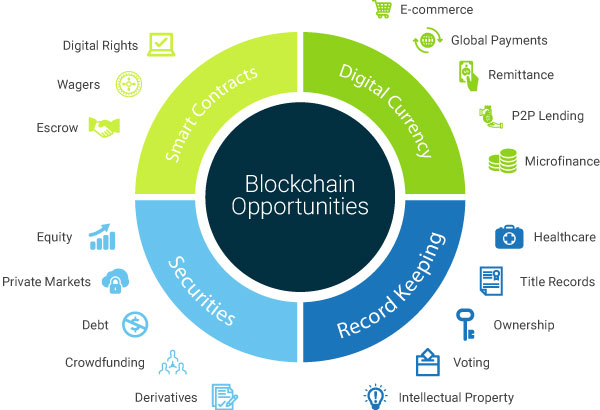
Opportunities
$ 10 trillion is the potential size of Blockchain technology ecosystem consisting of Cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology and decentralization – says Royal Bank of Canada report. Mark Cuban has announced that his basketball team Dallas Mavericks will begin accepting Cryptocurrency during next season. Companies, the owners of the logos in this picture, along with likes of 1800-flowers, Bloomberg, etc have started accepting cryptocurrencies. Blockchain ETFs attracted $ 240 million investment in a single week. All this point to, beginning of an era for Crypto economics and blockchain technology.

Currently focus and economic activity in this sector is concentrated on speculation in Cryptocurrencies and related activities. This involves mining and trading of bitcoins, Ethereum, etc. Sale of ASIC / GPU based mining equipments is big business with current market size of approx $ 7 Billion and growing fast, as more people are aspiring to be miners. There are exchanges hosting wallets and facilitating Cryptocurrency transactions, at fees per transaction.
However, bigger opportunity lies in underlying Blockchain technology (a system which enables migration of trust from entities to computing systems) and decentralization. Evolution of blockchain and crypto economics is triggering rainbow of opportunities. For example, development of platforms for various financial services, business platforms, IoT integration and development of decentralized applications (e.g. decentralized social networks, instant messengers, cloud storage, search engines, commodity exchanges, information aggregators, etc.). Broadly, this technology will expand many markets, more people will be connected online to embrace this evolution and entities would save transactional costs. Let us understand the opportunities in detail.
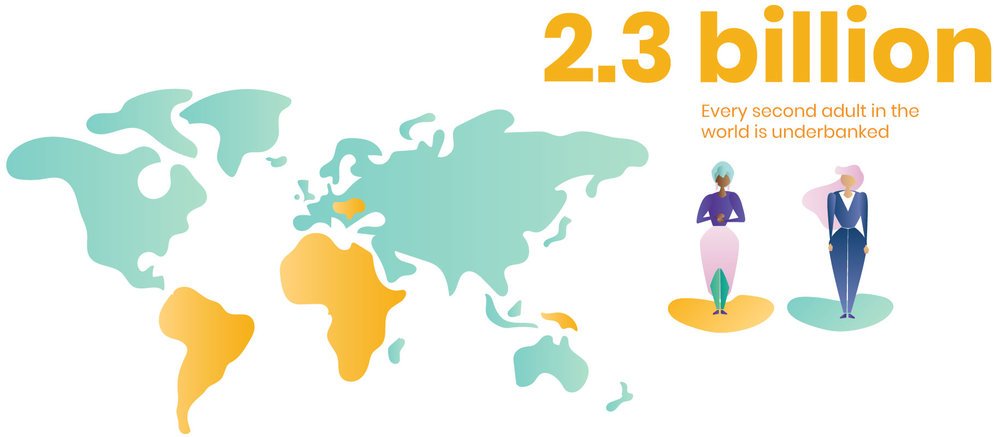
Currently, there are 2.3 billion unbanked adults across world. Most of them have access to internet, but they don’t have exposure to formal financial world, consisting of digital payments, personal finance, insurance, etc. At the same time, it is difficult to obtain information about these potential beneficiaries.

