигации делают покупки простыми и приятными для пользователей из любого города России.
alliancesgrowthcenter – Global alliance tips are useful, assisted in strengthening business relationships quickly.
mental wellness resource – The site communicates complex ideas in a patient and professional manner.
Manisa city tips – Found exactly what I needed without extra clutter, very convenient.
creative glass store – Such a cool vibe, the work stands out as truly handmade.
RI Tech platform – Layout is tidy and tech information is straightforward and concise.
Barling Collins platform – The site communicates value effectively and feels trustworthy.
creative media projects – Each project felt carefully crafted and meaningful, really enjoyable.
Агентство наружной рекламы Буквица https://bukvica.ru/ оказывает полный комплекс услуг в сфере наружной рекламы и оформления внутренних пространств. Мы разрабатываем дизайн, производим и монтируем вывески, объемные буквы, световые конструкции, навигацию, крышные установки, вывески из неона и брендирование. Берём на себя согласование вывесок в государственных органах и реализуем проекты под ключ, точно в срок.
a href=”https://qulavoholdings.bond/” />QulavoTracker – Navigating the platform was simple, and everything feels safe and reliable.
RixaroLine – User-friendly platform with a clear, easy-to-follow interface.
RixaroHoldings – Great information here, saved me a lot of unnecessary searching time.
RixaroDirect – Helpful interface and clear instructions, ideal for beginners.
LixorFlow – Practical and concise advice made the experience smooth and informative.
OrvixNavigator – Easy-to-follow directions made exploring the tools smooth and efficient.
main quixo – Found this earlier and the clean layout made a good impression.
explore cavaroline site – Clean design allows quick access to content and smooth browsing overall.
vexaro site – Came across the site today, everything feels organized and smooth to navigate.
trustco overview – Clean and organized pages make accessing content fast and effortless.
navirobond link – Layout is intuitive and helps access content smoothly.
this core platform – Easy to move around and the content is immediately understandable.
main platform – Browsing is smooth, and the site layout feels structured and reliable.
start here – Casual visit, but the site felt clean and approachable.
kavix link – Minimal design helps keep attention on essential information quickly.
Smooth browsing – Navigating the site is simple and visually appealing.
Belvarin online – A clean, attractive layout and carefully chosen products.
glintaro.shop – A sleek and stylish place to shop, with so many interesting finds.
Fresh selections – Products feel pure, natural, and carefully curated.
aislealchemy.shop – Always spotting interesting items here, the layout feels super smooth.
glintgarden.shop – A great place to find everything for your garden, love their range of products!
yavex online – Pleasant experience, content is accessible and the design is minimal.
Blanket Bay picks – High-quality, comfortable products and a smooth, pleasant shopping experience.
Auroriv online store – Modern look and lots of products make it a pleasure to browse.
Shop highlights – The selection feels well thought out and easy to explore.
Bloom Barrel favorites – Lovely selection of products with charming designs.
glintvogue.shop – Perfect for discovering chic and trendy pieces, highly recommended!
Modern elegance – Everything looks like it belongs in a well-designed space.
Gift shop picks – Beautiful items, easy to browse, and perfect for home or presents.
trustco info – Clean interface with readable, organized content throughout.
Ardenzo deals – Everything feels straightforward and easy to shop through.
goldenget.shop – An easy and convenient shopping experience with so many quality options!
Visual treats – The artwork selection feels diverse and engaging.
goldenparcel.shop – A wonderful place for high-quality items, always impressed with their selection.
Contemporary look – Everything feels stylish and nicely balanced.
goldgrove2.shop – Great shopping experience every time, unique products that stand out.
Standout shop – A solid choice for unique and well-crafted items.
online henvoria – Pleasant to look around, finding items didn’t take long.
greenguild.shop – Great eco-conscious products, and the site makes it so simple to shop and explore.
Interactive corner – A site that’s playful and easy to navigate.
home mood market – Light and comfortable browsing, nothing overwhelming.
grovegarnet.shop – A wonderful mix of products, I love coming here to see what’s new.
Home favorites – The site feels polished and makes discovering items fun.
honey finds online – Ran into this store, product pages are easy to follow.
halvessa.shop – Love the modern design and how easy it is to discover amazing and unique products.
Orivogue Boutique – Modern fashion pieces, shopping was simple and enjoyable.
online style hub – Browsing is simple, and product descriptions are very informative.
Spruce Spark Corner Picks – Modern aesthetic, site navigation is clear and shopping was enjoyable today.
Orla Corner – Plenty to choose from, checkout felt simple and quick.
Starlight Gems – Minimalistic and inviting, site navigation is simple and checkout worked perfectly.
Stitchery Select Online – Modern layout, categories are easy to find and checkout went perfectly.
Suave Basket Gems – Cheerful design, items are easy to explore and overall shopping was pleasant.
Suave Shelf Essentials – Inviting layout, products are displayed clearly and buying was quick and easy.
Useful Gear Online – Feels current, simple, and focused on real-world needs.
Tervina Style Market – Browsing is smooth, products look appealing, and pricing seems balanced.
Sunny Shopline Essentials Online – Clear and bright, site navigation is easy and checkout went without issues.
Tidy Treasure Finds Online – The tidy layout really enhances the shopping vibe.
MirStella Boutique – Well-organized layout, simple to navigate, and detailed product images stand out.
Tidy Treasure Finds – The tidy presentation makes browsing feel effortless.
Tea Terminal Studio – Friendly layout, items are easy to find and checkout went without problems.
Tool Tower Supply – Tools are showcased in a neat, logical way.
Passport Pocket Central – Perfect for travel, site navigation and checkout felt effortless.
Mod Merchant Showcase – Each product description guided me well, making selection easier.
Mod Mosaic Showcase – The modern selection is attractive and browsing was very pleasant.
Mod Mosaic Goods – Modern items are well chosen, exploring the site was a delightful experience.
Tool Tower Tools – Everything feels organized and easy to understand.