There as an opportunity to build a platform facilitating financial services with backbone infrastructure of decentralized blockchain technology offering data privacy, information sharing, immutability and a full stack of security protocols. This platform can facilitate creation of public, as well as private blockchains, for people to chose from, in the context of their unique requirement.
There should be interoperability between public and private blockchains. For example, KYC credentials, can be managed on private blockchain network and functions of public interest can be maintained on public blockchain, e.g. information systems, etc. It should offer tools to build & manage blockchains and develop APIs/ Rest APIs, particularly for lean businesses and small enterprises, who want to reduce or eliminate the effort required in creating, managing and terminating blockchains.

The platform should have infrastructure to facilitate development of decentralized apps for blockchain networks. It should facilitate developing smart contracts for process automation. It should facilitate deployment of blockchains to the cloud. Users can create and manage such blockchains through a user friendly dashboard and mobile users should get blockchain instance immediately. They should be able move in & out of the apps, seamlessly. This platform can enable the underserved people to avail financial services such as payment transfers, personal banking, insurance, microfinance, crowd funding, peer funding, payment wallets, etc. People can have online wallets and they can exchange funds among themselves instantaneously (without any intermediary, such as Bank, etc.) at fraction of cost. They can avail personal insurance or insurance for their house, crop (available in certain countries), automobiles, machinery, etc Due to tamperproof nature of blockchain records of their purchases and any subsequent modifications, repairs, etc. will create a trail of instances. This will be a record they can showcase, while selling/ mortgaging the house, machinery, etc. to peers or any institution.
Availability of their financial records on secured blockchain network, will create a seamless, tamperproof credit history. Which will be a reference for banking or microfinance institutions to offer them loan for education, automobile, marriage or any incidental reason, through the course of life, that too, at nominal rate. Typically, banks accept deposits at X rate of interest and offers loans to entities at X + Y rate of interest. On demand availability of credit history, can be a major enabler for peer to peer funding. People can seek loan among themselves, by showcasing their tamperproof credit history to peers, willing to finance them. Here the financer can bypass the banking institutions and offer loan to needy at X rate of interest and needy also saves Y rate of interest. Such peer to peer transactions, built on blockchain platform will be a game-changer in financial markets, as a cost saving mechanism. It will save cost for both consumers and institutions/ individuals offering financial services. This will realize global financial inclusion.

There is an opportunity to offer cost saving to the tune of 2-4% in manufacturing cost, by building a blockchain platform around Durable product lifecycle, which will maintain records about each durable product, right from the raw material stage, to production, to inspection, to product sale to customer and further covering stages, till end of product life cycle. It can be integrated with supply chain management to facilitate lean manufacturing. Integration of smart contracts across value chain will automate many inter corporate transactions, resulting in savings of financial cost. This platform will have mix of public and private blockchains. The public blockchain will carry records of product from raw material stage to end of life. Whereas, private blockchains will be implemented for intra organization operations, e.g. vendor, manufacturer, dealer, service centre, etc. will have their private blockchains.

A product blockchain, a permissionless one, flows through various organizations, across value chain. At every stage new record blocks will be added in the blockchain. First, manufacturer decides to manufacture a product. He generates bill of material. Places order with few vendors for material. Vendors send material to manufacturer. Here product blockchain will have genesis block, consisting of records of various components for product. As the manufacturing stages advance, so does, the product blockchain will add records related to specific recordable details about product during manufacturing. As the products are sold to end customer, the customer details get added in the blockchain. Whenever, customer services the product, details related to service get added in to product blockchain, till the product life cycle ends.
While, the product blockchain will be public, it will have interoperability with private blockchains, which will keep financial records with channels of privacy. They will be accessible only to restricted members. For example, price of particular component of the product, will be known only to purchase department user of manufacturer and sales department of the vendor of the product. In case of product failure, there would be trail of events, which can be scrutinized to find stage of the fault and accordingly remedial course correction can be implemented, to avoid future failures. At the end, the product blockchain will have transparent record of every instance of intervention with the product. For example, manufacturer receives parts of a car, the car is manufactured, sold through a retailer to end user, serviced multiple times across various service centers. Now there is a situation, the owner wants to sell that car to an interested buyer. At this stage, immutable records about the car, available on blockchain, will help buyer finalize his purchasing decision. Even, product financing peers or banks can refer to the blockchain records, to decide about financing. In such ecosystem, there are multiple stakeholder such as, vendor of parts, manufacturer, dealer, service centre, spare part dealer, etc. All of them must have consensus in accepting this system or compliance regulations enforces such a system, which will eliminate need of trust.
Different sectors of industry can have such decentralized platforms. These platforms should have tools for blockchain deployment, APIs for user applications. Smart contracts will automate financial procedures and other inter corporate transactions. By participating on such platform, businesses will have great opportunity to improve their credibility, reduce operating cost, increase efficiencies and improve transparency, by deployment of blockchain in end-to-end value chain, consisting of vendors and clients or dealers.
There will be 21 Billion Internet of Things (IoT)devices in 2020, up from 6.4 billion in 2016, according to Gartner and 10s of billion dollars are getting invested in this space. Smart city projects in many countries, manufacturing automation through AI/robotics and smart homes/ offices will be driving engines for this phenomenal growth projection. Intel, Cisco & Autodesk are some of the prominent players along with many startups, taking IoT forward. At local level IoT devices communicate through internet protocols, either through blue tooth, wireless Ethernet, etc. They are controlled through applications hosted in cloud with AWS, MS Azure, etc. However, in an IoT connected infrastructure, a network is only as strong as its weakest link. This means security will always be a necessary topic of discussion for the businesses and stakeholder at larger, participating in the IoT, including vendors and end users.
The future of cities, communities and businesses is getting shaped in their dependency on connected IoT devices and their controlling systems. As a result, the prize is getting bigger for hackers, to exploit these devices and systems for their own gain. The centralized security model in market today will struggle to deal with vulnerabilities in IoT infrastructure. They will increase with no of IoT devices, i.e. more the sensors, actuators and other devices in an IoT installation, more the threat of hacking attack. These devices collect lot of data at local level and dispersed in cloud for processing and monitoring. Security of this data at centralized & distributed level along with integrity at REST and transport level is challenging. Further, full potential of IoT can’t be realized without internet of value IoV (internet of value) and in turn MoIP (money over internet protocol). More the devices/ node, vulnerability of IoT increases, where as more such nodes, security of blockchain enhances. The adversities and challenges of IoT is a great opportunity for integrating blockchain technology in IoT installations.
There is an opportunity to build a platform, which will offer immutable and cryptographically secured blockchain layer, underneath IoT installations. This platform can have channels of private blockchains, to be made available for IoT installations. This platform should have choice of consensus algorithms for users to choose from, depending on their unique requirement. It should have cluster container approach, where in, low bandwidth wireless data from IoT devices can communicate well with platform given the lightweight virtualization in containers. The platform should have wide amount of APIs to connect with the wide range of devices, operating systems and languages involved in this ecosystem. More specifically, it should have a support for Java applications, as most of the existing IoT devices are working in Java environment. The platform should have following features :
- Interfacing and integrating capabilities for wide range of operating systems
- Highly responsive to large no. of IoT devices
- Security at every layer of stack
- Compatibility with wide standards of IoT devices
- Facility for scalability
- Support for step by step modular adoption of IoT
- Support for integrating financial services with IoT to realize IoV
Some of the IoT devices/ nodes collecting data from sensors and transporting to blockchain network, will themselves act as validators and as it goes in blockchain, more the validators, stronger the network. Such platforms will transform the way manufacturing, industrial process control and even financial processes in industrial arena, happen today. Blockchain will offer MoIP, in turn IOV to IoT to realize its full potential across value chain. Machine to machine manufacturing operations in IoT will extend to payments structure, which will enable machine-to-machine commerce. Such platform based on blockchain will eliminate the cyber security related vulnerabilities and IoT would evolve as a catalyst for Industrial Revolution 4.0
$ 335 Billion is the estimated size of sharing economy in 2025, meteoric rise from $ 14 billion in 2014, says report of Brookings. The sharing economy is “the peer-to-peer based activity of obtaining, giving, or sharing access to good and services”. Alternative names for this phenomenon include gig economy, platform economy, access economy and collaborative consumption. This augurs well with the peer-to-peer, decentralized network without any control of central authority, the hallmark of blockchain ecosystem.
Currently there is a large cost of aggregation required to be paid by people, to benefit from sharing economy; to that extent, it is centralized and needs to evolve as true peer-to-peer economy, with fractional cost of aggregation. There is an opportunity build a blockchain platform, which will act as a hub for peer-to-peer instances of economic activities at, local community/ city levels. For example, car hailing, home sharing, social networking, local business promotion, local exchange of used goods, crowd bidding for agriculture produce and many such activities. Deployment of blockchain can make it cheaper to create and operate an online platform. For example, transparency in offers & transactions will result in competitive environment, benefitting the consumer. The financial transactions can be coordinated by self-executing smart contracts, using native Cryptocurrency or fiat currency.
This platform can have public blockchain, where in anyone with internet connection can be part of this blockchain. There will be transparent record of all assets and their respective ownerships. It will offer chronologic sequence of offers and transactions, which will be guiding principles for future transaction. Consensus algorithm of proof of stake could be suitable for such platform, however there has to be choice of consensus algorithms. Trinity of blockchain, smart contracts and IoT will ensure speedy and automated processes. For example, A person can offer to rent out his house. Smart contract can enforce agreement with highest bidder and ensure automated transactions. Next level of automation using IoT can ensure, locking and opening property rights, through passwords.
This platform should support mobile devices, offer APIs for various IoT systems and easily programmable smart contracts.
Another case in point, used goods market. It is growing by year, not in absolute terms, but by virtue of higher discovery of those goods in each household, occupying storage spaces, without yielding any use benefit. Current mechanism facilitate transactions, but there are vulnerabilities in those transactions, e.g. stolen goods, duplicate goods, lack of transparency about offers, etc. An ecosystem with blockchain technology, offering options to households for renting, selling, exchanging, pawning, donating, etc. of such goods, will eliminate those vulnerabilities. Transparent blockchain will reveal ownership trails of the goods. It will help realize value for unused goods and immutable trail on blockchain will ensure transparency in each such transactions. Smart contracts can automate financial transactions, offering finality to the deals. A native digital coin within such system with blockchain backbone will be a negotiating tool for the users of this ecosystem.
There are going to be immense opportunities in Blockchain arena. But, what will matter is the first mover advantage.
Challenges with Blockchain
- Initial cost of migration to blockchain. Though blockchain is open source software, there is a definite cost of consultation for selection of right iteration of blockchain, development & customization of blockchain for existing applications, testing and commercial implementation, etc. It will be challenging to integrate the technology with existing legacy infrastructure.
- Storage space issues, especially in the public blockchains. As no. of transactions are increasing there is ever increasing need of resources like speed and capacity.
- Identification of peers and creating hierarchies who can be trusted to access the data.
- Privacy and security challenges that might arise from the decentralized access of data, in the context of legal framework, prevailing in respective countries.
- Probable resistance from existing market intermediaries, government staff.
- Developing a regulatory framework in guiding the application of the new technology and setting common standards.
- A key challenge with blockchains is ensuring that an industrialized version of these systems emerge that provide scalability, robustness and security required to handle the transactions required by large-scale supply chains and the associated governance issues.
- Security issues around the authentication and encryption of the database. While the database is considered highly secure, the accuracy of each entry ultimately rests on the entity in control of each private account.
- As with all areas of online security, there is also an increased need to protect against hacking. If tradeoff between flexibility & security falls apart, blockchain networks may be vulnerable to hack attacks or external threats.
- Scalability is viewed with skepticism, as it involved speed and storage. Since, early days of adoption for large data, pitfalls are yet to be realized.